Recent trends on the application of PGM-free catalysts at the cathode of anion exchange membrane fuel cells
Abstract
Anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) are becoming more and more attractive due to their alkaline environment, being less aggressive and favorable to the use of low-cost materials. Furthermore, the alkaline medium displays enhanced alcohol oxidation reaction kinetics, which favors the use of fuels different from hydrogen, ranging from alcohols to polyols, and enhanced oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) kinetics. This allows the use of non-noble transition metals to synthesize cathodic catalysts, avoiding the costly platinum-group metals (PGM). In particular, the most active catalysts developed so far are mostly synthesized by sacrificial support method, which allows the fine tuning of the morphology, favoring oxygen transport, water removal, density of Fe-Nx active sites, and thus an enhanced electrochemical ORR activity. This mini-review analyzes the best AEMFCs cell performance achieved so far in recent years when PGM-free catalysts based on Me-N-C (Me = Fe, Co) are used for ORR at the cathode side, for AEMFCs fed with hydrogen, methanol, and ethanol.
- Authors:
-
- National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Politecnico di Torino (Italy)
- Politecnico di Torino (Italy)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1461369
- Report Number(s):
- NREL/JA-5900-71988
Journal ID: ISSN 2451-9103
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC36-08GO28308
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Current Opinion in Electrochemistry
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 9; Journal Issue: C; Journal ID: ISSN 2451-9103
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 37 INORGANIC, ORGANIC, PHYSICAL, AND ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY; anion exchange membrane fuel cells; AEMFC; fuel cell performance; catalysts
Citation Formats
Osmieri, Luigi, Pezzolato, Lorenzo, and Specchia, Stefania. Recent trends on the application of PGM-free catalysts at the cathode of anion exchange membrane fuel cells. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.coelec.2018.05.011.
Osmieri, Luigi, Pezzolato, Lorenzo, & Specchia, Stefania. Recent trends on the application of PGM-free catalysts at the cathode of anion exchange membrane fuel cells. United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.05.011
Osmieri, Luigi, Pezzolato, Lorenzo, and Specchia, Stefania. Sat .
"Recent trends on the application of PGM-free catalysts at the cathode of anion exchange membrane fuel cells". United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2018.05.011. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1461369.
@article{osti_1461369,
title = {Recent trends on the application of PGM-free catalysts at the cathode of anion exchange membrane fuel cells},
author = {Osmieri, Luigi and Pezzolato, Lorenzo and Specchia, Stefania},
abstractNote = {Anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs) are becoming more and more attractive due to their alkaline environment, being less aggressive and favorable to the use of low-cost materials. Furthermore, the alkaline medium displays enhanced alcohol oxidation reaction kinetics, which favors the use of fuels different from hydrogen, ranging from alcohols to polyols, and enhanced oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) kinetics. This allows the use of non-noble transition metals to synthesize cathodic catalysts, avoiding the costly platinum-group metals (PGM). In particular, the most active catalysts developed so far are mostly synthesized by sacrificial support method, which allows the fine tuning of the morphology, favoring oxygen transport, water removal, density of Fe-Nx active sites, and thus an enhanced electrochemical ORR activity. This mini-review analyzes the best AEMFCs cell performance achieved so far in recent years when PGM-free catalysts based on Me-N-C (Me = Fe, Co) are used for ORR at the cathode side, for AEMFCs fed with hydrogen, methanol, and ethanol.},
doi = {10.1016/j.coelec.2018.05.011},
journal = {Current Opinion in Electrochemistry},
number = C,
volume = 9,
place = {United States},
year = {Sat May 19 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Sat May 19 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
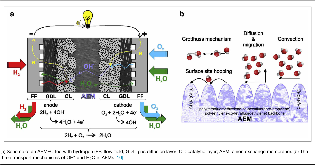 Figure 1: (a)Scheme of an AEMFC fed with hydrogen (FF: flow-field; GDL: gas diffusion layer; CL: catalytic layer; AEM: anion exchange membrane). (b) The three transport mechanisms of OH– and H2O in AEMs.
Figure 1: (a)Scheme of an AEMFC fed with hydrogen (FF: flow-field; GDL: gas diffusion layer; CL: catalytic layer; AEM: anion exchange membrane). (b) The three transport mechanisms of OH– and H2O in AEMs.
Works referenced in this record:
Direct Methanol Anion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with a Non-Platinum Group Metal Cathode based on Iron-Aminoantipyrine Catalyst
journal, September 2015
- Janarthanan, Rajeswari; Serov, Alexey; Pilli, Satyananda Kishore
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 175
DMFC performance and methanol cross-over: Experimental analysis and model validation
journal, October 2008
- Casalegno, A.; Marchesi, R.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 185, Issue 1
A high selectivity quaternized polysulfone membrane for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells
journal, April 2015
- Abuin, Graciela C.; Franceschini, Esteban A.; Nonjola, Patrick
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 279
A New Fuel Cell Cathode Catalyst
journal, March 1964
- Jasinski, Raymond
- Nature, Vol. 201, Issue 4925, p. 1212-1213
Temperature dependent performance and catalyst layer properties of PtRu supported on modified few-walled carbon nanotubes for the alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell
journal, May 2017
- Kanninen, Petri; Borghei, Maryam; Hakanpää, Janina
- Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Vol. 793
Alkaline Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
journal, July 2006
- Sarangapani, Srinivasan; Luczak, Frank; Enayetullah, Mohammad
- ECS Transactions, Vol. 1, Issue 32
Varying the morphology of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts by templating Iron Phthalocyanine precursor with different porous SiO 2 to promote the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
journal, September 2015
- Monteverde Videla, Alessandro H. A.; Osmieri, Luigi; Armandi, Marco
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 177
Investigations of conductivity in FEP-based radiation-grafted alkaline anion-exchange membranes
journal, February 2005
- Slade, R.; Varcoe, J.
- Solid State Ionics, Vol. 176, Issue 5-6
Enhancing the corrosion resistance of the 2205 duplex stainless steel bipolar plates in PEMFCs environment by surface enriched molybdenum
journal, January 2017
- Jinlong, Lv; Zhuqing, Wang; Tongxiang, Liang
- Results in Physics, Vol. 7
Synthesis and characterization of high performing Fe-N-C catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in Alkaline Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
journal, January 2018
- Hossen, Md Mosaddek; Artyushkova, Kateryna; Atanassov, Plamen
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 375
Synthesis and properties of anion-exchange membranes for fuel cells
journal, August 2010
- Shevchenko, V. V.; Gumennaya, M. A.
- Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry, Vol. 46, Issue 3
On the mechanism of the electrochemical conversion of ammonia to dinitrogen on Pt(1 0 0) in alkaline environment
journal, March 2018
- Katsounaros, Ioannis; Figueiredo, Marta C.; Calle-Vallejo, Federico
- Journal of Catalysis, Vol. 359
Carbon-Supported Fe–Nx Catalysts Synthesized by Pyrolysis of the Fe(II)–2,3,5,6-Tetra(2-pyridyl)pyrazine Complex: Structure, Electrochemical Properties, and Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity
journal, June 2011
- Velázquez-Palenzuela, Amado; Zhang, Lei; Wang, Liucheng
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 115, Issue 26
Alkaline fuel cells running at elevated temperature for regenerative fuel cell system applications in spacecrafts
journal, March 2012
- Markgraf, S.; Hörenz, M.; Schmiel, T.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 201
Anion-exchange membranes in electrochemical energy systems
journal, January 2014
- Varcoe, John R.; Atanassov, Plamen; Dekel, Dario R.
- Energy & Environmental Science, Vol. 7, Issue 10, p. 3135-3191
Review of cell performance in anion exchange membrane fuel cells
journal, January 2018
- Dekel, Dario R.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 375
Anion exchange membrane fuel cells: Current status and remaining challenges
journal, January 2018
- Gottesfeld, Shimshon; Dekel, Dario R.; Page, Miles
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 375
Investigations into the ex situ methanol, ethanol and ethylene glycol permeabilities of alkaline polymer electrolyte membranes
journal, November 2007
- Varcoe, John R.; Slade, Robert C. T.; Yee, Eric Lam How
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 173, Issue 1
Activity, Selectivity, and Anion-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Performance of Virtually Metal-Free Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanotube Electrodes for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
journal, February 2012
- Venkateswara Rao, Chitturi; Ishikawa, Yasuyuki
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 116, Issue 6
A Dusty Fluid Model for Predicting Hydroxyl Anion Conductivity in Alkaline Anion Exchange Membranes
journal, January 2010
- Grew, Kyle N.; Chiu, Wilson K. S.
- Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 157, Issue 3
Cathode flooding behaviour in alkaline direct ethanol fuel cells
journal, January 2011
- Li, Y. S.; Zhao, T. S.; Chen, R.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 196, Issue 1
A review of the state-of-the-art of the methanol crossover in direct methanol fuel cells
journal, November 1999
- Heinzel, A.; Barragán, V. M.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 84, Issue 1
DMFC performance and methanol cross-over: Experimental analysis and model validation
journal, October 2008
- Casalegno, A.; Marchesi, R.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 185, Issue 1
Fundamental Mechanistic Understanding of Electrocatalysis of Oxygen Reduction on Pt and Non-Pt Surfaces: Acid versus Alkaline Media
journal, March 2012
- Ramaswamy, Nagappan; Mukerjee, Sanjeev
- Advances in Physical Chemistry, Vol. 2012
Alkaline Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
journal, July 2006
- Sarangapani, Srinivasan; Luczak, Frank; Enayetullah, Mohammad
- ECS Transactions, Vol. 1, Issue 32
Study of the Exchange Current Density for the Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reactions
journal, January 2007
- Neyerlin, K. C.; Gu, Wenbin; Jorne, Jacob
- Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 154, Issue 7
Hydrogen Oxidation and Evolution Reaction Kinetics on Platinum: Acid vs Alkaline Electrolytes
journal, January 2010
- Sheng, Wenchao; Gasteiger, Hubert A.; Shao-Horn, Yang
- Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 157, Issue 11
New insights into the electrochemical hydrogen oxidation and evolution reaction mechanism
journal, January 2014
- Durst, J.; Siebel, A.; Simon, C.
- Energy Environ. Sci., Vol. 7, Issue 7
A Pd/C-CeO 2 Anode Catalyst for High-Performance Platinum-Free Anion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
journal, April 2016
- Miller, Hamish A.; Lavacchi, Alessandro; Vizza, Francesco
- Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Vol. 55, Issue 20
Highly active nanostructured palladium-ceria electrocatalysts for the hydrogen oxidation reaction in alkaline medium
journal, March 2017
- Miller, Hamish A.; Vizza, Francesco; Marelli, Marcello
- Nano Energy, Vol. 33
Oxidation of Alcohols in Acidic and Alkaline Environments
journal, October 2008
- Cremers, Carsten; Bayer, Domnik; Kintzel, Birgit
- ECS Transactions, Vol. 16, Issue 2
Determination of Carbonate Ion in MEA during the Alkaline Membrane Fuel Cell (AMFC) Operation
conference, January 2010
- Watanabe, Shin; Fukuta, Kenji; Yanagi, Hiroyuki
- 218th ECS Meeting, ECS Transactions
Advances and challenges in alkaline anion exchange membrane fuel cells
journal, May 2018
- Pan, Z. F.; An, L.; Zhao, T. S.
- Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, Vol. 66
Synthesis–Structure–Property Relationships for Hyperbranched Aminosilica CO 2 Adsorbents
journal, December 2009
- Drese, Jeffrey H.; Choi, Sunho; Lively, Ryan P.
- Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 19, Issue 23
Selective CO 2 Adsorption by Nitro Functionalized Metal Organic Frameworks
journal, January 2016
- Maity, Dilip Kumar; Halder, Arijit; Bhattacharya, Biswajit
- Crystal Growth & Design, Vol. 16, Issue 3
Recent Advances in Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
journal, February 2016
- Shao, Minhua; Chang, Qiaowan; Dodelet, Jean-Pol
- Chemical Reviews, Vol. 116, Issue 6
Importance of balancing membrane and electrode water in anion exchange membrane fuel cells
journal, January 2018
- Omasta, T. J.; Wang, L.; Peng, X.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 375
A New Fuel Cell Cathode Catalyst
journal, March 1964
- Jasinski, Raymond
- Nature, Vol. 201, Issue 4925, p. 1212-1213
Progress in preparation of non-noble electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cell reactions
journal, June 2006
- Zhang, Lei; Zhang, Jiujun; Wilkinson, David P.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 156, Issue 2
Does CO poison Fe-based catalysts for ORR?
journal, May 2010
- Birry, Laurent; Zagal, José H.; Dodelet, Jean-Pol
- Electrochemistry Communications, Vol. 12, Issue 5
Low and non-platinum electrocatalysts for PEMFCs: Current status, challenges and prospects
journal, October 2012
- Brouzgou, A.; Song, S. Q.; Tsiakaras, P.
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol. 127
ElectroCat: DOE's approach to PGM-free catalyst and electrode R&D
journal, June 2018
- Thompson, Simon T.; Wilson, Adria R.; Zelenay, Piotr
- Solid State Ionics, Vol. 319
Progress in nanostructured (Fe or Co)/N/C non-noble metal electrocatalysts for fuel cell oxygen reduction reaction
journal, February 2018
- Zhang, Lei; Wilkinson, David P.; Liu, Yuyu
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 262
Enhancing the corrosion resistance of the 2205 duplex stainless steel bipolar plates in PEMFCs environment by surface enriched molybdenum
journal, January 2017
- Jinlong, Lv; Zhuqing, Wang; Tongxiang, Liang
- Results in Physics, Vol. 7
A review of radiation-grafted polymer electrolyte membranes for alkaline polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells
journal, October 2015
- Zhou, Tianchi; Shao, Rong; Chen, Song
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 293
Multication Side Chain Anion Exchange Membranes
journal, January 2016
- Zhu, Liang; Pan, Jing; Wang, Ying
- Macromolecules, Vol. 49, Issue 3
Preparation of radiation-grafted powders for use as anion exchange ionomers in alkaline polymer electrolyte fuel cells
journal, January 2014
- Poynton, Simon D.; Slade, Robert C. T.; Omasta, Travis J.
- J. Mater. Chem. A, Vol. 2, Issue 14
Synthesis and properties of anion-exchange membranes for fuel cells
journal, August 2010
- Shevchenko, V. V.; Gumennaya, M. A.
- Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry, Vol. 46, Issue 3
A high selectivity quaternized polysulfone membrane for alkaline direct methanol fuel cells
journal, April 2015
- Abuin, Graciela C.; Franceschini, Esteban A.; Nonjola, Patrick
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 279
PtCu catalyst for the electro-oxidation of ethanol in an alkaline direct alcohol fuel cell
journal, November 2017
- Maya-Cornejo, J.; Carrera-Cerritos, R.; Sebastián, D.
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 42, Issue 46
Preparation and characterization of palladium-nickel on graphene oxide support as anode catalyst for alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell
journal, February 2017
- Tan, Joshua L.; De Jesus, Arvee M.; Chua, Stephanie L.
- Applied Catalysis A: General, Vol. 531
Temperature dependent performance and catalyst layer properties of PtRu supported on modified few-walled carbon nanotubes for the alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell
journal, May 2017
- Kanninen, Petri; Borghei, Maryam; Hakanpää, Janina
- Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Vol. 793
Fe-N/C catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction supported on different carbonaceous materials. Performance in acidic and alkaline direct alcohol fuel cells
journal, May 2017
- Osmieri, Luigi; Escudero-Cid, Ricardo; Armandi, Marco
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol. 205
Application of a non-noble Fe-N-C catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in an alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell
journal, January 2018
- Osmieri, Luigi; Escudero-Cid, Ricardo; Monteverde Videla, Alessandro H. A.
- Renewable Energy, Vol. 115
Palladium–copper electrocatalyst for the promotion of the electrochemical oxidation of polyalcohol fuels in the alkaline direct alcohol fuel cell
journal, September 2015
- Munoz, Fabian; Hua, Chau; Kwong, Tiffany
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol. 174-175
Supported Pt, Pd and Au nanoparticle anode catalysts for anion-exchange membrane fuel cells with glycerol and crude glycerol fuels
journal, June 2013
- Zhang, Zhiyong; Xin, Le; Qi, Ji
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol. 136-137
Optimizing operating conditions and electrochemical characterization of glucose–gluconate alkaline fuel cells
journal, February 2011
- Pasta, M.; La Mantia, F.; Ruffo, R.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 196, Issue 3
Review of implantable and external abiotically catalysed glucose fuel cells and the differences between their membranes and catalysts
journal, October 2016
- Santiago, Óscar; Navarro, Emilio; Raso, Miguel A.
- Applied Energy, Vol. 179
Current status of combined systems using alkaline fuel cells and ammonia as a hydrogen carrier
journal, February 2008
- Hejze, T.; Besenhard, J. O.; Kordesch, K.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 176, Issue 2
On the mechanism of the electrochemical conversion of ammonia to dinitrogen on Pt(1 0 0) in alkaline environment
journal, March 2018
- Katsounaros, Ioannis; Figueiredo, Marta C.; Calle-Vallejo, Federico
- Journal of Catalysis, Vol. 359
Highly durable direct hydrazine hydrate anion exchange membrane fuel cell
journal, January 2018
- Sakamoto, Tomokazu; Serov, Alexey; Masuda, Teruyuki
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 375
Kinetics of Non-Platinum Group Metal Catalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Alkaline Medium
journal, August 2009
- Piana, Michele; Catanorchi, Stefano; Gasteiger, H. A.
- ECS Transactions, Vol. 16, Issue 2
Nanocarbon Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction in Alkaline Media for Advanced Energy Conversion and Storage
journal, January 2014
- Li, Qing; Cao, Ruiguo; Cho, Jaephil
- Advanced Energy Materials, Vol. 4, Issue 6
Non-precious Co3O4 nano-rod electrocatalyst for oxygenreduction reaction in anion-exchange membranefuelcells
journal, January 2012
- Xu, Jianbo; Gao, Ping; Zhao, T. S.
- Energy Environ. Sci., Vol. 5, Issue 1
Investigations of conductivity in FEP-based radiation-grafted alkaline anion-exchange membranes
journal, February 2005
- Slade, R.; Varcoe, J.
- Solid State Ionics, Vol. 176, Issue 5-6
Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review
journal, July 2011
- Merle, Géraldine; Wessling, Matthias; Nijmeijer, Kitty
- Journal of Membrane Science, Vol. 377, Issue 1-2, p. 1-35
H2/air alkaline membrane fuel cell performance and durability, using novel ionomer and non-platinum group metal cathode catalyst
journal, September 2010
- Piana, Michele; Boccia, Massimiliano; Filpi, Antonio
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 195, Issue 18
Non-precious metal catalysts synthesized from precursors of carbon, nitrogen, and transition metal for oxygen reduction in alkaline fuel cells
journal, February 2011
- Li, Xuguang; Popov, Branko N.; Kawahara, Takeo
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 196, Issue 4
Synthesis and characterization of high performing Fe-N-C catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in Alkaline Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
journal, January 2018
- Hossen, Md Mosaddek; Artyushkova, Kateryna; Atanassov, Plamen
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 375
Influence of different transition metals on the properties of Me–N–C (Me = Fe, Co, Cu, Zn) catalysts synthesized using SBA-15 as tubular nano-silica reactor for oxygen reduction reaction
journal, December 2016
- Osmieri, Luigi; Monteverde Videla, Alessandro H. A.; Armandi, Marco
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 41, Issue 47
Soft-template synthesis of mesoporous non-precious metal catalyst with Fe-N x /C active sites for oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cells
journal, March 2018
- Mun, Yeongdong; Kim, Min Jeong; Park, Shin-Ae
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol. 222
Polypyrrole-Derived Fe−Co−N−C Catalyst for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction: Performance in Alkaline Hydrogen and Ethanol Fuel Cells
journal, May 2018
- Osmieri, Luigi; Zafferoni, Claudio; Wang, Lianqin
- ChemElectroChem, Vol. 5, Issue 14
Carbon-Supported Fe–Nx Catalysts Synthesized by Pyrolysis of the Fe(II)–2,3,5,6-Tetra(2-pyridyl)pyrazine Complex: Structure, Electrochemical Properties, and Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity
journal, June 2011
- Velázquez-Palenzuela, Amado; Zhang, Lei; Wang, Liucheng
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 115, Issue 26
Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Vesicles with Dual Iron-Based Sites for Efficient Oxygen Reduction
journal, January 2017
- Li, Qianru; Wan, Gang; Zhao, Han
- ChemSusChem, Vol. 10, Issue 3
Unveiling N-Protonation and Anion-Binding Effects on Fe/N/C Catalysts for O 2 Reduction in Proton-Exchange-Membrane Fuel Cells
journal, July 2011
- Herranz, Juan; Jaouen, Frédéric; Lefèvre, Michel
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 115, Issue 32
Highly active carbon supported palladium-rhodium PdXRh/C catalysts for methanol electrooxidation in alkaline media and their performance in anion exchange direct methanol fuel cells (AEM-DMFCs)
journal, September 2015
- Jurzinsky, T.; Bär, R.; Cremers, C.
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 176
Direct Methanol Anion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with a Non-Platinum Group Metal Cathode based on Iron-Aminoantipyrine Catalyst
journal, September 2015
- Janarthanan, Rajeswari; Serov, Alexey; Pilli, Satyananda Kishore
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 175
High-performance oxygen reduction electrocatalysts derived from uniform cobalt–adenine assemblies
journal, October 2015
- Shen, Mengxia; Zheng, Li-Rong; He, Wenhui
- Nano Energy, Vol. 17
Nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous carbon: synthesis and active sites for electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction reaction
journal, April 2015
- Wan, Kai; Long, Gui-Fa; Liu, Ming-Yao
- Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Vol. 165
A Fe-N-C catalyst with highly dispersed iron in carbon for oxygen reduction reaction and its application in direct methanol fuel cells
journal, April 2016
- Gu, Lingzheng; Jiang, Luhua; Li, Xuning
- Chinese Journal of Catalysis, Vol. 37, Issue 4
Comparative study between platinum supported on carbon and non-noble metal cathode catalyst in alkaline direct ethanol fuel cell (ADEFC)
journal, April 2011
- Zhiani, Mohammad; Gasteiger, Hubert A.; Piana, Michele
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 36, Issue 8
Pd and Pt–Ru anode electrocatalysts supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their use in passive and active direct alcohol fuel cells with an anion-exchange membrane (alcohol=methanol, ethanol, glycerol)
journal, May 2009
- Bambagioni, Valentina; Bianchini, Claudio; Marchionni, Andrea
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 190, Issue 2
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes with encapsulated Fe nanoparticles as efficient oxygen reduction catalyst for alkaline membrane direct ethanol fuel cells
journal, December 2017
- Rauf, Muhammad; Chen, Rongrong; Wang, Qiang
- Carbon, Vol. 125
High Performance and Cost-Effective Direct Methanol Fuel Cells: Fe-N-C Methanol-Tolerant Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalysts
journal, July 2016
- Sebastián, David; Serov, Alexey; Artyushkova, Kateryna
- ChemSusChem, Vol. 9, Issue 15
Non-platinum oxygen reduction electrocatalysts based on pyrolyzed transition metal macrocycles
journal, November 2008
- Pylypenko, Svitlana; Mukherjee, Sanjoy; Olson, Tim S.
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 53, Issue 27
Original Mechanochemical Synthesis of Non-Platinum Group Metals Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalysts Assisted by Sacrificial Support Method
journal, October 2015
- Serov, Alexey; Artyushkova, Kateryna; Andersen, Nalin I.
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 179
Varying the morphology of Fe-N-C electrocatalysts by templating Iron Phthalocyanine precursor with different porous SiO 2 to promote the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
journal, September 2015
- Monteverde Videla, Alessandro H. A.; Osmieri, Luigi; Armandi, Marco
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 177
Fe-N-C Oxygen Reduction Fuel Cell Catalyst Derived from Carbendazim: Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity
journal, March 2014
- Serov, Alexey; Artyushkova, Kateryna; Atanassov, Plamen
- Advanced Energy Materials, Vol. 4, Issue 10
Multitechnique Characterization of a Polyaniline–Iron–Carbon Oxygen Reduction Catalyst
journal, July 2012
- Ferrandon, Magali; Kropf, A. Jeremy; Myers, Deborah J.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 116, Issue 30
Correlations between Mass Activity and Physicochemical Properties of Fe/N/C Catalysts for the ORR in PEM Fuel Cell via 57 Fe Mössbauer Spectroscopy and Other Techniques
journal, January 2014
- Kramm, Ulrike I.; Lefèvre, Michel; Larouche, Nicholas
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 136, Issue 3

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal