Geochemical Exports to River From the Intrameander Hyporheic Zone Under Transient Hydrologic Conditions: East River Mountainous Watershed, Colorado
Abstract
©2018. American Geophysical Union. All Rights Reserved. To understand how redox processes influence carbon, nitrogen, and iron cycling within the intrameander hyporheic zone, we developed a biotic and abiotic reaction network and incorporated it into the reactive transport simulator PFLOTRAN. Two-dimensional reactive flow and transport simulations were performed (1) to evaluate how transient hydrological conditions control the lateral redox zonation within an intrameander region of the East River in Colorado and (2) to quantify the impact of a single meander on subsurface exports of carbon and other geochemical species to the river. The meander's overall contribution to the river was quantified by integrating geochemical outfluxes along the outside of the meander bend. The model was able to capture the field-observed trends of dissolved oxygen, nitrate, iron, pH, and total inorganic carbon along a 2-D transect. Consistent with field observations, simulated dissolved oxygen and nitrate decreased along the intrameander flow paths while iron (Fe2+) concentration increased. The simulation results further demonstrated that the reductive potential of the lateral redox zonation was controlled by groundwater velocities resulting from river stage fluctuations, with low-water conditions promoting reducing conditions. The sensitivity analysis results showed that permeability had a more significant impact on biogeochemical zonationmore »
- Authors:
-
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- The Desert Research Institute, Reno, NV (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1544196
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1480138; OSTI ID: 1563962
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231; AC02‐05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Water Resources Research
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 54; Journal Issue: 10; Journal ID: ISSN 0043-1397
- Publisher:
- American Geophysical Union (AGU)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 58 GEOSCIENCES; hyporheic zone; meanders; redox processes; iron; carbon; nitrogen
Citation Formats
Dwivedi, Dipankar, Steefel, Carl I., Arora, Bhavna, Newcomer, Michelle, Moulton, J. David, Dafflon, Baptiste, Faybishenko, Boris, Fox, Patricia, Nico, Peter, Spycher, Nicolas, Carroll, Rosemary, and Williams, Kenneth H. Geochemical Exports to River From the Intrameander Hyporheic Zone Under Transient Hydrologic Conditions: East River Mountainous Watershed, Colorado. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1029/2018WR023377.
Dwivedi, Dipankar, Steefel, Carl I., Arora, Bhavna, Newcomer, Michelle, Moulton, J. David, Dafflon, Baptiste, Faybishenko, Boris, Fox, Patricia, Nico, Peter, Spycher, Nicolas, Carroll, Rosemary, & Williams, Kenneth H. Geochemical Exports to River From the Intrameander Hyporheic Zone Under Transient Hydrologic Conditions: East River Mountainous Watershed, Colorado. United States. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR023377
Dwivedi, Dipankar, Steefel, Carl I., Arora, Bhavna, Newcomer, Michelle, Moulton, J. David, Dafflon, Baptiste, Faybishenko, Boris, Fox, Patricia, Nico, Peter, Spycher, Nicolas, Carroll, Rosemary, and Williams, Kenneth H. Thu .
"Geochemical Exports to River From the Intrameander Hyporheic Zone Under Transient Hydrologic Conditions: East River Mountainous Watershed, Colorado". United States. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR023377. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1544196.
@article{osti_1544196,
title = {Geochemical Exports to River From the Intrameander Hyporheic Zone Under Transient Hydrologic Conditions: East River Mountainous Watershed, Colorado},
author = {Dwivedi, Dipankar and Steefel, Carl I. and Arora, Bhavna and Newcomer, Michelle and Moulton, J. David and Dafflon, Baptiste and Faybishenko, Boris and Fox, Patricia and Nico, Peter and Spycher, Nicolas and Carroll, Rosemary and Williams, Kenneth H.},
abstractNote = {©2018. American Geophysical Union. All Rights Reserved. To understand how redox processes influence carbon, nitrogen, and iron cycling within the intrameander hyporheic zone, we developed a biotic and abiotic reaction network and incorporated it into the reactive transport simulator PFLOTRAN. Two-dimensional reactive flow and transport simulations were performed (1) to evaluate how transient hydrological conditions control the lateral redox zonation within an intrameander region of the East River in Colorado and (2) to quantify the impact of a single meander on subsurface exports of carbon and other geochemical species to the river. The meander's overall contribution to the river was quantified by integrating geochemical outfluxes along the outside of the meander bend. The model was able to capture the field-observed trends of dissolved oxygen, nitrate, iron, pH, and total inorganic carbon along a 2-D transect. Consistent with field observations, simulated dissolved oxygen and nitrate decreased along the intrameander flow paths while iron (Fe2+) concentration increased. The simulation results further demonstrated that the reductive potential of the lateral redox zonation was controlled by groundwater velocities resulting from river stage fluctuations, with low-water conditions promoting reducing conditions. The sensitivity analysis results showed that permeability had a more significant impact on biogeochemical zonation compared to the reaction pathways under transient hydrologic conditions. The simulation results further indicated that the meander acted as a sink for organic and inorganic carbon as well as iron during the extended baseflow and high-water conditions; however, these geochemical species were released into the river during the falling limb of the hydrograph.},
doi = {10.1029/2018WR023377},
journal = {Water Resources Research},
number = 10,
volume = 54,
place = {United States},
year = {Thu Oct 04 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Thu Oct 04 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
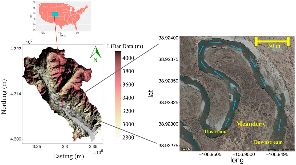 Figure 1: Location of the East River floodplain and meander C study site in Colorado. Blue arrows show the flow direction in the river.
Figure 1: Location of the East River floodplain and meander C study site in Colorado. Blue arrows show the flow direction in the river.
Works referenced in this record:
Evolution of porosity and geochemistry in Marcellus Formation black shale during weathering
journal, October 2013
- Jin, Lixin; Mathur, Ryan; Rother, Gernot
- Chemical Geology, Vol. 356
Mobility of rhenium, platinum group elements and organic carbon during black shale weathering
journal, May 2002
- Jaffe, Lillie A.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, Bernhard; Petsch, Steven T.
- Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 198, Issue 3-4
A multiscale model for integrating hyporheic exchange from ripples to meanders: A 3-D FLOW MODEL FOR HYPORHEIC EXCHANGE
journal, December 2010
- Stonedahl, Susa H.; Harvey, Judson W.; Wörman, Anders
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 46, Issue 12
THE ECOLOGY OF INTERFACES:Riparian Zones
journal, November 1997
- Naiman and, Robert J.; Décamps, Henri
- Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, Vol. 28, Issue 1
Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media
journal, January 1975
- Bear, Jacob
- Soil Science, Vol. 120, Issue 2
Effects of physical and geochemical heterogeneities on mineral transformation and biomass accumulation during biostimulation experiments at Rifle, Colorado
journal, March 2010
- Li, Li; Steefel, Carl I.; Kowalsky, Michael B.
- Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, Vol. 112, Issue 1-4
Hot Spots and Hot Moments of Nitrogen in a Riparian Corridor
journal, January 2018
- Dwivedi, Dipankar; Arora, Bhavna; Steefel, Carl I.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 54, Issue 1
Thermodynamics of iron oxides: Part III. Enthalpies of formation and stability of ferrihydrite (∼Fe(OH)3), schwertmannite (∼FeO(OH)3/4(SO4)1/8), and ε-Fe2O3
journal, March 2004
- Majzlan, J.; Navrotsky, A.; Schwertmann, U.
- Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 68, Issue 5, p. 1049-1059
Naturally Occurring Contamination in the Mancos Shale
journal, January 2012
- Morrison, Stan J.; Goodknight, Craig S.; Tigar, Aaron D.
- Environmental Science & Technology, Vol. 46, Issue 3
A numerical transport model for oxygen- and nitrate-based respiration linked to substrate and nutrient availability in porous media
journal, September 1988
- Widdowson, Mark A.; Molz, Fred J.; Benefield, Larry D.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 24, Issue 9
River bank filtration: modelling of the changes in water chemistry with emphasis on nitrogen species
journal, February 1997
- Doussan, Claude; Poitevin, Guillemette; Ledoux, Emmanuel
- Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, Vol. 25, Issue 1-2
Evaluating the performance of parallel subsurface simulators: An illustrative example with PFLOTRAN: Evaluating the Parallel Performance of Pflotran
journal, January 2014
- Hammond, G. E.; Lichtner, P. C.; Mills, R. T.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 50, Issue 1
Effect of enhanced manganese oxidation in the hyporheic zone on basin-scale geochemical mass balance
journal, April 1998
- Harvey, Judson W.; Fuller, Christopher C.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 34, Issue 4
Probing deep weathering in the Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory, Pennsylvania (USA): the hypothesis of nested chemical reaction fronts in the subsurface: NESTED REACTION FRONTS
journal, April 2013
- Brantley, Susan L.; Holleran, Molly E.; Jin, Lixin
- Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, Vol. 38, Issue 11
Metatranscriptomic evidence of pervasive and diverse chemolithoautotrophy relevant to C, S, N and Fe cycling in a shallow alluvial aquifer
journal, March 2016
- Jewell, Talia N. M.; Karaoz, Ulas; Brodie, Eoin L.
- The ISME Journal, Vol. 10, Issue 9
Using geochemical indicators to distinguish high biogeochemical activity in floodplain soils and sediments
journal, September 2016
- Kenwell, Amy; Navarre-Sitchler, Alexis; Prugue, Rodrigo
- Science of The Total Environment, Vol. 563-564
Dynamics of nitrate production and removal as a function of residence time in the hyporheic zone
journal, January 2011
- Zarnetske, Jay P.; Haggerty, Roy; Wondzell, Steven M.
- Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 116, Issue G1
Benchmark problems for reactive transport modeling of the generation and attenuation of acid rock drainage
journal, May 2015
- Mayer, K. Ulrich; Alt-Epping, Peter; Jacques, Diederik
- Computational Geosciences, Vol. 19, Issue 3
Biogeochemical zonation due to intrameander hyporheic flow: INTRAMEANDER BIOGEOCHEMICAL ZONATION
journal, February 2010
- Boano, F.; Demaria, A.; Revelli, R.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 46, Issue 2
Residence time control on hot moments of net nitrate production and uptake in the hyporheic zone: RESIDENCE TIME CONTROL ON TEMPORAL HYPORHEIC NITRATE CYCLING
journal, June 2013
- Briggs, Martin A.; Lautz, Laura K.; Hare, Danielle K.
- Hydrological Processes, Vol. 28, Issue 11
Multicomponent reactive transport modeling in variably saturated porous media using a generalized formulation for kinetically controlled reactions: REACTIVE TRANSPORT MODELING IN VARIABLY SATURATED MEDIA
journal, September 2002
- Mayer, K. Ulrich; Frind, Emil O.; Blowes, David W.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 38, Issue 9
Biogeochemical Evolution of a Landfill Leachate Plume, Norman, Oklahoma
journal, February 2011
- Cozzarelli, I. M.; Böhlke, J. K.; Masoner, J.
- Ground Water, Vol. 49, Issue 5
Association of Novel and Highly Diverse Acid-Tolerant Denitrifiers with N2O Fluxes of an Acidic Fen
journal, December 2009
- Palmer, K.; Drake, H. L.; Horn, M. A.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 76, Issue 4
Nutrient cycling in bedform induced hyporheic zones
journal, May 2012
- Bardini, L.; Boano, F.; Cardenas, M. B.
- Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 84
The Dual Arrhenius and Michaelis-Menten kinetics model for decomposition of soil organic matter at hourly to seasonal time scales
journal, October 2011
- Davidson, Eric A.; Samanta, Sudeep; Caramori, Samantha S.
- Global Change Biology, Vol. 18, Issue 1
The East River, Colorado, Watershed: A Mountainous Community Testbed for Improving Predictive Understanding of Multiscale Hydrological–Biogeochemical Dynamics
journal, January 2018
- Hubbard, Susan S.; Williams, Kenneth Hurst; Agarwal, Deb
- Vadose Zone Journal, Vol. 17, Issue 1
A mechanistic treatment of the dominant soil nitrogen cycling processes: Model development, testing, and application: NITROGEN CYCLE MODELING
journal, April 2008
- Maggi, F.; Gu, C.; Riley, W. J.
- Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, Vol. 113, Issue G2
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Sulfide Oxidation by Oxygen: A Look at Inorganically Controlled Reactions and Biologically Mediated Processes in the Environment
journal, January 2011
- Luther, George W.; Findlay, Alyssa J.; MacDonald, Daniel J.
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 2
Modelling hyporheic processes for regulated rivers under transient hydrological and hydrogeological conditions
journal, January 2015
- Siergieiev, D.; Ehlert, L.; Reimann, T.
- Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, Vol. 19, Issue 1
The weathering of sedimentary organic matter as a control on atmospheric O2: I. Analysis of a black shale
journal, March 2004
- Wildman, R. A.
- American Journal of Science, Vol. 304, Issue 3
Inorganic species in geologic fluids: Correlations among standard molal thermodynamic properties of aqueous ions and hydroxide complexes
journal, March 1997
- Shock, Everett L.; Sassani, David C.; Willis, Marc
- Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 61, Issue 5
Semianalytical analysis of hyporheic flow induced by alternate bars: HYPORHEIC FLOW INDUCED BY ALTERNATE BARS
journal, July 2010
- Marzadri, A.; Tonina, D.; Bellin, A.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 46, Issue 7
Nitrate reduction in streambed sediments: Effects of flow and biogeochemical kinetics: NITRATE ATTENUATION DURING GROUNDWATER DISCHARGE
journal, December 2007
- Gu, Chuanhui; Hornberger, George M.; Mills, Aaron L.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 43, Issue 12
The kinetics and electrochemical rate-determining step of aqueous pyrite oxidation
journal, December 1994
- Williamson, Mark A.; Rimstidt, J. Donald
- Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 58, Issue 24
Stream-aquifer interactions and hyporheic exchange in gaining and losing sinuous streams: STREAM-AQUIFER INTERACTION IN GAINING/LOSING STREAMS
journal, June 2009
- Cardenas, M. Bayani
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 45, Issue 6
Spatiotemporal scaling of hydrological and agrochemical export dynamics in a tile-drained Midwestern watershed: SCALING OF HYDROLOGICAL AND AGROCHEMICAL EXPORT
journal, May 2011
- Guan, K.; Thompson, S. E.; Harman, C. J.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 47, Issue 10
Potential contribution of topography-driven regional groundwater flow to fractal stream chemistry: Residence time distribution analysis of Tóth flow: RESIDENCE TIME DISTRIBUTION ANALYSIS OF TÓTH FLOW
journal, March 2007
- Cardenas, M. Bayani
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 34, Issue 5
Identifying geochemical hot moments and their controls on a contaminated river floodplain system using wavelet and entropy approaches
journal, November 2016
- Arora, Bhavna; Dwivedi, Dipankar; Hubbard, Susan S.
- Environmental Modelling & Software, Vol. 85
Influence of hydrological, biogeochemical and temperature transients on subsurface carbon fluxes in a flood plain environment
journal, February 2016
- Arora, Bhavna; Spycher, Nicolas F.; Steefel, Carl I.
- Biogeochemistry, Vol. 127, Issue 2-3
Geophysical monitoring and reactive transport modeling of ureolytically-driven calcium carbonate precipitation
journal, September 2011
- Wu, Yuxin; Ajo-Franklin, Jonathan B.; Spycher, Nicolas
- Geochemical Transactions, Vol. 12, Issue 1
Residence time distributions in sinuosity-driven hyporheic zones and their biogeochemical effects: RTD IN HYPORHEIC ZONES AND BIOGEOCHEMICAL EFFECTS
journal, September 2012
- Gomez, Jesus D.; Wilson, John L.; Cardenas, M. Bayani
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 48, Issue 9
Harvesting Effects on Microclimatic Gradients from Small Streams to Uplands in Western Washington
journal, November 1997
- Brosofske, Kimberley D.; Chen, Jiquan; Naiman, Robert J.
- Ecological Applications, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Lead mobilisation in the hyporheic zone and river bank sediments of a contaminated stream: contribution to diffuse pollution
journal, July 2012
- Palumbo-Roe, Barbara; Wragg, Joanna; Banks, Vanessa J.
- Journal of Soils and Sediments, Vol. 12, Issue 10
Biostimulation induces syntrophic interactions that impact C, S and N cycling in a sediment microbial community
journal, November 2012
- Handley, Kim M.; VerBerkmoes, Nathan C.; Steefel, Carl I.
- The ISME Journal, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Intra-meander hyporheic flow in alluvial rivers: HYPORHEIC EXCHANGE IN MEANDERING RIVERS
journal, December 2008
- Revelli, Roberto; Boano, Fulvio; Camporeale, Carlo
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 44, Issue 12
Impact of the Linked Surface Water-Soil Water-Groundwater System on Transport of E. coli in the Subsurface
journal, August 2016
- Dwivedi, Dipankar; Mohanty, Binayak P.; Lesikar, Bruce J.
- Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, Vol. 227, Issue 9
Hyporheic exchange in gravel bed rivers with pool-riffle morphology: Laboratory experiments and three-dimensional modeling: HYPORHEIC EXCHANGE IN GRAVEL BED RIVERS
journal, January 2007
- Tonina, Daniele; Buffington, John M.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 43, Issue 1
Reduction of the hyporheic zone volume due to the stream-aquifer interaction
journal, January 2008
- Boano, Fulvio; Revelli, Roberto; Ridolfi, Luca
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 35, Issue 9
Impact of Intra-meander Hyporheic Flow on Nitrogen Cycling
journal, January 2017
- Dwivedi, Dipankar; Steefel, I. Carl; Arora, Bhavna
- Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, Vol. 17
Sinuosity-driven hyporheic exchange in meandering rivers: HYPORHEIC EXCHANGE IN MEANDERING RIVERS
journal, September 2006
- Boano, Fulvio; Camporeale, Carlo; Revelli, Roberto
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 33, Issue 18
A compilation of rate parameters of water-mineral interaction kinetics for application to geochemical modeling
report, January 2004
- Palandri, James L.; Kharaka, Yousif K.
- U.S. Geological Survey (USGS)
Temporal dynamics of biogeochemical processes at the Norman Landfill site: Temporal Dynamics at the Norman Landfill Site
journal, October 2013
- Arora, Bhavna; Mohanty, Binayak P.; McGuire, Jennifer T.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 49, Issue 10
Hot Spots and Persistence of Nitrate in Aquifers Across Scales
journal, January 2016
- Dwivedi, Dipankar; Mohanty, Binayak
- Entropy, Vol. 18, Issue 1
Snowmelt controls on concentration-discharge relationships and the balance of oxidative and acid-base weathering fluxes in an alpine catchment, East River, Colorado: ACID-BASE VERSUS OXIDATIVE WEATHERING FLUXES
journal, March 2017
- Winnick, Matthew J.; Carroll, Rosemary W. H.; Williams, Kenneth H.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 53, Issue 3
Dynamics of fluids in Porous Media
journal, October 1973
- Childs, E. C.
- Engineering Geology, Vol. 7, Issue 2
Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media: By J. Bear. American Elsevier Publishing Company, Inc., 52 Vanderbilt Avenue, New York, N.Y. 10017 or Elsevier Publishing Company, 335 Jan Van Galenst
journal, July 1973
- Raats, P. A. C.
- Soil Science Society of America Journal, Vol. 37, Issue 4
Works referencing / citing this record:
Depth‐ and Time‐Resolved Distributions of Snowmelt‐Driven Hillslope Subsurface Flow and Transport and Their Contributions to Surface Waters
journal, November 2019
- Tokunaga, Tetsu K.; Wan, Jiamin; Williams, Kenneth H.
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 55, Issue 11
The effect of unsteady streamflow and stream-groundwater interactions on oxygen consumption in a sandy streambed
journal, December 2019
- Galloway, Jason; Fox, Aryeh; Lewandowski, Jörg
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Hydrogeologic Controls of Surface Water‐Groundwater Nitrogen Dynamics Within a Tidal Freshwater Zone
journal, November 2019
- Barnes, Rebecca T.; Sawyer, Audrey H.; Tight, Delaney M.
- Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, Vol. 124, Issue 11
Dam Operations and Subsurface Hydrogeology Control Dynamics of Hydrologic Exchange Flows in a Regulated River Reach
journal, April 2019
- Shuai, Pin; Chen, Xingyuan; Song, Xuehang
- Water Resources Research, Vol. 55, Issue 4
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal