Using multiple neutron time of flight detectors to determine the hot spot velocity
Abstract
An important diagnostic value of a shot at the National Ignition Facility is the resultant center-of-mass motion of the imploding capsule. This residual velocity reduces the efficiency of converting laser energy into plasma temperature. A new analysis method extracts the effective hot spot motion by using information from multiple neutron time-of-flight (nToF) lines-of-sight (LoSs). This technique fits a near Gaussian spectrum to the nToF scope traces and overcomes reliance on models to relate the plasma temperature to the mean energy of the emitted neutrons. This method requires having at least four nToF LoSs. The results of this analysis will be compared to an approach where each LoS is analyzed separately and a model is employed to infer the mean energy of the emitted neutrons
- Authors:
-
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1545515
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1477910
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Review of Scientific Instruments
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 89; Journal Issue: 10; Conference: 22. Topical Conference on High-Temperature Plasma Diagnostics, San Diego, CA (United States), Apr. 2018; Journal ID: ISSN 0034-6748
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 71 CLASSICAL AND QUANTUM MECHANICS, GENERAL PHYSICS; 72 PHYSICS OF ELEMENTARY PARTICLES AND FIELDS; 47 OTHER INSTRUMENTATION
Citation Formats
Hatarik, R., Nora, R. C., Spears, B. K., Eckart, M. J., Grim, G. P., Hartouni, E. P., Moore, A. S., and Schlossberg, D. J. Using multiple neutron time of flight detectors to determine the hot spot velocity. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.5039372.
Hatarik, R., Nora, R. C., Spears, B. K., Eckart, M. J., Grim, G. P., Hartouni, E. P., Moore, A. S., & Schlossberg, D. J. Using multiple neutron time of flight detectors to determine the hot spot velocity. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5039372
Hatarik, R., Nora, R. C., Spears, B. K., Eckart, M. J., Grim, G. P., Hartouni, E. P., Moore, A. S., and Schlossberg, D. J. Wed .
"Using multiple neutron time of flight detectors to determine the hot spot velocity". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5039372. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1545515.
@article{osti_1545515,
title = {Using multiple neutron time of flight detectors to determine the hot spot velocity},
author = {Hatarik, R. and Nora, R. C. and Spears, B. K. and Eckart, M. J. and Grim, G. P. and Hartouni, E. P. and Moore, A. S. and Schlossberg, D. J.},
abstractNote = {An important diagnostic value of a shot at the National Ignition Facility is the resultant center-of-mass motion of the imploding capsule. This residual velocity reduces the efficiency of converting laser energy into plasma temperature. A new analysis method extracts the effective hot spot motion by using information from multiple neutron time-of-flight (nToF) lines-of-sight (LoSs). This technique fits a near Gaussian spectrum to the nToF scope traces and overcomes reliance on models to relate the plasma temperature to the mean energy of the emitted neutrons. This method requires having at least four nToF LoSs. The results of this analysis will be compared to an approach where each LoS is analyzed separately and a model is employed to infer the mean energy of the emitted neutrons},
doi = {10.1063/1.5039372},
journal = {Review of Scientific Instruments},
number = 10,
volume = 89,
place = {United States},
year = {Wed Oct 17 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Wed Oct 17 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
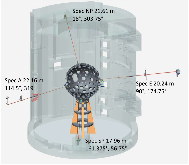 FIG. 1: Location of the four nToF detectors relative to the NIF target chamber.
FIG. 1: Location of the four nToF detectors relative to the NIF target chamber.
Works referenced in this record:
Progress towards ignition on the National Ignition Facility
journal, August 2011
- Lindl, J. D.; Atherton, L. J.; Amednt, P. A.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 51, Issue 9
Progress towards ignition on the National Ignition Facility
journal, July 2013
- Edwards, M. J.; Patel, P. K.; Lindl, J. D.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 7
Metrics for long wavelength asymmetries in inertial confinement fusion implosions on the National Ignition Facility
journal, April 2014
- Kritcher, A. L.; Town, R.; Bradley, D.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 21, Issue 4
Neutron spectrometry—An essential tool for diagnosing implosions at the National Ignition Facility (invited)
journal, October 2012
- Johnson, M. Gatu; Frenje, J. A.; Casey, D. T.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 83, Issue 10
Relativistic calculation of fusion product spectra for thermonuclear plasmas
journal, November 1998
- Ballabio, L.; Källne, J.; Gorini, G.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 38, Issue 11
Engineering architecture of the neutron Time-of-Flight (nToF) diagnostic suite at the National Ignition Facility
conference, September 2014
- Clancy, T. J.; Caggiano, J.; McNaney, J.
- SPIE Optical Engineering + Applications, SPIE Proceedings
A fused silica Cherenkov radiator for high precision time-of-flight measurement of DT γ and neutron spectra (invited)
journal, October 2018
- Moore, A. S.; Schlossberg, D. J.; Hartouni, E. P.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Uncertainty analysis of response functions and γ-backgrounds on T ion and t 0 measurements from Cherenkov neutron detectors at the National Ignition Facility (NIF)
journal, October 2018
- Hartouni, E. P.; Beeman, B.; Eckart, M. J.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Analysis of the neutron time-of-flight spectra from inertial confinement fusion experiments
journal, November 2015
- Hatarik, R.; Sayre, D. B.; Caggiano, J. A.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 118, Issue 18
The effect of turbulent kinetic energy on inferred ion temperature from neutron spectra
journal, July 2014
- Murphy, T. J.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 21, Issue 7
Diagnosing inertial confinement fusion gamma ray physics (invited)
journal, October 2010
- Herrmann, H. W.; Hoffman, N.; Wilson, D. C.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 81, Issue 10
Interpreting inertial fusion neutron spectra
journal, February 2016
- Munro, David H.
- Nuclear Fusion, Vol. 56, Issue 3
Works referencing / citing this record:
Velocity correction for neutron activation diagnostics at the NIF
journal, October 2018
- Rinderknecht, Hans G.; Bionta, R.; Grim, G.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 10
A fused silica Cherenkov radiator for high precision time-of-flight measurement of DT γ and neutron spectra (invited)
journal, October 2018
- Moore, A. S.; Schlossberg, D. J.; Hartouni, E. P.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Neutron backscatter edge: A measure of the hydrodynamic properties of the dense DT fuel at stagnation in ICF experiments
journal, January 2020
- Crilly, A. J.; Appelbe, B. D.; Mannion, O. M.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 27, Issue 1
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal