Sedentary behavior associated with reduced medial temporal lobe thickness in middle-aged and older adults
Abstract
Atrophy of the medial temporal lobe (MTL) occurs with aging, resulting in impaired episodic memory. Aerobic fitness is positively correlated with total hippocampal volume, a heavily studied memory-critical region within the MTL. However, research on associations between sedentary behavior and MTL subregion integrity is limited. Here we explore associations between thickness of the MTL and its subregions (namely CA1, CA23DG, fusiform gyrus, subiculum, parahippocampal, perirhinal and entorhinal cortex,), physical activity, and sedentary behavior. We assessed 35 non-demented middle-aged and older adults (25 women, 10 men; 45–75 years) using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire for older adults, which quantifies physical activity levels in MET-equivalent units and asks about the average number of hours spent sitting per day. All participants had high resolution MRI scans performed on a Siemens Allegra 3T MRI scanner, which allows for detailed investigation of the MTL. Controlling for age, total MTL thickness correlated inversely with hours of sitting/day (r = -0.37, p = 0.03). In MTL subregion analysis, parahippocampal (r = -0.45, p = 0.007), entorhinal (r = -0.33, p = 0.05) cortical and subiculum (r = -0.36, p = .04) thicknesses correlated inversely with hours of sitting/day. No significant correlations were observed between physical activity levelsmore »
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of California, Los Angeles, CA (United States). Semel Inst. for Neuroscience and Human Behavior
- Univ. of California, Los Angeles, CA (United States). Center for Cognitive Neurosciences
- Univ. of Adelaide, SA (Australia). Discipline of Psychiatry
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of California, Los Angeles, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE; National Inst. of Health (NIH) (United States)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1505148
- Grant/Contract Number:
- FC03-87ER60615; MH077650; AT003480; P01-AG024831; AG13308; P50 AG 16570; MH/AG58156; AG10123; M01-RR00865; 5P30AG028748; UL1TR000124
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- PLoS ONE
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 13; Journal Issue: 4; Journal ID: ISSN 1932-6203
- Publisher:
- Public Library of Science
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 60 APPLIED LIFE SCIENCES; physical activity; elderly; Alzheimer's disease; behavior; central nervous system; magnetic resonance imaging; entorhinal cortex; temporal lobe
Citation Formats
Siddarth, Prabha, Burggren, Alison C., Eyre, Harris A., Small, Gary W., and Merrill, David A. Sedentary behavior associated with reduced medial temporal lobe thickness in middle-aged and older adults. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0195549.
Siddarth, Prabha, Burggren, Alison C., Eyre, Harris A., Small, Gary W., & Merrill, David A. Sedentary behavior associated with reduced medial temporal lobe thickness in middle-aged and older adults. United States. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195549
Siddarth, Prabha, Burggren, Alison C., Eyre, Harris A., Small, Gary W., and Merrill, David A. Thu .
"Sedentary behavior associated with reduced medial temporal lobe thickness in middle-aged and older adults". United States. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195549. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1505148.
@article{osti_1505148,
title = {Sedentary behavior associated with reduced medial temporal lobe thickness in middle-aged and older adults},
author = {Siddarth, Prabha and Burggren, Alison C. and Eyre, Harris A. and Small, Gary W. and Merrill, David A.},
abstractNote = {Atrophy of the medial temporal lobe (MTL) occurs with aging, resulting in impaired episodic memory. Aerobic fitness is positively correlated with total hippocampal volume, a heavily studied memory-critical region within the MTL. However, research on associations between sedentary behavior and MTL subregion integrity is limited. Here we explore associations between thickness of the MTL and its subregions (namely CA1, CA23DG, fusiform gyrus, subiculum, parahippocampal, perirhinal and entorhinal cortex,), physical activity, and sedentary behavior. We assessed 35 non-demented middle-aged and older adults (25 women, 10 men; 45–75 years) using the International Physical Activity Questionnaire for older adults, which quantifies physical activity levels in MET-equivalent units and asks about the average number of hours spent sitting per day. All participants had high resolution MRI scans performed on a Siemens Allegra 3T MRI scanner, which allows for detailed investigation of the MTL. Controlling for age, total MTL thickness correlated inversely with hours of sitting/day (r = -0.37, p = 0.03). In MTL subregion analysis, parahippocampal (r = -0.45, p = 0.007), entorhinal (r = -0.33, p = 0.05) cortical and subiculum (r = -0.36, p = .04) thicknesses correlated inversely with hours of sitting/day. No significant correlations were observed between physical activity levels and MTL thickness. Though preliminary, our results suggest that more sedentary non-demented individuals have less MTL thickness. Future studies should include longitudinal analyses and explore mechanisms, as well as the efficacy of decreasing sedentary behaviors to reverse this association.},
doi = {10.1371/journal.pone.0195549},
journal = {PLoS ONE},
number = 4,
volume = 13,
place = {United States},
year = {Thu Apr 12 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Thu Apr 12 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
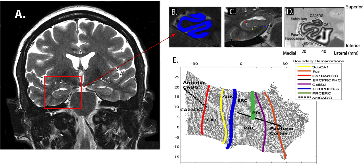 Figure 1: Methods for producing flat maps. Oblique coronal images are acquired to cover the long axis of the hippocampus as shown in image A. This image is cropped over the area of interest (red square) and shown in greater detail in image B. The gray matter ribbon (shown inmore »
Figure 1: Methods for producing flat maps. Oblique coronal images are acquired to cover the long axis of the hippocampus as shown in image A. This image is cropped over the area of interest (red square) and shown in greater detail in image B. The gray matter ribbon (shown inmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Physical Activity Predicts Microstructural Integrity in Memory-Related Networks in Very Old Adults
journal, January 2014
- Tian, Q.; Erickson, K. I.; Simonsick, E. M.
- The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, Vol. 69, Issue 10
APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer's disease
journal, December 2013
- Donix, Markus; Burggren, Alison C.; Scharf, Maria
- Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, Vol. 214, Issue 3
The effect of midlife physical activity on structural brain changes in the elderly
journal, November 2010
- Rovio, Suvi; Spulber, Gabriela; Nieminen, Lasse J.
- Neurobiology of Aging, Vol. 31, Issue 11
Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory
journal, January 2011
- Erickson, K. I.; Voss, M. W.; Prakash, R. S.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 108, Issue 7
Biochemical Markers of Physical Exercise on Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Systematic Review and Perspectives
journal, August 2015
- Jensen, Camilla Steen; Hasselbalch, Steen Gregers; Waldemar, Gunhild
- Frontiers in Neurology, Vol. 6
Evidence that women meeting physical activity guidelines do not sit less: An observational inclinometry study
journal, January 2012
- Craft, Lynette L.; Zderic, Theodore W.; Gapstur, Susan M.
- International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Brain mapping as a tool to study neurodegeneration
journal, July 2007
- Apostolova, Liana G.; Thompson, Paul M.
- Neurotherapeutics, Vol. 4, Issue 3
The Assessment of Anxiety States by Rating
journal, March 1959
- Hamilton, Max
- British Journal of Medical Psychology, Vol. 32, Issue 1
Imaging markers of structural and functional brain changes that precede cognitive symptoms in risk for Alzheimer’s disease
journal, December 2013
- Burggren, Alison; Brown, Jesse
- Brain Imaging and Behavior, Vol. 8, Issue 2
Reduced cortical thickness in hippocampal subregions among cognitively normal apolipoprotein E e4 carriers
journal, July 2008
- Burggren, A. C.; Zeineh, M. M.; Ekstrom, A. D.
- NeuroImage, Vol. 41, Issue 4
A Rating Scale for Depression
journal, February 1960
- Hamilton, M.
- Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, Vol. 23, Issue 1
Comparison of self-reported measure of sitting time (IPAQ) with objective measurement (activPAL)
journal, October 2014
- Chastin, S. F. M.; Culhane, B.; Dall, P. M.
- Physiological Measurement, Vol. 35, Issue 11
Cessation of voluntary wheel running increases anxiety-like behavior and impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis in mice
journal, May 2013
- Nishijima, Takeshi; Llorens-Martín, María; Tejeda, Gonzalo Sanchez
- Behavioural Brain Research, Vol. 245
Exercise Is Associated with Reduced Risk for Incident Dementia among Persons 65 Years of Age and Older
journal, January 2006
- Larson, Eric B.; Wang, Li; Bowen, James D.
- Annals of Internal Medicine, Vol. 144, Issue 2
What is the association between sedentary behaviour and cognitive function? A systematic review
journal, May 2016
- Falck, Ryan S.; Davis, Jennifer C.; Liu-Ambrose, Teresa
- British Journal of Sports Medicine, Vol. 51, Issue 10
Advances in high-resolution imaging and computational unfolding of the human hippocampus
journal, August 2009
- Ekstrom, Arne D.; Bazih, Adam J.; Suthana, Nanthia A.
- NeuroImage, Vol. 47, Issue 1
Towards a functional organization of episodic memory in the medial temporal lobe
journal, August 2012
- Eichenbaum, Howard; Sauvage, Magdalena; Fortin, Norbert
- Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, Vol. 36, Issue 7
Sedentary behavior and health outcomes among older adults: a systematic review
journal, April 2014
- Rezende, Leandro Fornias Machado de; Rey-López, Juan Pablo; Matsudo, Victor Keihan Rodrigues
- BMC Public Health, Vol. 14, Issue 1
Structural and functional brain changes related to different types of physical activity across the life span
journal, November 2013
- Voelcker-Rehage, Claudia; Niemann, Claudia
- Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, Vol. 37, Issue 9
An in vivo correlate of exercise-induced neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus
journal, March 2007
- Pereira, A. C.; Huddleston, D. E.; Brickman, A. M.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 104, Issue 13
Effect of Physical Activity on Cognitive Function in Older Adults at Risk for Alzheimer Disease: A Randomized Trial
journal, September 2008
- Lautenschlager, Nicola T.; Cox, Kay L.; Flicker, Leon
- JAMA, Vol. 300, Issue 9
Physical Exercise as a Preventive or Disease-Modifying Treatment of Dementia and Brain Aging
journal, September 2011
- Ahlskog, J. Eric; Geda, Yonas E.; Graff-Radford, Neill R.
- Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Vol. 86, Issue 9
Revenge of the “sit” II: Does lifestyle impact neuronal and cognitive health through distinct mechanisms associated with sedentary behavior and physical activity?
journal, March 2014
- Voss, Michelle W.; Carr, Lucas J.; Clark, Rachel
- Mental Health and Physical Activity, Vol. 7, Issue 1
Sedentary Behaviors and Subsequent Health Outcomes in Adults
journal, August 2011
- Thorp, Alicia A.; Owen, Neville; Neuhaus, Maike
- American Journal of Preventive Medicine, Vol. 41, Issue 2
Longitudinal changes in medial temporal cortical thickness in normal subjects with the APOE-4 polymorphism
journal, October 2010
- Donix, Markus; Burggren, Alison C.; Suthana, Nanthia A.
- NeuroImage, Vol. 53, Issue 1
The influence of aerobic fitness on cerebral white matter integrity and cognitive function in older adults: Results of a one-year exercise intervention: Aerobic Fitness, White Matter, and Aging
journal, June 2012
- Voss, Michelle W.; Heo, Susie; Prakash, Ruchika S.
- Human Brain Mapping, Vol. 34, Issue 11
The Effects of Aerobic Activity on Brain Structure
journal, January 2012
- Thomas, Adam G.; Dennis, Andrea; Bandettini, Peter A.
- Frontiers in Psychology, Vol. 3
Regional Brain Atrophy Rate Predicts Future Cognitive Decline: 6-year Longitudinal MR Imaging Study of Normal Aging
journal, December 2003
- Rusinek, Henry; De Santi, Susan; Frid, Dina
- Radiology, Vol. 229, Issue 3
The projected effect of risk factor reduction on Alzheimer's disease prevalence
journal, September 2011
- Barnes, Deborah E.; Yaffe, Kristine
- The Lancet Neurology, Vol. 10, Issue 9
Differential effects of aging and Alzheimer's disease on medial temporal lobe cortical thickness and surface area
journal, March 2009
- Dickerson, Bradford C.; Feczko, Eric; Augustinack, Jean C.
- Neurobiology of Aging, Vol. 30, Issue 3
Family History of Alzheimer's Disease and Hippocampal Structure in Healthy People
journal, November 2010
- Donix, Markus; Burggren, Alison C.; Suthana, Nanthia A.
- American Journal of Psychiatry, Vol. 167, Issue 11
A meta-analysis of prospective studies on the role of physical activity and the prevention of Alzheimer’s disease in older adults
journal, February 2015
- Beckett, Michael W.; Ardern, Christopher I.; Rotondi, Michael A.
- BMC Geriatrics, Vol. 15, Issue 1
Entorhinal volume, aerobic fitness, and recognition memory in healthy young adults: A voxel-based morphometry study
journal, February 2016
- Whiteman, Andrew S.; Young, Daniel E.; Budson, Andrew E.
- NeuroImage, Vol. 126
Loss and atrophy of layer II entorhinal cortex neurons in elderly people with mild cognitive impairment
journal, January 2001
- Kordower, Jeffrey H.; Chu, Yaping; Stebbins, Glenn T.
- Annals of Neurology, Vol. 49, Issue 2
Association of change in brain structure to objectively measured physical activity and sedentary behavior in older adults: Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility-Reykjavik Study
journal, January 2016
- Arnardottir, Nanna Yr; Koster, Annemarie; Domelen, Dane R. Van
- Behavioural Brain Research, Vol. 296
Bridging animal and human models of exercise-induced brain plasticity
journal, October 2013
- Voss, Michelle W.; Vivar, Carmen; Kramer, Arthur F.
- Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 17, Issue 10
Assessment of Physical Activity: An International Perspective
journal, June 2000
- Booth, Michael
- Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, Vol. 71, Issue sup2
International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity
journal, January 2003
- Craig, Cora L.; Marshall, Alison L.; Sj??Str??M, Michael
- Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, Vol. 35, Issue 8
Profound Loss of Layer II Entorhinal Cortex Neurons Occurs in Very Mild Alzheimer’s Disease
journal, July 1996
- Gómez-Isla, Teresa; Price, Joseph L.; McKeel Jr., Daniel W.
- The Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 16, Issue 14
Loss and atrophy of layer II entorhinal cortex neurons in elderly people with mild cognitive impairment
journal, February 2001
- Kordower, Jeffrey H.; Chu, Yaping; Stebbins, Glenn T.
- Annals of Neurology, Vol. 49, Issue 2
A Rating Scale for Depression
journal, October 1960
- Ostwald, Peter F.
- American Journal of Psychotherapy, Vol. 14, Issue 4
Exercise is associated with reduced risk for incident dementia among persons 65 years of age and older
journal, August 2006
- Larson, E. B.; Wang, L.; Bowen, J. D.
- Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, Vol. 16, Issue 4
Imaging markers of structural and functional brain changes that precede cognitive symptoms in risk for Alzheimer’s disease
journal, December 2013
- Burggren, Alison; Brown, Jesse
- Brain Imaging and Behavior, Vol. 8, Issue 2
Association of change in brain structure to objectively measured physical activity and sedentary behavior in older adults: Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility-Reykjavik Study
journal, January 2016
- Arnardottir, Nanna Yr; Koster, Annemarie; Domelen, Dane R. Van
- Behavioural Brain Research, Vol. 296
Structural and functional brain changes related to different types of physical activity across the life span
journal, November 2013
- Voelcker-Rehage, Claudia; Niemann, Claudia
- Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, Vol. 37, Issue 9
Differential effects of aging and Alzheimer's disease on medial temporal lobe cortical thickness and surface area
journal, March 2009
- Dickerson, Bradford C.; Feczko, Eric; Augustinack, Jean C.
- Neurobiology of Aging, Vol. 30, Issue 3
The effect of midlife physical activity on structural brain changes in the elderly
journal, November 2010
- Rovio, Suvi; Spulber, Gabriela; Nieminen, Lasse J.
- Neurobiology of Aging, Vol. 31, Issue 11
Advances in high-resolution imaging and computational unfolding of the human hippocampus
journal, August 2009
- Ekstrom, Arne D.; Bazih, Adam J.; Suthana, Nanthia A.
- NeuroImage, Vol. 47, Issue 1
Longitudinal changes in medial temporal cortical thickness in normal subjects with the APOE-4 polymorphism
journal, October 2010
- Donix, Markus; Burggren, Alison C.; Suthana, Nanthia A.
- NeuroImage, Vol. 53, Issue 1
APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer's disease
journal, December 2013
- Donix, Markus; Burggren, Alison C.; Scharf, Maria
- Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, Vol. 214, Issue 3
Bridging animal and human models of exercise-induced brain plasticity
journal, October 2013
- Voss, Michelle W.; Vivar, Carmen; Kramer, Arthur F.
- Trends in Cognitive Sciences, Vol. 17, Issue 10
Prevention of cognitive decline in ageing: dementia as the target, delayed onset as the goal
journal, September 2011
- Fratiglioni, Laura; Qiu, Chengxuan
- The Lancet Neurology, Vol. 10, Issue 9
The International Physical Activity Questionnaire modified for the elderly: aspects of validity and feasibility
journal, March 2010
- Hurtig-Wennlöf, Anita; Hagströmer, Maria; Olsson, Lovisa A.
- Public Health Nutrition, Vol. 13, Issue 11
An in vivo correlate of exercise-induced neurogenesis in the adult dentate gyrus
journal, March 2007
- Pereira, A. C.; Huddleston, D. E.; Brickman, A. M.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 104, Issue 13
Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory
journal, January 2011
- Erickson, K. I.; Voss, M. W.; Prakash, R. S.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 108, Issue 7
Assessment of Physical Activity: An International Perspective
journal, June 2000
- Booth, Michael
- Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport, Vol. 71, Issue sup2
Comparison of self-reported measure of sitting time (IPAQ) with objective measurement (activPAL)
journal, October 2014
- Chastin, S. F. M.; Culhane, B.; Dall, P. M.
- Physiological Measurement, Vol. 35, Issue 11
Physical Activity Predicts Microstructural Integrity in Memory-Related Networks in Very Old Adults
journal, January 2014
- Tian, Q.; Erickson, K. I.; Simonsick, E. M.
- The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, Vol. 69, Issue 10
Physical Activity, Brain Volume, and Dementia Risk: The Framingham Study
journal, July 2016
- Tan, Zaldy S.; Spartano, Nicole L.; Beiser, Alexa S.
- The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences
What is the association between sedentary behaviour and cognitive function? A systematic review
journal, May 2016
- Falck, Ryan S.; Davis, Jennifer C.; Liu-Ambrose, Teresa
- British Journal of Sports Medicine, Vol. 51, Issue 10
Physical activity improves cognitive function in people with memory impairment
journal, April 2009
- Stewart, R.
- Evidence-Based Mental Health, Vol. 12, Issue 2
The Hamilton Depression Scale--accelerator or break on antidepressant drug discovery?
journal, January 2014
- Nutt, D.
- Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, Vol. 85, Issue 2
Regional Brain Atrophy Rate Predicts Future Cognitive Decline: 6-year Longitudinal MR Imaging Study of Normal Aging
journal, December 2003
- Rusinek, Henry; De Santi, Susan; Frid, Dina
- Radiology, Vol. 229, Issue 3
Family History of Alzheimer's Disease and Hippocampal Structure in Healthy People
journal, November 2010
- Donix, Markus; Burggren, Alison C.; Suthana, Nanthia A.
- American Journal of Psychiatry, Vol. 167, Issue 11
Symptom burden in community-dwelling older people with multimorbidity: a cross-sectional study
journal, January 2015
- Eckerblad, Jeanette; Theander, Kersti; Ekdahl, Anne
- BMC Geriatrics, Vol. 15, Issue 1
Evidence that women meeting physical activity guidelines do not sit less: An observational inclinometry study
journal, January 2012
- Craft, Lynette L.; Zderic, Theodore W.; Gapstur, Susan M.
- International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity, Vol. 9, Issue 1
The Effects of Breaking up Prolonged Sitting Time: A Review of Experimental Studies
journal, January 2015
- Benatti, Fabiana Braga; Ried-Larsen, Mathias
- Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, Vol. 47, Issue 10
Sedentary behavior as a risk factor for cognitive decline? A focus on the influence of glycemic control in brain health.
journalarticle, January 2017
- Wheeler, Michael J.; Dempsey, Paddy C.; Grace, Megan S.
- Wiley
Increased Hippocampal Blood Flow in Sedentary Older Adults at Genetic Risk for Alzheimer's Disease
journal, July 2014
- Zlatar, Zvinka Z.; Wierenga, Christina E.; Bangen, Katherine J.
- Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, Vol. 41, Issue 3
Biochemical Markers of Physical Exercise on Mild Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: Systematic Review and Perspectives
journal, August 2015
- Jensen, Camilla Steen; Hasselbalch, Steen Gregers; Waldemar, Gunhild
- Frontiers in Neurology, Vol. 6
The Effects of Aerobic Activity on Brain Structure
journal, January 2012
- Thomas, Adam G.; Dennis, Andrea; Bandettini, Peter A.
- Frontiers in Psychology, Vol. 3
Physical Exercise as a Preventive or Disease-Modifying Treatment of Dementia and Brain Aging
journal, September 2011
- Ahlskog, J. Eric; Geda, Yonas E.; Graff-Radford, Neill R.
- Mayo Clinic Proceedings, Vol. 86, Issue 9
Works referencing / citing this record:
Sedentary behaviours, cognitive function, and possible mechanisms in older adults: a systematic review
journal, February 2020
- Olanrewaju, O.; Stockwell, S.; Stubbs, B.
- Aging Clinical and Experimental Research
Effects of acute prolonged sitting on cerebral perfusion and executive function in young adults: A randomized cross‐over trial
journal, August 2019
- Stoner, Lee; Willey, Quentin; Evans, William S.
- Psychophysiology, Vol. 56, Issue 12
Morning exercise mitigates the impact of prolonged sitting on cerebral blood flow in older adults
journal, April 2019
- Wheeler, Michael J.; Dunstan, David W.; Smith, Brianne
- Journal of Applied Physiology, Vol. 126, Issue 4
The effects of physical exercise on parahippocampal function
journal, June 2019
- Loprinzi, Pd
- Physiology International, Vol. 106, Issue 2
Effects of Combined Aerobic Exercise and Cognitive Training on Verbal Fluency in Older Adults
journal, January 2020
- Nocera, Joe R.; Mammino, Kevin; Kommula, Yash
- Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine, Vol. 6
Re: Non-radiation occupational hazards and health issues faced by radiologists – A cross-sectional study of indian radiologists’ by Kawthalkar AS et al.
journal, July 2019
- Venkatraman, Venkatraman Indiran; Kokilavani, Jagannathan
- Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging, Vol. 29, Issue 03
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal