Enhanced Capacities of Mixed Fatty Acid-Modified Sawdust Aggregators for Remediation of Crude Oil Spill
Abstract
Mixed fatty acid-modified aggregators have been developed as potential crude oil sorbents. Cheap pine wood flour was first modified with oleic acid (OA) and further modified with second fatty acid by a leaving group chemistry, where a surface hydroxyl group is first replaced by p-toluenesulfonyl (p-Ts) group and a fatty acid forms a covalent bond on sawdust surface through esterification at the elevated temperature (55 C). Two OA-modified base materials, pine/OA-106 and pine/OA-124 with different OA-coverage were first prepared and the second fatty acids with C3, C6, C8, C10, C12, C14, or C16 alkyl chains were applied to cover the rest of surface hydroxyl groups. The crude oil sorption capacities of the mixed fatty acid-modified aggregators were studied and compared with those of the base materials. The results showed that mixed fatty acid-modified aggregators increased up to 45.6% more crude oil sorption than those of OA-modified base materials. A correlation between surface property and sorption capacity was studied by moisture sorption, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), 13C cross polarization and magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (CP/MAS NMR), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
- Authors:
-
- Materials Sciences, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 902 Battelle Blvd, Richland, Washington 99352, United States
- Marine Science Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, 1529 West Sequim Bay Road, Sequim, Washington 98382, United States
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER); PNNL Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) Program
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1489889
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1507395; OSTI ID: 1512783
- Report Number(s):
- PNNL-SA-135555
Journal ID: ISSN 2470-1343
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-76RL01830
- Resource Type:
- Published Article
- Journal Name:
- ACS Omega
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: ACS Omega Journal Volume: 4 Journal Issue: 1; Journal ID: ISSN 2470-1343
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- Superhydrophobic, Sorption capacity, Crude oil, Aggregator, fatty acids; 37 INORGANIC, ORGANIC, PHYSICAL, AND ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY; carbonyl compounds (organic); granular materials; phase; remediation; water purification
Citation Formats
Shin, Yongsoon, Winder, Eric M., Han, Kee Sung, Lee, Hongkyung, and Bonheyo, George T. Enhanced Capacities of Mixed Fatty Acid-Modified Sawdust Aggregators for Remediation of Crude Oil Spill. United States: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1021/acsomega.8b02293.
Shin, Yongsoon, Winder, Eric M., Han, Kee Sung, Lee, Hongkyung, & Bonheyo, George T. Enhanced Capacities of Mixed Fatty Acid-Modified Sawdust Aggregators for Remediation of Crude Oil Spill. United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02293
Shin, Yongsoon, Winder, Eric M., Han, Kee Sung, Lee, Hongkyung, and Bonheyo, George T. Mon .
"Enhanced Capacities of Mixed Fatty Acid-Modified Sawdust Aggregators for Remediation of Crude Oil Spill". United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02293.
@article{osti_1489889,
title = {Enhanced Capacities of Mixed Fatty Acid-Modified Sawdust Aggregators for Remediation of Crude Oil Spill},
author = {Shin, Yongsoon and Winder, Eric M. and Han, Kee Sung and Lee, Hongkyung and Bonheyo, George T.},
abstractNote = {Mixed fatty acid-modified aggregators have been developed as potential crude oil sorbents. Cheap pine wood flour was first modified with oleic acid (OA) and further modified with second fatty acid by a leaving group chemistry, where a surface hydroxyl group is first replaced by p-toluenesulfonyl (p-Ts) group and a fatty acid forms a covalent bond on sawdust surface through esterification at the elevated temperature (55 C). Two OA-modified base materials, pine/OA-106 and pine/OA-124 with different OA-coverage were first prepared and the second fatty acids with C3, C6, C8, C10, C12, C14, or C16 alkyl chains were applied to cover the rest of surface hydroxyl groups. The crude oil sorption capacities of the mixed fatty acid-modified aggregators were studied and compared with those of the base materials. The results showed that mixed fatty acid-modified aggregators increased up to 45.6% more crude oil sorption than those of OA-modified base materials. A correlation between surface property and sorption capacity was studied by moisture sorption, Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), 13C cross polarization and magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (CP/MAS NMR), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM).},
doi = {10.1021/acsomega.8b02293},
journal = {ACS Omega},
number = 1,
volume = 4,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Jan 07 00:00:00 EST 2019},
month = {Mon Jan 07 00:00:00 EST 2019}
}
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02293
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
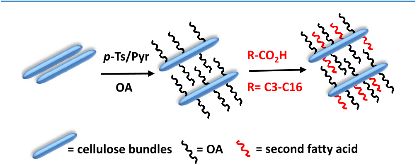 Figure 1: Illustration of hydrophobic modification of cellulose networks in sawdust.
Figure 1: Illustration of hydrophobic modification of cellulose networks in sawdust.
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal