Muon Tracing and Image Reconstruction Algorithms for Cosmic Ray Muon Computed Tomography
Abstract
Cosmic ray muon-computed tomography (μCT) is a new imaging modality with unique characteristics that could be particularly important for diverse applications including nuclear nonproliferation, spent nuclear fuel monitoring, cargo scanning, and volcano imaging. The strong scattering dependence of muons on atomic number Z in combination with high penetration range could offer a significant advantage over existing techniques when dense, shielded containers must be imaged. However, μCT reconstruction using conventional filtered back-projection is limited due to the overly simple assumptions that do not consider the curved path caused by multiple Coulomb scattering prompting the need for more sophisticated approaches to be developed. Here, we argue that the use of improved muon tracing and scattering angle projection algorithms as well as an algebraic reconstruction technique should produce muon tomographic images with improved quality–or require fewer muons to produce the same image quality–compared to the case where conventional methods are used. We report on the development and assessment of three novel muon tracing methods and two scattering angle projection methods for μCT. Simulated dry storage casks with single and partial missing fuel assemblies were used as numerical examples to assess and compare the proposed methods. The reconstructed images showed an expected improvement inmore »
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN (United States). Dept. of Nuclear Engineering
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Oregon State Univ., Corvallis, OR (United States). Dept. of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Health Physics
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Nuclear Energy (NE); USDOE Laboratory Directed Research and Development (LDRD) Program
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1474448
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725; NE0008292
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- IEEE Transactions on Image Processing
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 28; Journal Issue: 1; Journal ID: ISSN 1057-7149
- Publisher:
- IEEE
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 72 PHYSICS OF ELEMENTARY PARTICLES AND FIELDS; 97 MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTING; Dry storage cask; muon computed tomography; algebraic reconstruction technique; mesons; scattering; image reconstruction; x-rays; fuels
Citation Formats
Liu, Zhengzhi, Chatzidakis, Stylianos, Scaglione, John M., Liao, Can, Yang, Haori, and Hayward, Jason P. Muon Tracing and Image Reconstruction Algorithms for Cosmic Ray Muon Computed Tomography. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1109/TIP.2018.2869667.
Liu, Zhengzhi, Chatzidakis, Stylianos, Scaglione, John M., Liao, Can, Yang, Haori, & Hayward, Jason P. Muon Tracing and Image Reconstruction Algorithms for Cosmic Ray Muon Computed Tomography. United States. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2869667
Liu, Zhengzhi, Chatzidakis, Stylianos, Scaglione, John M., Liao, Can, Yang, Haori, and Hayward, Jason P. Mon .
"Muon Tracing and Image Reconstruction Algorithms for Cosmic Ray Muon Computed Tomography". United States. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2869667. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1474448.
@article{osti_1474448,
title = {Muon Tracing and Image Reconstruction Algorithms for Cosmic Ray Muon Computed Tomography},
author = {Liu, Zhengzhi and Chatzidakis, Stylianos and Scaglione, John M. and Liao, Can and Yang, Haori and Hayward, Jason P.},
abstractNote = {Cosmic ray muon-computed tomography (μCT) is a new imaging modality with unique characteristics that could be particularly important for diverse applications including nuclear nonproliferation, spent nuclear fuel monitoring, cargo scanning, and volcano imaging. The strong scattering dependence of muons on atomic number Z in combination with high penetration range could offer a significant advantage over existing techniques when dense, shielded containers must be imaged. However, μCT reconstruction using conventional filtered back-projection is limited due to the overly simple assumptions that do not consider the curved path caused by multiple Coulomb scattering prompting the need for more sophisticated approaches to be developed. Here, we argue that the use of improved muon tracing and scattering angle projection algorithms as well as an algebraic reconstruction technique should produce muon tomographic images with improved quality–or require fewer muons to produce the same image quality–compared to the case where conventional methods are used. We report on the development and assessment of three novel muon tracing methods and two scattering angle projection methods for μCT. Simulated dry storage casks with single and partial missing fuel assemblies were used as numerical examples to assess and compare the proposed methods. The reconstructed images showed an expected improvement in image quality when compared with conventional techniques, even without muon momentum information, which should lead to improved detection capability, even for partial defects.},
doi = {10.1109/TIP.2018.2869667},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Image Processing},
number = 1,
volume = 28,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Sep 24 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Mon Sep 24 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
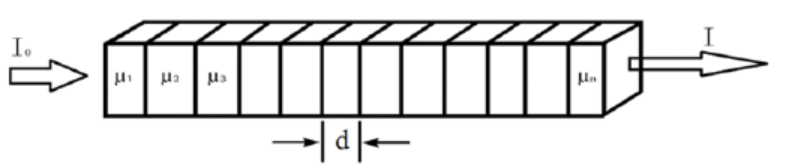 Fig. 1: Illustration of neutral beam crossing a discretized object
Fig. 1: Illustration of neutral beam crossing a discretized object
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal