The Bacterial Symbiont Phaeobacter inhibens Shapes the Life History of Its Algal Host Emiliania huxleyi
Abstract
Marine microbes form host-associated biofilm communities that are shaped by complex interactions between bacteria and their host. The roseobacter Phaeobacter inhibens exploits both symbiotic and pathogenic niches while interacting with its microalgal host Emiliania huxleyi. During co-cultivation over extended periods with E. huxleyi, we show that P. inhibens selectively kills two host cell types, the diploid calcifying strain and the haploid flagellated strain. Meanwhile, various non-calcifying diploid strains are resistant to this pathogen or the pathogen is avirulent to this cell type. This differential pathogenesis has the potential of dramatically altering the composition of E. huxleyi blooms, which are typically dominated by the roseobacter-susceptible calcifying strain. This cell type makes calcite plates, which are an important sink in the marine carbon cycle and forms part of the marine paleobotanic record. P. inhibens kills the haploid cells, which have been proposed as critical to the survival of the algae, as they readily escape both eukaryotic predation and viral infection. Consequently, bacteria such as P. inhibens could influence E. huxleyi's life history by selective pathogenesis, thereby altering the composition of cell types within E. huxleyi populations and its bloom-bust lifestyle.
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Alberta, Edmonton, AB (Canada)
- USDOE Joint Genome Institute (JGI), Walnut Creek, CA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Biological and Environmental Research (BER)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1477299
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Frontiers in Marine Science
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 5; Journal Issue: MAY; Journal ID: ISSN 2296-7745
- Publisher:
- Frontiers Research Foundation
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 59 BASIC BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Citation Formats
Bramucci, Anna R., Labeeuw, Leen, Orata, Fabini D., Ryan, Elizabeth M., Malmstrom, Rex R., and Case, Rebecca J. The Bacterial Symbiont Phaeobacter inhibens Shapes the Life History of Its Algal Host Emiliania huxleyi. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.3389/fmars.2018.00188.
Bramucci, Anna R., Labeeuw, Leen, Orata, Fabini D., Ryan, Elizabeth M., Malmstrom, Rex R., & Case, Rebecca J. The Bacterial Symbiont Phaeobacter inhibens Shapes the Life History of Its Algal Host Emiliania huxleyi. United States. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00188
Bramucci, Anna R., Labeeuw, Leen, Orata, Fabini D., Ryan, Elizabeth M., Malmstrom, Rex R., and Case, Rebecca J. Tue .
"The Bacterial Symbiont Phaeobacter inhibens Shapes the Life History of Its Algal Host Emiliania huxleyi". United States. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00188. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1477299.
@article{osti_1477299,
title = {The Bacterial Symbiont Phaeobacter inhibens Shapes the Life History of Its Algal Host Emiliania huxleyi},
author = {Bramucci, Anna R. and Labeeuw, Leen and Orata, Fabini D. and Ryan, Elizabeth M. and Malmstrom, Rex R. and Case, Rebecca J.},
abstractNote = {Marine microbes form host-associated biofilm communities that are shaped by complex interactions between bacteria and their host. The roseobacter Phaeobacter inhibens exploits both symbiotic and pathogenic niches while interacting with its microalgal host Emiliania huxleyi. During co-cultivation over extended periods with E. huxleyi, we show that P. inhibens selectively kills two host cell types, the diploid calcifying strain and the haploid flagellated strain. Meanwhile, various non-calcifying diploid strains are resistant to this pathogen or the pathogen is avirulent to this cell type. This differential pathogenesis has the potential of dramatically altering the composition of E. huxleyi blooms, which are typically dominated by the roseobacter-susceptible calcifying strain. This cell type makes calcite plates, which are an important sink in the marine carbon cycle and forms part of the marine paleobotanic record. P. inhibens kills the haploid cells, which have been proposed as critical to the survival of the algae, as they readily escape both eukaryotic predation and viral infection. Consequently, bacteria such as P. inhibens could influence E. huxleyi's life history by selective pathogenesis, thereby altering the composition of cell types within E. huxleyi populations and its bloom-bust lifestyle.},
doi = {10.3389/fmars.2018.00188},
journal = {Frontiers in Marine Science},
number = MAY,
volume = 5,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue May 29 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Tue May 29 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
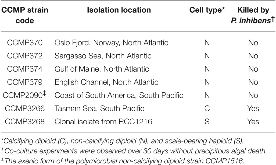 TABLE 1: Axenic E. huxleyi strains and their susceptibility to P. inhibens pathogenesis.
TABLE 1: Axenic E. huxleyi strains and their susceptibility to P. inhibens pathogenesis.
Works referenced in this record:
Probiotic effect in vivo of Roseobacter strain 27-4 against Vibrio (Listonella) anguillarum infections in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.) larvae
journal, May 2006
- Planas, Miquel; Pérez-Lorenzo, María; Hjelm, Mette
- Aquaculture, Vol. 255, Issue 1-4
Organic matter exudation by <I>Emiliania huxleyi</I> under simulated future ocean conditions
journal, January 2012
- Borchard, C.; Engel, A.
- Biogeosciences, Vol. 9, Issue 8
Exoproteome Analysis of the Seaweed Pathogen Nautella italica R11 Reveals Temperature-Dependent Regulation of RTX-Like Proteins
journal, June 2017
- Gardiner, Melissa; Bournazos, Adam M.; Maturana-Martinez, Claudia
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 8
Chemoattraction to Dimethylsulfoniopropionate Throughout the Marine Microbial Food Web
journal, July 2010
- Seymour, J. R.; Simo, R.; Ahmed, T.
- Science, Vol. 329, Issue 5989
Nautella italica gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a marine electroactive biofilm
journal, April 2009
- Vandecandelaere, I.; Nercessian, O.; Segaert, E.
- INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMATIC AND EVOLUTIONARY MICROBIOLOGY, Vol. 59, Issue 4
Life-cycle modification in open oceans accounts for genome variability in a cosmopolitan phytoplankton
journal, December 2014
- von Dassow, Peter; John, Uwe; Ogata, Hiroyuki
- The ISME Journal, Vol. 9, Issue 6
Temperature induced bacterial virulence and bleaching disease in a chemically defended marine macroalga: Temperature, disease and algal chemical defense
journal, October 2010
- Case, Rebecca J.; Longford, Sharon R.; Campbell, Alexandra H.
- Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 13, Issue 2
7000 Years of Emiliania huxleyi Viruses in the Black Sea
journal, July 2011
- Coolen, M. J. L.
- Science, Vol. 333, Issue 6041
A dual-species co-cultivation system to study the interactions between Roseobacters and dinoflagellates
journal, June 2014
- Wang, Hui; Tomasch, Jürgen; Jarek, Michael
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 5
Bacterial Diversity Associated with the Coccolithophorid Algae Emiliania huxleyi and Coccolithus pelagicus f. braarudii
journal, January 2015
- Green, David H.; Echavarri-Bravo, Virginia; Brennan, Debra
- BioMed Research International, Vol. 2015
Viral activation and recruitment of metacaspases in the unicellular coccolithophore, Emiliania huxleyi
journal, March 2007
- Bidle, K. D.; Haramaty, L.; Barcelos e. Ramos, J.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 104, Issue 14
Temperature-Induced Viral Resistance in Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae)
journal, November 2014
- Kendrick, B. Jacob; DiTullio, Giacomo R.; Cyronak, Tyler J.
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 9, Issue 11
A Bacterial Pathogen Displaying Temperature-Enhanced Virulence of the Microalga Emiliania huxleyi
journal, June 2016
- Mayers, Teaghan J.; Bramucci, Anna R.; Yakimovich, Kurt M.
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 7
Dynamic metabolic exchange governs a marine algal-bacterial interaction
journal, November 2016
- Segev, Einat; Wyche, Thomas P.; Kim, Ki Hyun
- eLife, Vol. 5
Phaeobacter gallaeciensis Reduces Vibrio anguillarum in Cultures of Microalgae and Rotifers, and Prevents Vibriosis in Cod Larvae
journal, August 2012
- D’Alvise, Paul W.; Lillebø, Siril; Prol-Garcia, Maria J.
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 7, Issue 8
Genomes and Virulence Factors of Novel Bacterial Pathogens Causing Bleaching Disease in the Marine Red Alga Delisea pulchra
journal, December 2011
- Fernandes, Neil; Case, Rebecca J.; Longford, Sharon R.
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 6, Issue 12
Classification of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009
journal, October 2008
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Vandenabeele, P.
- Cell Death & Differentiation, Vol. 16, Issue 1
Low Densities of Epiphytic Bacteria from the Marine Alga Ulva australis Inhibit Settlement of Fouling Organisms
journal, October 2007
- Rao, D.; Webb, J. S.; Holmstrom, C.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 73, Issue 24
Phaeobacter gallaeciensis genomes from globally opposite locations reveal high similarity of adaptation to surface life
journal, June 2012
- Thole, Sebastian; Kalhoefer, Daniela; Voget, Sonja
- The ISME Journal, Vol. 6, Issue 12
Virus dynamics in a coccolithophore-dominated bloom in the North Sea
journal, January 2002
- Wilson, William H.; Tarran, Glen; Zubkov, Mikhail V.
- Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, Vol. 49, Issue 15
Disruption of Cell-to-Cell Signaling Does Not Abolish the Antagonism of Phaeobacter gallaeciensis toward the Fish Pathogen Vibrio anguillarum in Algal Systems
journal, June 2013
- Prol García, M. J.; D'Alvise, P. W.; Gram, L.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 79, Issue 17
Investigation of the Genetics and Biochemistry of Roseobacticide Production in the Roseobacter Clade Bacterium Phaeobacter inhibens
journal, March 2016
- Wang, Rurun; Gallant, Étienne; Seyedsayamdost, Mohammad R.
- mBio, Vol. 7, Issue 2
Rapid Quantification of Mutant Fitness in Diverse Bacteria by Sequencing Randomly Bar-Coded Transposons
journal, May 2015
- Wetmore, Kelly M.; Price, Morgan N.; Waters, Robert J.
- mBio, Vol. 6, Issue 3, Article No. e00306-15
A biogeochemical study of the coccolithophore, Emiliania huxleyi , in the North Atlantic
journal, December 1993
- Holligan, Patrick M.; Fernández, Emilio; Aiken, James
- Global Biogeochemical Cycles, Vol. 7, Issue 4
The Toxic Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium Catenatum (Dinophyceae) Requires Marine Bacteria for Growth1: Bacteria Required for g. Catenatum Growth
journal, August 2011
- Bolch, Christopher J. S.; Subramanian, Thaila A.; Green, David H.
- Journal of Phycology, Vol. 47, Issue 5
Ultrastructural polysaccharide localization in calcifying and naked cells of the coccolithophoridEmiliania huxleyi
journal, June 1983
- van der Wal, P.; de Jong, E. W.; Westbroek, P.
- Protoplasma, Vol. 118, Issue 2
Microzones surrounding phytoplankton form the basis for a stratified marine microbial ecosystem
journal, July 1985
- Mitchell, James G.; Okubo, Akira; Fuhrman, Jed A.
- Nature, Vol. 316, Issue 6023
Ancient origin of the biosynthesis of lignin precursors
journal, May 2015
- Labeeuw, Leen; Martone, Patrick T.; Boucher, Yan
- Biology Direct, Vol. 10, Issue 1
Stichochrysis immobilis is a diatom, not a chrysophyte
journal, May 1993
- Guillard, R. R. L.; Hargraves, P. E.
- Phycologia, Vol. 32, Issue 3
Molecular mechanisms underlying roseobacter–phytoplankton symbioses
journal, June 2010
- Geng, Haifeng; Belas, Robert
- Current Opinion in Biotechnology, Vol. 21, Issue 3
The Jekyll-and-Hyde chemistry of Phaeobacter gallaeciensis
journal, February 2011
- Seyedsayamdost, Mohammad R.; Case, Rebecca J.; Kolter, Roberto
- Nature Chemistry, Vol. 3, Issue 4
Dual function of tropodithietic acid as antibiotic and signaling molecule in global gene regulation of the probiotic bacterium Phaeobacter inhibens
journal, April 2017
- Beyersmann, Paul G.; Tomasch, Jürgen; Son, Kwangmin
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 7, Issue 1
Coccolithophores Gephyrocapsa oceanica and Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae = Haptophyceae) in New Zealand's coastal waters: Characteristics of blooms and growth in laboratory culture
journal, September 1995
- Rhodes, Lesley L.; Peake, Barry M.; MacKenzie, A. Lincoln
- New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, Vol. 29, Issue 3
Continuous recording of photochemical and non-photochemical chlorophyll fluorescence quenching with a new type of modulation fluorometer
journal, January 1986
- Schreiber, U.; Schliwa, U.; Bilger, W.
- Photosynthesis Research, Vol. 10, Issue 1-2
The production of dissolved organic matter by phytoplankton and its importance to bacteria: Patterns across marine and freshwater systems
journal, September 1991
- Baines, Stephen B.; Pace, Michael L.
- Limnology and Oceanography, Vol. 36, Issue 6
Chemotaxis of Silicibacter sp. Strain TM1040 toward Dinoflagellate Products
journal, August 2004
- Miller, T. R.; Hnilicka, K.; Dziedzic, A.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 70, Issue 8
Resource Partitioning and Sympatric Differentiation Among Closely Related Bacterioplankton
journal, May 2008
- Hunt, D. E.; David, L. A.; Gevers, D.
- Science, Vol. 320, Issue 5879
SAR11 marine bacteria require exogenous reduced sulphur for growth
journal, March 2008
- Tripp, H. James; Kitner, Joshua B.; Schwalbach, Michael S.
- Nature, Vol. 452, Issue 7188
Release and consumption of DMSP from Emiliania huxleyi during grazing by Oxyrrhis manna
journal, January 1994
- Wolfe, Gv; Sherr, Eb; Sherr, Bf
- Marine Ecology Progress Series, Vol. 111
Catabolism of dimethylsulphoniopropionate: microorganisms, enzymes and genes
journal, October 2011
- Curson, Andrew R. J.; Todd, Jonathan D.; Sullivan, Matthew J.
- Nature Reviews Microbiology, Vol. 9, Issue 12
Draft Genome Sequences of Four Bacterial Strains Isolated from a Polymicrobial Culture of Naked (N-Type) Emiliania huxleyi CCMP1516: TABLE 1
journal, July 2016
- Orata, Fabini D.; Rosana, Albert Remus R.; Xu, Yue
- Genome Announcements, Vol. 4, Issue 4
Species-Specific Bacterial Communities in the Phycosphere of Microalgae?
journal, January 2007
- Sapp, Melanie; Schwaderer, Anne S.; Wiltshire, Karen H.
- Microbial Ecology, Vol. 53, Issue 4
Molecular and phenotypic analyses reveal the non-identity of the Phaeobacter gallaeciensis type strain deposits CIP 105210T and DSM 17395
journal, November 2013
- Buddruhs, N.; Pradella, S.; Goker, M.
- INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SYSTEMATIC AND EVOLUTIONARY MICROBIOLOGY, Vol. 63, Issue Pt 11
In situ survey of life cycle phases of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi (Haptophyta): Emiliania huxleyi life cycling
journal, April 2012
- Frada, Miguel J.; Bidle, Kay D.; Probert, Ian
- Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 14, Issue 6
Marine Microbes See a Sea of Gradients
journal, November 2012
- Stocker, R.
- Science, Vol. 338, Issue 6107
The Exometabolome of Two Model Strains of the Roseobacter Group: A Marketplace of Microbial Metabolites
journal, October 2017
- Wienhausen, Gerrit; Noriega-Ortega, Beatriz E.; Niggemann, Jutta
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 8
Tropodithietic Acid Production in Phaeobacter gallaeciensis Is Regulated by N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone-Mediated Quorum Sensing
journal, September 2011
- Berger, M.; Neumann, A.; Schulz, S.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 193, Issue 23
OCEANOGRAPHY: Microbial Control of Oceanic Carbon Flux: The Plot Thickens
journal, May 1998
- Azam, F.
- Science, Vol. 280, Issue 5364
Hybrid Biosynthesis of Roseobacticides from Algal and Bacterial Precursor Molecules
journal, October 2014
- Seyedsayamdost, Mohammad R.; Wang, Rurun; Kolter, Roberto
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 136, Issue 43
Interactions of Pathogenic Bacteria with Autophagy Systems
journal, July 2012
- Cemma, Marija; Brumell, John H.
- Current Biology, Vol. 22, Issue 13
Roseochelin B, an Algaecidal Natural Product Synthesized by the Roseobacter Phaeobacter inhibens in Response to Algal Sinapic Acid
journal, September 2017
- Wang, Rurun; Seyedsayamdost, Mohammad R.
- Organic Letters, Vol. 19, Issue 19
Grazing-activated chemical defence in a unicellular marine alga
journal, June 1997
- Wolfe, Gordon V.; Steinke, Michael; Kirst, Gunter O.
- Nature, Vol. 387, Issue 6636
An inducible antipredatory defense in haploid cells of the marine microalga Emiliania huxleyi (Prymnesiophyceae)
journal, May 2013
- Kolb, Amelia; Strom, Suzanne
- Limnology and Oceanography, Vol. 58, Issue 3
The "Cheshire Cat" escape strategy of the coccolithophore Emiliania huxleyi in response to viral infection
journal, September 2008
- Frada, M.; Probert, I.; Allen, M. J.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 105, Issue 41
Schrödinger’s Cheshire Cat: Are Haploid Emiliania huxleyi Cells Resistant to Viral Infection or Not?
journal, March 2017
- Mordecai, Gideon; Verret, Frederic; Highfield, Andrea
- Viruses, Vol. 9, Issue 3
Roseobacticides: Small Molecule Modulators of an Algal-Bacterial Symbiosis
journal, November 2011
- Seyedsayamdost, Mohammad R.; Carr, Gavin; Kolter, Roberto
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 133, Issue 45
Characterization of the Small RNA Transcriptome of the Marine Coccolithophorid, Emiliania huxleyi
journal, April 2016
- Zhang, Xiaoyu; Gamarra, Jaime; Castro, Steven
- PLOS ONE, Vol. 11, Issue 4
A Small Volume Bioassay to Assess Bacterial/Phytoplankton Co-culture Using WATER-Pulse-Amplitude-Modulated (WATER-PAM) Fluorometry
journal, January 2015
- Bramucci, Anna R.; Labeeuw, Leen; Mayers, Teaghan J.
- Journal of Visualized Experiments, Issue 97
A Novel Inducer of Roseobacter Motility Is Also a Disruptor of Algal Symbiosis
journal, November 2012
- Sule, P.; Belas, R.
- Journal of Bacteriology, Vol. 195, Issue 4
Gc-Sim-Ms Detection and Quantification of free Indole-3-Acetic acid in Bacterial Galls on the Marine alga Prionitis Lanceolata (Rhodophyta)
journal, June 1999
- Ashen, Jon B.; Cohen, Jerry D.; Goff, Lynda J.
- Journal of Phycology, Vol. 35, Issue 3
Identification of senescence and death in Emiliania huxleyi and Thalassiosira pseudonana : Cell staining, chlorophyll alterations, and dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) metabolism
journal, January 2012
- Franklin, Daniel J.; Airs, Ruth L.; Fernandes, Michelle
- Limnology and Oceanography, Vol. 57, Issue 1
Bacterial Community Structure Associated with a Dimethylsulfoniopropionate-Producing North Atlantic Algal Bloom
journal, October 2000
- Gonzalez, J. M.; Simo, R.; Massana, R.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 66, Issue 10
A Comparison of the Costs and Benefits of Bacterial Gene Expression
journal, October 2016
- Price, Morgan N.; Wetmore, Kelly M.; Deutschbauer, Adam M.
- PLOS ONE, Vol. 11, Issue 10
Chemotactic and Growth Responses of Marine Bacteria to Algal Extracellular Products
journal, October 1972
- Bell, Wayne; Mitchell, Ralph
- The Biological Bulletin, Vol. 143, Issue 2
Genome-wide identification of bacterial plant colonization genes
journal, September 2017
- Cole, Benjamin J.; Feltcher, Meghan E.; Waters, Robert J.
- PLOS Biology, Vol. 15, Issue 9
Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria
journal, May 2015
- Amin, S. A.; Hmelo, L. R.; van Tol, H. M.
- Nature, Vol. 522, Issue 7554
Hijacking of an autophagy-like process is critical for the life cycle of a DNA virus infecting oceanic algal blooms
journal, September 2014
- Schatz, Daniella; Shemi, Adva; Rosenwasser, Shilo
- New Phytologist, Vol. 204, Issue 4
Indole-3-Acetic Acid Is Produced by Emiliania huxleyi Coccolith-Bearing Cells and Triggers a Physiological Response in Bald Cells
journal, June 2016
- Labeeuw, Leen; Khey, Joleen; Bramucci, Anna R.
- Frontiers in Microbiology, Vol. 7
Genetic Dissection of Tropodithietic Acid Biosynthesis by Marine Roseobacters
journal, January 2008
- Geng, H.; Bruhn, J. B.; Nielsen, K. F.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 74, Issue 5
Chlorophyll Fluorescence: A Probe of Photosynthesis In Vivo
journal, June 2008
- Baker, Neil R.
- Annual Review of Plant Biology, Vol. 59, Issue 1
Viral Glycosphingolipids Induce Lytic Infection and Cell Death in Marine Phytoplankton
journal, November 2009
- Vardi, A.; Van Mooy, B. A. S.; Fredricks, H. F.
- Science, Vol. 326, Issue 5954
Dimethylsulfoniopropionate Metabolism by Pfiesteria-Associated Roseobacter spp.
journal, June 2004
- Miller, T. R.; Belas, R.
- Applied and Environmental Microbiology, Vol. 70, Issue 6
Draft genomes of Nautella italica strains CECT 7645T and CECT 7321: Two roseobacters with potential pathogenic and biotechnological traits
journal, April 2016
- Rodrigo-Torres, Lidia; Pujalte, María J.; Arahal, David R.
- Marine Genomics, Vol. 26
Complete genome sequence of the Phaeobacter gallaeciensis type strain CIP 105210T (= DSM 26640T = BS107T)
journal, March 2014
- Frank, Oliver; Pradella, Silke; Rohde, Manfred
- Standards in Genomic Sciences, Vol. 9, Issue 3
Works referencing / citing this record:
A microbial factory for defensive kahalalides in a tripartite marine symbiosis
journal, June 2019
- Zan, Jindong; Li, Zhiyuan; Tianero, Ma. Diarey
- Science, Vol. 364, Issue 6445
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal