Self-similar solutions for multi-species plasma mixing by gradient driven transport
Abstract
We report that multi-species transport of plasma ions across an initial interface between DT and CH is shown to exhibit self-similar species density profiles under 1D isobaric conditions. Results using transport theory from recent studies and using a Maxwell–Stephan multi-species approximation are found to be in good agreement for the self-similar mix profiles of the four ions under isothermal and isobaric conditions. The individual ion species mass flux and molar flux profile results through the mixing layer are examined using transport theory. The sum over species mass flux is confirmed to be zero as required, and the sum over species molar flux is related to a local velocity divergence needed to maintain pressure equilibrium during the transport process. The light ion species mass fluxes are dominated by the diagonal coefficients of the diffusion transport matrix, while for the heaviest ion species (C in this case), the ion flux with only the diagonal term is reduced by about a factor two from that using the full diffusion matrix, implying the heavy species moves more by frictional collisions with the lighter species than by its own gradient force. Temperature gradient forces were examined by comparing profile results with and without imposing constantmore »
- Authors:
-
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1484638
- Report Number(s):
- LA-UR-17-31274
Journal ID: ISSN 0741-3335
- Grant/Contract Number:
- 89233218CNA000001; AC52-06NA25396
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 60; Journal Issue: 5; Journal ID: ISSN 0741-3335
- Publisher:
- IOP Science
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 70 PLASMA PHYSICS AND FUSION TECHNOLOGY; plasma transport; ICF; multi-species diffusion
Citation Formats
Vold, Erik Lehman, Kagan, Grigory, Simakov, Andrei N., Molvig, Kim, and Yin, Lin. Self-similar solutions for multi-species plasma mixing by gradient driven transport. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1088/1361-6587/aab38e.
Vold, Erik Lehman, Kagan, Grigory, Simakov, Andrei N., Molvig, Kim, & Yin, Lin. Self-similar solutions for multi-species plasma mixing by gradient driven transport. United States. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6587/aab38e
Vold, Erik Lehman, Kagan, Grigory, Simakov, Andrei N., Molvig, Kim, and Yin, Lin. Fri .
"Self-similar solutions for multi-species plasma mixing by gradient driven transport". United States. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6587/aab38e. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1484638.
@article{osti_1484638,
title = {Self-similar solutions for multi-species plasma mixing by gradient driven transport},
author = {Vold, Erik Lehman and Kagan, Grigory and Simakov, Andrei N. and Molvig, Kim and Yin, Lin},
abstractNote = {We report that multi-species transport of plasma ions across an initial interface between DT and CH is shown to exhibit self-similar species density profiles under 1D isobaric conditions. Results using transport theory from recent studies and using a Maxwell–Stephan multi-species approximation are found to be in good agreement for the self-similar mix profiles of the four ions under isothermal and isobaric conditions. The individual ion species mass flux and molar flux profile results through the mixing layer are examined using transport theory. The sum over species mass flux is confirmed to be zero as required, and the sum over species molar flux is related to a local velocity divergence needed to maintain pressure equilibrium during the transport process. The light ion species mass fluxes are dominated by the diagonal coefficients of the diffusion transport matrix, while for the heaviest ion species (C in this case), the ion flux with only the diagonal term is reduced by about a factor two from that using the full diffusion matrix, implying the heavy species moves more by frictional collisions with the lighter species than by its own gradient force. Temperature gradient forces were examined by comparing profile results with and without imposing constant temperature gradients chosen to be of realistic magnitude for ICF experimental conditions at a fuel-capsule interface (10 μm scale length or greater). The temperature gradients clearly modify the relative concentrations of the ions, for example near the fuel center, however the mixing across the fuel-capsule interface appears to be minimally influenced by the temperature gradient forces within the expected compression and burn time. Finally, discussion considers the application of the self-similar profiles to specific conditions in ICF.},
doi = {10.1088/1361-6587/aab38e},
journal = {Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion},
number = 5,
volume = 60,
place = {United States},
year = {Fri Mar 02 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Fri Mar 02 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
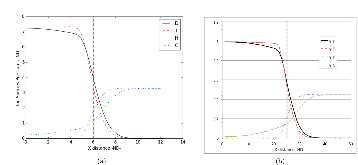 Figure 1: Profiles of relative molar concentrations for the DT and CH mixing (a) using the MaxwellStephan multi-species diffusive approximation and (b) using the self-consistent transport theory. Both cases assume isothermal pressure equilibrium is maintained during the transport process as described in the text, so ion molar concentration is directlymore »
Figure 1: Profiles of relative molar concentrations for the DT and CH mixing (a) using the MaxwellStephan multi-species diffusive approximation and (b) using the self-consistent transport theory. Both cases assume isothermal pressure equilibrium is maintained during the transport process as described in the text, so ion molar concentration is directlymore »
Works referenced in this record:
Thermo-diffusion in inertially confined plasmas
journal, April 2014
- Kagan, Grigory; Tang, Xian-Zhu
- Physics Letters A, Vol. 378, Issue 21
Plasma viscosity in spherical ICF implosion simulations
journal, May 2016
- Vold, E.; Joglekar, A.; Ortega, M.
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 717
Plasma kinetic effects on interfacial mix
journal, November 2016
- Yin, L.; Albright, B. J.; Taitano, W.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 11
The effect of mix on capsule yields as a function of shell thickness and gas fill
journal, June 2014
- Bradley, P. A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 21, Issue 6
Atomic mix in directly driven inertial confinement implosions
journal, November 2011
- Wilson, D. C.; Ebey, P. S.; Sangster, T. C.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 18, Issue 11
Hydrodynamic description of an unmagnetized plasma with multiple ion species. I. General formulation
journal, March 2016
- Simakov, Andrei N.; Molvig, Kim
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 3
Application of fall-line mix models to understand degraded yield
journal, July 2008
- Welser-Sherrill, L.; Cooley, J. H.; Haynes, D. A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 15, Issue 7
Electro-diffusion in a plasma with two ion species
journal, August 2012
- Kagan, Grigory; Tang, Xian-Zhu
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 19, Issue 8
Laser Compression of Matter to Super-High Densities: Thermonuclear (CTR) Applications
journal, September 1972
- Nuckolls, John; Wood, Lowell; Thiessen, Albert
- Nature, Vol. 239, Issue 5368, p. 139-142
Real viscosity effects in inertial confinement fusion target deuterium–tritium micro-implosions
journal, February 2014
- Mason, R. J.; Kirkpatrick, R. C.; Faehl, R. J.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 21, Issue 2
The effects of plasma diffusion and viscosity on turbulent instability growth
journal, September 2014
- Haines, Brian M.; Vold, Erik L.; Molvig, Kim
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 21, Issue 9
Classical transport equations for burning gas-metal plasmas
journal, September 2014
- Molvig, Kim; Simakov, Andrei N.; Vold, Erik L.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 21, Issue 9
Observation of interspecies ion separation in inertial-confinement-fusion implosions
journal, September 2016
- Hsu, S. C.; Joshi, T. R.; Hakel, P.
- EPL (Europhysics Letters), Vol. 115, Issue 6
Direct-drive inertial confinement fusion: A review
journal, November 2015
- Craxton, R. S.; Anderson, K. S.; Boehly, T. R.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 11
Development of the indirect‐drive approach to inertial confinement fusion and the target physics basis for ignition and gain
journal, November 1995
- Lindl, John
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 2, Issue 11
Transport Properties of Ionized Monatomic Gases
journal, January 1966
- Devoto, R. S.
- Physics of Fluids, Vol. 9, Issue 6
The physical basis for numerical fluid simulations in laser fusion
journal, November 1987
- Atzeni, S.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 29, Issue 11
The RAGE radiation-hydrodynamic code
journal, October 2008
- Gittings, Michael; Weaver, Robert; Clover, Michael
- Computational Science & Discovery, Vol. 1, Issue 1
Kinetic physics in ICF: present understanding and future directions
journal, April 2018
- Rinderknecht, Hans G.; Amendt, P. A.; Wilks, S. C.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 60, Issue 6
Plasma viscosity with mass transport in spherical inertial confinement fusion implosion simulations
journal, November 2015
- Vold, E. L.; Joglekar, A. S.; Ortega, M. I.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 11
Approximate models for the ion-kinetic regime in inertial-confinement-fusion capsule implosions
journal, May 2015
- Hoffman, Nelson M.; Zimmerman, George B.; Molvig, Kim
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 5
Plasma transport in an Eulerian AMR code
journal, April 2017
- Vold, E. L.; Rauenzahn, R. M.; Aldrich, C. H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 24, Issue 4
Exploration of the Transition from the Hydrodynamiclike to the Strongly Kinetic Regime in Shock-Driven Implosions
journal, May 2014
- Rosenberg, M. J.; Rinderknecht, H. G.; Hoffman, N. M.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 112, Issue 18
Inhibition of turbulence in inertial-confinement-fusion hot spots by viscous dissipation
journal, May 2014
- Weber, C. R.; Clark, D. S.; Cook, A. W.
- Physical Review E, Vol. 89, Issue 5
Nonlinear Structure of the Diffusing Gas-Metal Interface in a Thermonuclear Plasma
journal, October 2014
- Molvig, Kim; Vold, Erik L.; Dodd, Evan S.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 113, Issue 14
Electro-diffusion in a plasma with two ion species
text, January 2012
- Kagan, Grigory; Tang, Xian-Zhu
- arXiv
Works referencing / citing this record:
Multi-species plasma transport in 1D direct-drive ICF simulations
journal, March 2019
- Vold, E.; Rauenzahn, R.; Simakov, A. N.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 26, Issue 3
Kinetic physics in ICF: present understanding and future directions
journal, April 2018
- Rinderknecht, Hans G.; Amendt, P. A.; Wilks, S. C.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 60, Issue 6
Diffusion-driven fluid dynamics in ideal gases and plasmas
journal, June 2018
- Vold, E. L.; Yin, L.; Taitano, W.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 25, Issue 6
Plasma kinetic effects on interfacial mix and burn rates in multispatial dimensions
journal, June 2019
- Yin, L.; Albright, B. J.; Vold, E. L.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 26, Issue 6
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal