Effect of alumina incorporation on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system for reduction of nitrogen oxides under lean conditions
Abstract
Presence of sulfur or sulfur additives in natural gas lead to the formation of sulfur dioxide in the exhaust stream of natural gas-fired lean-burn engines. The sulfur tolerance and hydrothermal stability of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system comprising a reduction catalyst (palladium supported on sulfated zirconia- Pd/SZ) and an oxidation catalyst (cobalt oxide supported on ceria- CoOx/CeO2) for NOx reduction under lean-burn conditions has been tested under simulated engine exhaust conditions. Alumina-incorporated Pd/SZ (Pd/SZ(Alumina)) reduction catalyst as part of the dual catalyst bed demonstrated superior sulfur tolerance in the presence of 5 ppm SO2 in the feed. The ratio of the reduction to oxidation catalyst was also seen to affect the hydrothermal stability under wet conditions with SO2 in the reaction medium. The effect of hydrocarbon and water concentration in the reaction mixture on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst bed was studied. Increasing the reaction temperature from 450°C to 500°C demonstrated very stable NOx conversion and improved CH4 conversions when the dual-catalyst bed was kept on-stream for 40 h-1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy on samples poisoned with SO2 ex-situ revealed the deposition of surface sulfates on the Pd/SZ catalyst samples and a combination of sulfates and sulfites on the CoOx/CeO2 onmore »
- Authors:
-
- The Ohio State Univ., Columbus, OH (United States). William G. Lowrie Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering; Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- The Ohio State Univ., Columbus, OH (United States). William G. Lowrie Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States); The Ohio State Univ., Columbus, OH (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE; Caterpillar Inc., Peoria, IL (United States)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1471840
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Catalysis Today
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 320; Journal ID: ISSN 0920-5861
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 03 NATURAL GAS; 37 INORGANIC, ORGANIC, PHYSICAL, AND ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY; 33 ADVANCED PROPULSION SYSTEMS; NOx reduction; Lean-burn; SO2 tolerance; XPS; 27Al MAS NMR
Citation Formats
Sinha Majumdar, Sreshtha, Alexander, Anne-Marie, Gawade, Preshit, Celik, Gokhan, and Ozkan, Umit S. Effect of alumina incorporation on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system for reduction of nitrogen oxides under lean conditions. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2018.01.027.
Sinha Majumdar, Sreshtha, Alexander, Anne-Marie, Gawade, Preshit, Celik, Gokhan, & Ozkan, Umit S. Effect of alumina incorporation on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system for reduction of nitrogen oxides under lean conditions. United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.01.027
Sinha Majumdar, Sreshtha, Alexander, Anne-Marie, Gawade, Preshit, Celik, Gokhan, and Ozkan, Umit S. Wed .
"Effect of alumina incorporation on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system for reduction of nitrogen oxides under lean conditions". United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.01.027. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1471840.
@article{osti_1471840,
title = {Effect of alumina incorporation on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system for reduction of nitrogen oxides under lean conditions},
author = {Sinha Majumdar, Sreshtha and Alexander, Anne-Marie and Gawade, Preshit and Celik, Gokhan and Ozkan, Umit S.},
abstractNote = {Presence of sulfur or sulfur additives in natural gas lead to the formation of sulfur dioxide in the exhaust stream of natural gas-fired lean-burn engines. The sulfur tolerance and hydrothermal stability of the dual-catalyst aftertreatment system comprising a reduction catalyst (palladium supported on sulfated zirconia- Pd/SZ) and an oxidation catalyst (cobalt oxide supported on ceria- CoOx/CeO2) for NOx reduction under lean-burn conditions has been tested under simulated engine exhaust conditions. Alumina-incorporated Pd/SZ (Pd/SZ(Alumina)) reduction catalyst as part of the dual catalyst bed demonstrated superior sulfur tolerance in the presence of 5 ppm SO2 in the feed. The ratio of the reduction to oxidation catalyst was also seen to affect the hydrothermal stability under wet conditions with SO2 in the reaction medium. The effect of hydrocarbon and water concentration in the reaction mixture on the sulfur tolerance of the dual-catalyst bed was studied. Increasing the reaction temperature from 450°C to 500°C demonstrated very stable NOx conversion and improved CH4 conversions when the dual-catalyst bed was kept on-stream for 40 h-1. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy on samples poisoned with SO2 ex-situ revealed the deposition of surface sulfates on the Pd/SZ catalyst samples and a combination of sulfates and sulfites on the CoOx/CeO2 on treatment with SO2. The presence of alumina in the Pd/SZ sample protects the support from SO2 poisoning as the oxidation state of the zirconia support remained largely unchanged on poisoning while in the CoOx/CeO2 sample, sulfur poisoning likely affects the cerium redox cycle (Ce3+-Ce4+). 27Al magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR) revealed redistribution of the octahedral and tetrahedral Al-O coordination on SO2 poisoning. Due to association with deposited sulfates on the catalyst, shielding effect on the Al nuclei resulted in an increased octahedral Al-O coordination in the poisoned sample.},
doi = {10.1016/j.cattod.2018.01.027},
journal = {Catalysis Today},
number = ,
volume = 320,
place = {United States},
year = {Wed Jan 31 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Wed Jan 31 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
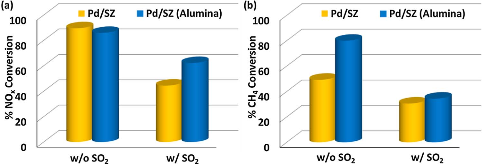 Figure 1: Sulfur tolerance of the mixed bed with the Pd/SZ or Pd/SZ (Alumina) reduction catalyst component under dry conditions at 450 °C for 40 h in terms of (a) NOx and (b) CH4 conversions. Feed conditions: 180 ppm NO2, 1737 ppm CH4, 208 ppm C2H6, 104 ppm C3H8, 650more »
Figure 1: Sulfur tolerance of the mixed bed with the Pd/SZ or Pd/SZ (Alumina) reduction catalyst component under dry conditions at 450 °C for 40 h in terms of (a) NOx and (b) CH4 conversions. Feed conditions: 180 ppm NO2, 1737 ppm CH4, 208 ppm C2H6, 104 ppm C3H8, 650more »
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal