Effects of Interlayer Coupling on Hot-Carrier Dynamics in Graphene-Derived van der Waals Heterostructures
Abstract
Graphene exhibits promise as a plasmonic material with high mode confinement that could enable efficient hot carrier extraction. The lifetimes and mean free paths of energetic carriers have been investigated in free-standing graphene, graphite, and a heterostructure consisting of alternating graphene and hexagonal boron nitride layers using ab initio calculations of electron–electron and electron–phonon scattering in these materials. It is found that the extremely high lifetimes (3 ps) of low-energy carriers near the Dirac point in graphene, which are a 100 times larger than that in noble metals, are reduced by an order of magnitude due to interlayer coupling in graphite, but enhanced in the heterostructure due to phonon mode clamping. However, these lifetimes drop precipitously with increasing carrier energy and are smaller than those in noble metals at energies exceeding 0.5 eV. By analyzing the contribution of different scattering mechanisms and interlayer interactions, desirable spacer layer characteristics—high dielectric constant and heavy atoms—that could pave the way for plasmonic heterostructures with improved hot carrier transport have been identified.
- Authors:
-
- Harvard Univ., Cambridge, MA (United States)
- Rensselaer Polytechnic Inst., Troy, NY (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC); Univ. of California, Oakland, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES). Scientific User Facilities Division
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1543462
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1401286
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Advanced Optical Materials
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 5; Journal Issue: 15; Journal ID: ISSN 2195-1071
- Publisher:
- Wiley
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 36 MATERIALS SCIENCE; Materials Science; Optics
Citation Formats
Narang, Prineha, Zhao, Litao, Claybrook, Steven, and Sundararaman, Ravishankar. Effects of Interlayer Coupling on Hot-Carrier Dynamics in Graphene-Derived van der Waals Heterostructures. United States: N. p., 2017.
Web. doi:10.1002/adom.201600914.
Narang, Prineha, Zhao, Litao, Claybrook, Steven, & Sundararaman, Ravishankar. Effects of Interlayer Coupling on Hot-Carrier Dynamics in Graphene-Derived van der Waals Heterostructures. United States. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201600914
Narang, Prineha, Zhao, Litao, Claybrook, Steven, and Sundararaman, Ravishankar. Fri .
"Effects of Interlayer Coupling on Hot-Carrier Dynamics in Graphene-Derived van der Waals Heterostructures". United States. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201600914. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1543462.
@article{osti_1543462,
title = {Effects of Interlayer Coupling on Hot-Carrier Dynamics in Graphene-Derived van der Waals Heterostructures},
author = {Narang, Prineha and Zhao, Litao and Claybrook, Steven and Sundararaman, Ravishankar},
abstractNote = {Graphene exhibits promise as a plasmonic material with high mode confinement that could enable efficient hot carrier extraction. The lifetimes and mean free paths of energetic carriers have been investigated in free-standing graphene, graphite, and a heterostructure consisting of alternating graphene and hexagonal boron nitride layers using ab initio calculations of electron–electron and electron–phonon scattering in these materials. It is found that the extremely high lifetimes (3 ps) of low-energy carriers near the Dirac point in graphene, which are a 100 times larger than that in noble metals, are reduced by an order of magnitude due to interlayer coupling in graphite, but enhanced in the heterostructure due to phonon mode clamping. However, these lifetimes drop precipitously with increasing carrier energy and are smaller than those in noble metals at energies exceeding 0.5 eV. By analyzing the contribution of different scattering mechanisms and interlayer interactions, desirable spacer layer characteristics—high dielectric constant and heavy atoms—that could pave the way for plasmonic heterostructures with improved hot carrier transport have been identified.},
doi = {10.1002/adom.201600914},
journal = {Advanced Optical Materials},
number = 15,
volume = 5,
place = {United States},
year = {Fri Mar 24 00:00:00 EDT 2017},
month = {Fri Mar 24 00:00:00 EDT 2017}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
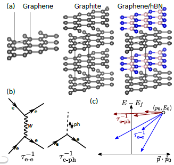 FIG. 1: (a) Schematic structures of 2D materials and graphene-derived vdW heterostructures in which we investigate hot carrier relaxation dynamics. (b) Feynman diagrams for the intrinsic carrier relaxation mechanisms: electronphonon (e-ph) scattering and and electron-electron (e-e) scattering. (c) Roles of the two mechanisms in energy and momentum relaxation: both processesmore »
FIG. 1: (a) Schematic structures of 2D materials and graphene-derived vdW heterostructures in which we investigate hot carrier relaxation dynamics. (b) Feynman diagrams for the intrinsic carrier relaxation mechanisms: electronphonon (e-ph) scattering and and electron-electron (e-e) scattering. (c) Roles of the two mechanisms in energy and momentum relaxation: both processesmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Plasmon-induced hot carrier science and technology
journal, January 2015
- Brongersma, Mark L.; Halas, Naomi J.; Nordlander, Peter
- Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 10, Issue 1
Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple
journal, October 1996
- Perdew, John P.; Burke, Kieron; Ernzerhof, Matthias
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 77, Issue 18, p. 3865-3868
Mixed-dimensional van der Waals heterostructures
journal, August 2016
- Jariwala, Deep; Marks, Tobin J.; Hersam, Mark C.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 16, Issue 2
Regularization of the Coulomb singularity in exact exchange by Wigner-Seitz truncated interactions: Towards chemical accuracy in nontrivial systems
journal, April 2013
- Sundararaman, Ravishankar; Arias, T. A.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 87, Issue 16
Two-dimensional material nanophotonics
journal, November 2014
- Xia, Fengnian; Wang, Han; Xiao, Di
- Nature Photonics, Vol. 8, Issue 12
Carrier Transport in Two-Dimensional Graphene Layers
journal, May 2007
- Hwang, E. H.; Adam, S.; Sarma, S. Das
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 98, Issue 18, Article No. 186806
First-Principles Study of Electron Linewidths in Graphene
journal, February 2009
- Park, Cheol-Hwan; Giustino, Feliciano; Spataru, Catalin D.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 102, Issue 7
Ultrafast Carrier Dynamics in Graphite
journal, February 2009
- Breusing, Markus; Ropers, Claus; Elsaesser, Thomas
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 102, Issue 8
Ultrafast graphene photodetector
journal, October 2009
- Xia, Fengnian; Mueller, Thomas; Lin, Yu-ming
- Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 4, Issue 12, p. 839-843
Van der Waals heterostructures
journal, July 2013
- Geim, A. K.; Grigorieva, I. V.
- Nature, Vol. 499, Issue 7459, p. 419-425
Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films
journal, October 2004
- Novoselov, K. S.
- Science, Vol. 306, Issue 5696, p. 666-669
Anisotropic behaviours of massless Dirac fermions in graphene under periodic potentials
journal, February 2008
- Park, Cheol-Hwan; Yang, Li; Son, Young-Woo
- Nature Physics, Vol. 4, Issue 3
Photoexcitation cascade and multiple hot-carrier generation in graphene
journal, February 2013
- Tielrooij, K. J.; Song, J. C. W.; Jensen, S. A.
- Nature Physics, Vol. 9, Issue 4
Theoretical predictions for hot-carrier generation from surface plasmon decay
journal, December 2014
- Sundararaman, Ravishankar; Narang, Prineha; Jermyn, Adam S.
- Nature Communications, Vol. 5, Issue 1
First-principles calculation of hot-electron scattering in metals
journal, December 2004
- Ladstädter, Florian; Hohenester, Ulrich; Puschnig, Peter
- Physical Review B, Vol. 70, Issue 23
Hot Electron Cooling by Acoustic Phonons in Graphene
journal, August 2012
- Betz, A. C.; Vialla, F.; Brunel, D.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 109, Issue 5
Plasmonics in graphene at infrared frequencies
journal, December 2009
- Jablan, Marinko; Buljan, Hrvoje; Soljačić, Marin
- Physical Review B, Vol. 80, Issue 24
Disorder-Assisted Electron-Phonon Scattering and Cooling Pathways in Graphene
journal, September 2012
- Song, Justin C. W.; Reizer, Michael Y.; Levitov, Leonid S.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 109, Issue 10
Plasmonic hot carrier dynamics in solid-state and chemical systems for energy conversion
journal, January 2016
- Narang, Prineha; Sundararaman, Ravishankar; Atwater, Harry A.
- Nanophotonics, Vol. 5, Issue 1
Atomic layers of hybridized boron nitride and graphene domains
journal, February 2010
- Ci, Lijie; Song, Li; Jin, Chuanhong
- Nature Materials, Vol. 9, Issue 5, p. 430-435
Observation of Ultrafast Carrier Dynamics and Phonon Relaxation of Graphene from the Deep-Ultraviolet to the Visible Region
journal, March 2014
- Oum, Kawon; Lenzer, Thomas; Scholz, Mirko
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 118, Issue 12
Relaxation of optically excited carriers in graphene
journal, August 2011
- Kim, Raseong; Perebeinos, Vasili; Avouris, Phaedon
- Physical Review B, Vol. 84, Issue 7
Four-Dimensional Electron Microscopy
journal, April 2010
- Zewail, A. H.
- Science, Vol. 328, Issue 5975
Ultrafast core-loss spectroscopy in four-dimensional electron microscopy
journal, March 2015
- van der Veen, Renske M.; Penfold, Thomas J.; Zewail, Ahmed H.
- Structural Dynamics, Vol. 2, Issue 2
The rise of graphene
journal, March 2007
- Geim, A. K.; Novoselov, K. S.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 6, Issue 3, p. 183-191
Graphene photonics and optoelectronics
journal, August 2010
- Bonaccorso, F.; Sun, Z.; Hasan, T.
- Nature Photonics, Vol. 4, Issue 9
The electronic properties of graphene
journal, January 2009
- Castro Neto, A. H.; Guinea, F.; Peres, N. M. R.
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 81, Issue 1, p. 109-162
Boron nitride substrates for high-quality graphene electronics
journal, August 2010
- Dean, C. R.; Young, A. F.; Meric, I.
- Nature Nanotechnology, Vol. 5, Issue 10, p. 722-726
Theory of electron-plasmon coupling in semiconductors
journal, September 2016
- Caruso, Fabio; Giustino, Feliciano
- Physical Review B, Vol. 94, Issue 11
Optimization algorithm for the generation of ONCV pseudopotentials
journal, November 2015
- Schlipf, Martin; Gygi, François
- Computer Physics Communications, Vol. 196
Nonradiative Plasmon Decay and Hot Carrier Dynamics: Effects of Phonons, Surfaces, and Geometry
journal, December 2015
- Brown, Ana M.; Sundararaman, Ravishankar; Narang, Prineha
- ACS Nano, Vol. 10, Issue 1
Femtosecond pump–probe nondestructive examination of materials (invited)
journal, January 2003
- Norris, Pamela M.; Caffrey, Andrew P.; Stevens, Robert J.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 74, Issue 1
Substrate-induced band gap in graphene on hexagonal boron nitride: Ab initio density functional calculations
journal, August 2007
- Giovannetti, Gianluca; Khomyakov, Petr A.; Brocks, Geert
- Physical Review B, Vol. 76, Issue 7
Supercollision cooling in undoped graphene
journal, December 2012
- Betz, A. C.; Jhang, S. H.; Pallecchi, E.
- Nature Physics, Vol. 9, Issue 2
Quantum Transport of Massless Dirac Fermions
journal, February 2007
- Nomura, Kentaro; MacDonald, A. H.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 98, Issue 7
Maximally localized Wannier functions for entangled energy bands
journal, December 2001
- Souza, Ivo; Marzari, Nicola; Vanderbilt, David
- Physical Review B, Vol. 65, Issue 3
Carrier Relaxation in Epitaxial Graphene Photoexcited Near the Dirac Point
journal, November 2011
- Winnerl, S.; Orlita, M.; Plochocka, P.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 107, Issue 23
Ab initio phonon coupling and optical response of hot electrons in plasmonic metals
journal, August 2016
- Brown, Ana M.; Sundararaman, Ravishankar; Narang, Prineha
- Physical Review B, Vol. 94, Issue 7
Femtosecond carrier dynamics in bulk graphite and graphene paper
journal, February 2011
- Carbone, F.; Aubock, G.; Cannizzo, A.
- Chemical Physics Letters, Vol. 504, Issue 1-3
Hot electron relaxation and phonon dynamics in graphene
journal, November 2007
- Butscher, S.; Milde, F.; Hirtschulz, M.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 91, Issue 20
Works referencing / citing this record:
2D Layered Material-Based van der Waals Heterostructures for Optoelectronics
journal, January 2018
- Zhou, Xing; Hu, Xiaozong; Yu, Jing
- Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 28, Issue 14
A Hexanuclear Niobium Cluster Compound Crystallizing as Macroscopic Tubes
journal, September 2019
- König, Jonas; Köckerling, Martin
- Chemistry – A European Journal, Vol. 25, Issue 61
Tailoring far-infrared surface plasmon polaritons of a single-layer graphene using plasmon-phonon hybridization in graphene-LiF heterostructures
journal, September 2018
- Hajian, Hodjat; Serebryannikov, Andriy E.; Ghobadi, Amir
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Carrier dynamics and spin–valley–layer effects in bilayer transition metal dichalcogenides
journal, January 2019
- Ciccarino, Christopher J.; Chakraborty, Chitraleema; Englund, Dirk R.
- Faraday Discussions, Vol. 214
Similar ultrafast dynamics of several dissimilar Dirac and Weyl semimetals
journal, December 2017
- Weber, Chris P.; Berggren, Bryan S.; Masten, Madison G.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 122, Issue 22
Hot carrier dynamics in plasmonic transition metal nitrides
journal, May 2018
- Habib, Adela; Florio, Fred; Sundararaman, Ravishankar
- Journal of Optics, Vol. 20, Issue 6
Optoelectronic response of the type-I Weyl semimetals TaAs and NbAs from first principles
journal, January 2020
- Garcia, Christina A. C.; Coulter, Jennifer; Narang, Prineha
- Physical Review Research, Vol. 2, Issue 1
Direct determination of mode-projected electron-phonon coupling in the time domain
journal, December 2019
- Na, M. X.; Mills, A. K.; Boschini, F.
- Science, Vol. 366, Issue 6470
Hot carrier dynamics in plasmonic transition metal nitrides
text, January 2018
- Habib, Adela; Florio, Fred; Sundararaman, Ravishankar
- arXiv
Direct determination of mode-projected electron-phonon coupling in the time-domain
text, January 2019
- Na, MengXing; Mills, Arthur K.; Boschini, Fabio
- arXiv
Tailoring far-infrared surface plasmon polaritons of a single-layer graphene using plasmon-phonon hybridization in graphene-LiF heterostructures
journal, September 2018
- Hajian, Hodjat; Serebryannikov, Andriy E.; Ghobadi, Amir
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 8, Issue 1

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal