The ecology of flows and drift wave turbulence in CSDX: A model
Abstract
This paper describes the ecology of drift wave turbulence and mean flows in the coupled drift-ion acoustic wave plasma of a CSDX linear device. A 1D reduced model that studies the spatiotemporal evolution of plasma mean density $$\bar{n}$$, and mean flows $$\bar{v}$$y and $$\bar{v}$$z, in addition to fluctuation intensity ε, is presented. Here, is the conserved energy field. The model uses a mixing length lmix inversely proportional to both axial and azimuthal flow shear. This form of lmix closes the loop on total energy. The model self-consistently describes variations in plasma profiles, including mean flows and turbulent stresses. It investigates the energy exchange between the fluctuation intensity and mean profiles via particle flux and Reynolds stresses and Acoustic coupling breaks parallel symmetry and generates a parallel residual stress Π res xz . The model uses a set of equations to explain the acceleration of $$\bar{v}_y$$ and $$\bar{v}_z$$ via and . Flow dynamics in the parallel direction are related to those in the perpendicular direction through an empirical coupling constant σVT. This constant measures the degree of symmetry breaking in the 〈$$k_mk_z$$〉 correlator and determines the efficiency of ∇$$\bar{n}$$ in driving $$\bar{v}_z$$. The model also establishes a relation between ∇$$\bar{v}_y$$ and ∇$$\bar{v}_z$$, via the ratio of the stresses Π res xy and Π res xz . When parallel to perpendicular flow coupling is weak, axial Reynolds power is less than the azimuthal Reynolds power ∇$$\bar{v}_y$$. The model is then reduced to a 2-field predator/prey model where $$\bar{v}_z$$ is parasitic to the system and fluctuations evolve self-consistently. Finally, turbulent diffusion in CSDX follows the scaling: , where DB is the Bohm diffusion coefficient and ρ* is the ion gyroradius normalized to the density gradient
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States). Center for Energy Research
- Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States). Center for Energy Research, Center for Astrophysics and Space Sciences; Center for Fusion Sciences, Southwestern Inst. of Physics, Chengdu, Sichuan (China)
- Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States). Center for Energy Research; Center for Fusion Sciences, Southwestern Inst. of Physics, Chengdu, Sichuan (China)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of California, San Diego, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1524572
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1420214
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FG02-04ER54738
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Physics of Plasmas
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 25; Journal Issue: 2; Journal ID: ISSN 1070-664X
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 70 PLASMA PHYSICS AND FUSION TECHNOLOGY
Citation Formats
Hajjar, R. J., Diamond, P. H., and Tynan, G. R. The ecology of flows and drift wave turbulence in CSDX: A model. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.5018320.
Hajjar, R. J., Diamond, P. H., & Tynan, G. R. The ecology of flows and drift wave turbulence in CSDX: A model. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5018320
Hajjar, R. J., Diamond, P. H., and Tynan, G. R. Thu .
"The ecology of flows and drift wave turbulence in CSDX: A model". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5018320. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1524572.
@article{osti_1524572,
title = {The ecology of flows and drift wave turbulence in CSDX: A model},
author = {Hajjar, R. J. and Diamond, P. H. and Tynan, G. R.},
abstractNote = {This paper describes the ecology of drift wave turbulence and mean flows in the coupled drift-ion acoustic wave plasma of a CSDX linear device. A 1D reduced model that studies the spatiotemporal evolution of plasma mean density $\bar{n}$, and mean flows $\bar{v}$y and $\bar{v}$z, in addition to fluctuation intensity ε, is presented. Here, ε=〈n~2+(∇⊥Φ~)2+v~z2〉 is the conserved energy field. The model uses a mixing length lmix inversely proportional to both axial and azimuthal flow shear. This form of lmix closes the loop on total energy. The model self-consistently describes variations in plasma profiles, including mean flows and turbulent stresses. It investigates the energy exchange between the fluctuation intensity and mean profiles via particle flux 〈n~v~x〉 and Reynolds stresses 〈v~xv~y〉 and 〈 v~xv~z〉 Acoustic coupling breaks parallel symmetry and generates a parallel residual stress Π res xz . The model uses a set of equations to explain the acceleration of $\bar{v}_y$ and $\bar{v}_z$ via Πxyres∝∇n- and Πxyres∝∇n-. Flow dynamics in the parallel direction are related to those in the perpendicular direction through an empirical coupling constant σVT. This constant measures the degree of symmetry breaking in the 〈$k_mk_z$〉 correlator and determines the efficiency of ∇$\bar{n}$ in driving $\bar{v}_z$. The model also establishes a relation between ∇$\bar{v}_y$ and ∇$\bar{v}_z$, via the ratio of the stresses Π res xy and Π res xz . When parallel to perpendicular flow coupling is weak, axial Reynolds power PxzRe=-〈v~xv~z〉∇v-z is less than the azimuthal Reynolds power PxyRe=-〈v~xv~y〉∇v-y∇$\bar{v}_y$. The model is then reduced to a 2-field predator/prey model where $\bar{v}_z$ is parasitic to the system and fluctuations evolve self-consistently. Finally, turbulent diffusion in CSDX follows the scaling: DCSDX=DBρ*0.6, where DB is the Bohm diffusion coefficient and ρ* is the ion gyroradius normalized to the density gradient |∇n-/n-|-1},
doi = {10.1063/1.5018320},
journal = {Physics of Plasmas},
number = 2,
volume = 25,
place = {United States},
year = {Thu Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Thu Feb 01 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
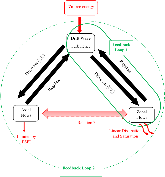 FIG. 1: A schematic of the ecology of drift wave turbulence, zonal, and axial flows. The first feedback loop relates the drift waves to the zonal flows via (~vx~vy). A second feedback loop exists as a result of a potential relation between $\bar{v}$y and $\bar{v}$z. The second loop relates themore »
FIG. 1: A schematic of the ecology of drift wave turbulence, zonal, and axial flows. The first feedback loop relates the drift waves to the zonal flows via (~vx~vy). A second feedback loop exists as a result of a potential relation between $\bar{v}$y and $\bar{v}$z. The second loop relates themore »
Works referenced in this record:
Role of the geodesic acoustic mode shearing feedback loop in transport bifurcations and turbulence spreading
journal, March 2010
- Miki, K.; Diamond, P. H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 17, Issue 3
The role of the electric field in confinement
journal, January 1996
- Itoh, Kimitaka; Itoh, Sanae-I
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 38, Issue 1
How does drift wave turbulence convert parallel compression into perpendicular flows?
journal, August 2012
- Wang, Lu; Diamond, P. H.; Hahm, T. S.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 54, Issue 9
Intrinsic rotation and electric field shear
journal, April 2007
- Gürcan, Ö. D.; Diamond, P. H.; Hahm, T. S.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 14, Issue 4
Nonlinear energy transfer during the transition to drift-interchange turbulence
journal, July 2011
- Manz, P.; Xu, M.; Thakur, S. C.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 53, Issue 9
Dynamics of intrinsic axial flows in unsheared, uniform magnetic fields
journal, May 2016
- Li, J. C.; Diamond, P. H.; Xu, X. Q.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 5
Scale interactions and scaling laws in rotating flows at moderate Rossby numbers and large Reynolds numbers
journal, January 2009
- Mininni, P. D.; Alexakis, A.; Pouquet, A.
- Physics of Fluids, Vol. 21, Issue 1
TOKAM-3D: A 3D fluid code for transport and turbulence in the edge plasma of Tokamaks
journal, January 2010
- Tamain, P.; Ghendrih, Ph.; Tsitrone, E.
- Journal of Computational Physics, Vol. 229, Issue 2
Physical Mechanism behind Zonal-Flow Generation in Drift-Wave Turbulence
journal, October 2009
- Manz, P.; Ramisch, M.; Stroth, U.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 103, Issue 16
Eddy Motion in the Atmosphere
journal, January 1915
- Taylor, G. I.
- Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, Vol. 215, Issue 523-537
Upscale energy transfer in thick turbulent fluid layers
journal, February 2011
- Xia, H.; Byrne, D.; Falkovich, G.
- Nature Physics, Vol. 7, Issue 4
The new SOLPS-ITER code package
journal, August 2015
- Wiesen, S.; Reiter, D.; Kotov, V.
- Journal of Nuclear Materials, Vol. 463
Spatial and spectral evolution of turbulence
journal, May 2007
- Gürcan, Ö. D.; Diamond, P. H.; Hahm, T. S.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 14, Issue 5
Particle and energy confinement bifurcation in tokamaks
journal, April 1993
- Hinton, F. L.; Staebler, G. M.
- Physics of Fluids B: Plasma Physics, Vol. 5, Issue 4
Plasma Edge Turbulence
journal, February 1983
- Hasegawa, Akira; Wakatani, Masahiro
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 50, Issue 9
Nonadiabatic electron response in the Hasegawa-Wakatani equations
journal, August 2013
- Stoltzfus-Dueck, T.; Scott, B. D.; Krommes, J. A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 8
Self-organization of electrostatic turbulence in a cylindrical plasma
journal, October 1987
- Hasegawa, Akira; Wakatani, Masahiro
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 59, Issue 14
Transport matrix for particles and momentum in collisional drift waves turbulence in linear plasma devices
journal, February 2016
- Ashourvan, Arash; Diamond, P. H.; Gürcan, Ö. D.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 2
An overview of intrinsic torque and momentum transport bifurcations in toroidal plasmas
journal, September 2013
- Diamond, P. H.; Kosuga, Y.; Gürcan, Ö. D.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 53, Issue 10
Turbulence Dynamics with the Coupling of Density Gradient and Parallel Velocity Gradient in the Edge Plasmas: Turbulence Dynamics with the Coupling of Density Gradient and Parallel Velocity Gradient in the Edge Plasmas
journal, June 2016
- Kosuga, Y.; Itoh, S. -I.; Itoh, K.
- Contributions to Plasma Physics, Vol. 56, Issue 6-8
Energetics of the interaction between electromagnetic ExB turbulence and zonal flows
journal, January 2005
- Scott, Bruce D.
- New Journal of Physics, Vol. 7
Direct Observation of the Resistive Wall Mode in a Tokamak and Its Interaction with Plasma Rotation
journal, May 1999
- Garofalo, A. M.; Turnbull, A. D.; Austin, M. E.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 82, Issue 19
Density Peaking by Parallel Flow Shear Driven Instability
journal, January 2015
- Kosuga, Yusuke; Itoh, Sanae-I.; Itoh, Kimitaka
- Plasma and Fusion Research, Vol. 10, Issue 0
Drift waves and transport
journal, April 1999
- Horton, W.
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 71, Issue 3
Negative viscosity from negative compressibility and axial flow shear stiffness in a straight magnetic field
journal, March 2017
- Li, J. C.; Diamond, P. H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 24, Issue 3
Intrinsic rotation, hysteresis and back transition in reversed shear internal transport barriers
journal, June 2011
- Kim, S. S.; Jhang, Hogun; Diamond, P. H.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 51, Issue 7
Spontaneous profile self-organization in a simple realization of drift-wave turbulence
journal, March 2016
- Cui, L.; Ashourvan, A.; Thakur, S. C.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 5
Structure formation in parallel ion flow and density profiles by cross-ferroic turbulent transport in linear magnetized plasma
journal, October 2016
- Kobayashi, T.; Inagaki, S.; Kosuga, Y.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 10
Radial transport of fluctuation energy in a two-field model of drift-wave turbulence
journal, May 2006
- Gürcan, Ö. D.; Diamond, P. H.; Hahm, T. S.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 13, Issue 5
On the efficiency of intrinsic rotation generation in tokamaks
journal, October 2010
- Kosuga, Y.; Diamond, P. H.; Gürcan, Ö. D.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 17, Issue 10
Modelling enhanced confinement in drift-wave turbulence
journal, June 2017
- Hajjar, R. J.; Diamond, P. H.; Ashourvan, A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 24, Issue 6
Increased understanding of the dynamics and transport in ITB plasmas from multi-machine comparisons
journal, August 2003
- Gohil, P.; Kinsey, J.; Parail, V.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 43, Issue 8
Influence of sheared poloidal rotation on edge turbulence
journal, January 1990
- Biglari, H.; Diamond, P. H.; Terry, P. W.
- Physics of Fluids B: Plasma Physics, Vol. 2, Issue 1
Zonal flow generation in parallel flow shear driven turbulence
journal, March 2017
- Kosuga, Y.; Itoh, S. -I.; Itoh, K.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 24, Issue 3
Development of core ion temperature gradients and edge sheared flows in a helicon plasma device investigated by laser induced fluorescence measurements
journal, August 2016
- Thakur, S. C.; Gosselin, J. J.; McKee, J.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 8
Suppression of turbulence and transport by sheared flow
journal, January 2000
- Terry, P. W.
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 72, Issue 1
Inverse Energy Cascade in Three-Dimensional Isotropic Turbulence
journal, April 2012
- Biferale, Luca; Musacchio, Stefano; Toschi, Federico
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 108, Issue 16
Self-Regulating Shear Flow Turbulence: A Paradigm for the L to H Transition
journal, April 1994
- Diamond, P. H.; Liang, Y. -M.; Carreras, B. A.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 72, Issue 16
A fully implicit, time dependent 2-D fluid code for modeling tokamak edge plasmas
journal, December 1992
- Rognlien, T. D.; Milovich, J. L.; Rensink, M. E.
- Journal of Nuclear Materials, Vol. 196-198
A Concept of Cross-Ferroic Plasma Turbulence
journal, February 2016
- Inagaki, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kosuga, Y.
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 6, Issue 1
Zonal Flows and Transient Dynamics of the Transition
journal, May 2003
- Kim, Eun-jin; Diamond, P. H.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 90, Issue 18
Works referencing / citing this record:
Generation of parasitic axial flow by drift wave turbulence with broken symmetry: Theory and experiment
journal, May 2018
- Hong, R.; Li, J. C.; Hajjar, R.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 25, Issue 5
How shear increments affect the flow production branching ratio in CSDX
journal, June 2018
- Li, J. C.; Diamond, P. H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 25, Issue 6
Simultaneous measurements of turbulent Reynolds stresses and particle flux in both parallel and perpendicular directions in a linear magnetized plasma device
journal, October 2018
- Chakraborty Thakur, Saikat; Hong, Rongjie; Tynan, George R.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Scale selection and feedback loops for patterns in drift wave-zonal flow turbulence
journal, August 2019
- Guo, Weixin; Diamond, Patrick H.; Hughes, David W.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 61, Issue 10
Generation of parasitic axial flow by drift wave turbulence with broken symmetry: Theory and experiment
text, January 2018
- Hong, R.; Li, J. C.; Thakur, R. Hajjar. Chakraborty
- arXiv

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal