Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the Angular Power Spectrum of a Combined 2500 deg2 SPT-SZ and Planck Gravitational Lensing Map
Abstract
We report constraints on cosmological parameters from the angular power spectrum of a cosmic microwave background (CMB) gravitational lensing potential map created using temperature data from 2500 deg2 of South Pole Telescope (SPT) data supplemented with data from Planck in the same sky region, with the statistical power in the combined map primarily from the SPT data. We fit the lensing power spectrum to a model including cold dark matter and a cosmological constant (λCDM), and to models with single-parameter extensions to λCDM. We find constraints that are comparable to and consistent with those found using the full-sky Planck CMB lensing data, e.g., σ8ωm0.25 = 0.598 ± 0.024 from the lensing data alone with weak priors placed on other parameters. Combining with primary CMB data, we explore single-parameter extensions to λCDM. We find or ωk = -0.012-0.0230.021 or Mv < 0.70 eV at 95%25 confidence, in good agreement with results including the lensing potential as measured by Planck. We include two parameters that scale the effect of lensing on the CMB: AL, which scales the lensing power spectrum in both the lens reconstruction power and in the smearing of the acoustic peaks, and Aφφ, which scales only the amplitude ofmore »
- Authors:
-
more »
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada)
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Stanford Univ., Stanford, CA (United States)
- Univ. of California, Davis, CA (United States)
- Univ. of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA (United States); Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States); Fermi National Accelerator Lab. (FNAL), Batavia, IL (United States)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States); Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States)
- SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Menlo Park, CA (United States)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States); California Inst. of Technology (CalTech), Pasadena, CA (United States)
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States)
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Canadian Institute for Advanced Research, Toronto, ON (Canada)
- Univ. of Colorado, Boulder, CO (United States)
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States); European Southern Observatory, Garching (Germany)
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States)
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Canadian Institute for Advanced Research, Toronto, ON (Canada); Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL (United States)
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States); Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Univ. of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI (United States)
- Ludwig-Maximilians-Univ., Munchen (Germany); Excellence Cluster Universe, Garching (Germany); Max-Planck-Institut fur extraterrestrische Physik, Garching (Germany)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States); Univ. of Toronto, Toronto, ON (Canada)
- Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN (United States)
- Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States); Univ. of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC (Australia)
- Case Western Reserve Univ., Cleveland, OH (United States)
- Univ. of Colorado, Boulder, CO (United States); Case Western Reserve Univ., Cleveland, OH (United States)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States); School of the Art Institute of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States)
- Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States); Univ. of California, Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Case Western Reserve Univ., Cleveland, OH (United States); California Inst. of Technology (CalTech), Pasadena, CA (United States)
- Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA (United States)
- Stanford Univ., Stanford, CA (United States); Univ. of Chicago, Chicago, IL (United States)
- Univ. of Toronto, Toronto, ON (Canada)
- Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States); Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States); SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Menlo Park, CA (United States); Fermi National Accelerator Lab. (FNAL), Batavia, IL (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), High Energy Physics (HEP); National Science Foundation (NSF); Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation; Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC)
- Contributing Org.:
- SPT
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1431574
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1460984; OSTI ID: 1490702
- Report Number(s):
- FERMILAB-PUB-17-608-AE; arXiv:1712.07541
Journal ID: ISSN 1538-4357; 1644334; TRN: US1802319
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-07CH11359; AC02-06CH11357; AC02-05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- The Astrophysical Journal (Online)
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: The Astrophysical Journal (Online); Journal Volume: 860; Journal Issue: 2; Journal ID: ISSN 1538-4357
- Publisher:
- Institute of Physics (IOP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 79 ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS; cosmic background radiation; cosmological parameters; gravitational lensing; weak
Citation Formats
Simard, G., Omori, Y., Aylor, K., Baxter, E. J., Benson, B. A., Bleem, L. E., Carlstrom, J. E., Chang, C. L., Cho, H-M., Chown, R., Crawford, T. M., Crites, A. T., Haan, T. de, Dobbs, M. A., Everett, W. B., George, E. M., Halverson, N. W., Harrington, N. L., Henning, J. W., Holder, G. P., Hou, Z., Holzapfel, W. L., Hrubes, J. D., Knox, L., Lee, A. T., Leitch, E. M., Luong-Van, D., Manzotti, A., McMahon, J. J., Meyer, S. S., Mocanu, L. M., Mohr, J. J., Natoli, T., Padin, S., Pryke, C., Reichardt, C. L., Ruhl, J. E., Sayre, J. T., Schaffer, K. K., Shirokoff, E., Staniszewski, Z., Stark, A. A., Story, K. T., Vanderlinde, K., Vieira, J. D., Williamson, R., and Wu, W. L. K. Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the Angular Power Spectrum of a Combined 2500 deg2 SPT-SZ and Planck Gravitational Lensing Map. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aac264.
Simard, G., Omori, Y., Aylor, K., Baxter, E. J., Benson, B. A., Bleem, L. E., Carlstrom, J. E., Chang, C. L., Cho, H-M., Chown, R., Crawford, T. M., Crites, A. T., Haan, T. de, Dobbs, M. A., Everett, W. B., George, E. M., Halverson, N. W., Harrington, N. L., Henning, J. W., Holder, G. P., Hou, Z., Holzapfel, W. L., Hrubes, J. D., Knox, L., Lee, A. T., Leitch, E. M., Luong-Van, D., Manzotti, A., McMahon, J. J., Meyer, S. S., Mocanu, L. M., Mohr, J. J., Natoli, T., Padin, S., Pryke, C., Reichardt, C. L., Ruhl, J. E., Sayre, J. T., Schaffer, K. K., Shirokoff, E., Staniszewski, Z., Stark, A. A., Story, K. T., Vanderlinde, K., Vieira, J. D., Williamson, R., & Wu, W. L. K. Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the Angular Power Spectrum of a Combined 2500 deg2 SPT-SZ and Planck Gravitational Lensing Map. United States. https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/aac264
Simard, G., Omori, Y., Aylor, K., Baxter, E. J., Benson, B. A., Bleem, L. E., Carlstrom, J. E., Chang, C. L., Cho, H-M., Chown, R., Crawford, T. M., Crites, A. T., Haan, T. de, Dobbs, M. A., Everett, W. B., George, E. M., Halverson, N. W., Harrington, N. L., Henning, J. W., Holder, G. P., Hou, Z., Holzapfel, W. L., Hrubes, J. D., Knox, L., Lee, A. T., Leitch, E. M., Luong-Van, D., Manzotti, A., McMahon, J. J., Meyer, S. S., Mocanu, L. M., Mohr, J. J., Natoli, T., Padin, S., Pryke, C., Reichardt, C. L., Ruhl, J. E., Sayre, J. T., Schaffer, K. K., Shirokoff, E., Staniszewski, Z., Stark, A. A., Story, K. T., Vanderlinde, K., Vieira, J. D., Williamson, R., and Wu, W. L. K. Wed .
"Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the Angular Power Spectrum of a Combined 2500 deg2 SPT-SZ and Planck Gravitational Lensing Map". United States. https://doi.org/10.3847/1538-4357/aac264. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1431574.
@article{osti_1431574,
title = {Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the Angular Power Spectrum of a Combined 2500 deg2 SPT-SZ and Planck Gravitational Lensing Map},
author = {Simard, G. and Omori, Y. and Aylor, K. and Baxter, E. J. and Benson, B. A. and Bleem, L. E. and Carlstrom, J. E. and Chang, C. L. and Cho, H-M. and Chown, R. and Crawford, T. M. and Crites, A. T. and Haan, T. de and Dobbs, M. A. and Everett, W. B. and George, E. M. and Halverson, N. W. and Harrington, N. L. and Henning, J. W. and Holder, G. P. and Hou, Z. and Holzapfel, W. L. and Hrubes, J. D. and Knox, L. and Lee, A. T. and Leitch, E. M. and Luong-Van, D. and Manzotti, A. and McMahon, J. J. and Meyer, S. S. and Mocanu, L. M. and Mohr, J. J. and Natoli, T. and Padin, S. and Pryke, C. and Reichardt, C. L. and Ruhl, J. E. and Sayre, J. T. and Schaffer, K. K. and Shirokoff, E. and Staniszewski, Z. and Stark, A. A. and Story, K. T. and Vanderlinde, K. and Vieira, J. D. and Williamson, R. and Wu, W. L. K.},
abstractNote = {We report constraints on cosmological parameters from the angular power spectrum of a cosmic microwave background (CMB) gravitational lensing potential map created using temperature data from 2500 deg2 of South Pole Telescope (SPT) data supplemented with data from Planck in the same sky region, with the statistical power in the combined map primarily from the SPT data. We fit the lensing power spectrum to a model including cold dark matter and a cosmological constant (λCDM), and to models with single-parameter extensions to λCDM. We find constraints that are comparable to and consistent with those found using the full-sky Planck CMB lensing data, e.g., σ8ωm0.25 = 0.598 ± 0.024 from the lensing data alone with weak priors placed on other parameters. Combining with primary CMB data, we explore single-parameter extensions to λCDM. We find or ωk = -0.012-0.0230.021 or Mv < 0.70 eV at 95%25 confidence, in good agreement with results including the lensing potential as measured by Planck. We include two parameters that scale the effect of lensing on the CMB: AL, which scales the lensing power spectrum in both the lens reconstruction power and in the smearing of the acoustic peaks, and Aφφ, which scales only the amplitude of the lensing reconstruction power spectrum. We find Aφφ × AL = 1.01 ± 0.08 for the lensing map made from combined SPT and Planck data, indicating that the amount of lensing is in excellent agreement with expectations from the observed CMB angular power spectrum when not including the information from smearing of the acoustic peaks.},
doi = {10.3847/1538-4357/aac264},
journal = {The Astrophysical Journal (Online)},
number = 2,
volume = 860,
place = {United States},
year = {Wed Jun 20 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Wed Jun 20 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
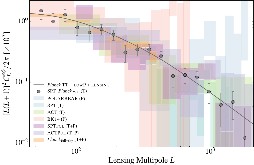 Figure 1: SPT + Planck lensing bandpowers from O17 along with earlier lensing estimates from the SPT-SZ survey (van Engelen et al. 2012) and recent lensing bandpowers obtained from temperature and polarization measurements from SPTPOL (Story et al. 2015). Also plotted are the most recent lensing autospectrum measurements from BICEP2+KECKmore »
Figure 1: SPT + Planck lensing bandpowers from O17 along with earlier lensing estimates from the SPT-SZ survey (van Engelen et al. 2012) and recent lensing bandpowers obtained from temperature and polarization measurements from SPTPOL (Story et al. 2015). Also plotted are the most recent lensing autospectrum measurements from BICEP2+KECKmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Neutrino physics from the cosmic microwave background and large scale structure
journal, March 2015
- Abazajian, K. N.; Arnold, K.; Austermann, J.
- Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 63
Bicep2/ KECK ARRAY VIII: MEASUREMENT OF GRAVITATIONAL LENSING FROM LARGE-SCALE B -MODE POLARIZATION
journal, December 2016
- Ade, P. A. R.; Ahmed, Z.; Aikin, R. W.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 833, Issue 2
Bias to CMB lensing measurements from the bispectrum of large-scale structure
journal, August 2016
- Böhm, Vanessa; Schmittfull, Marcel; Sherwin, Blake D.
- Physical Review D, Vol. 94, Issue 4
Lensed CMB power spectra from all-sky correlation functions
journal, May 2005
- Challinor, Anthony; Lewis, Antony
- Physical Review D, Vol. 71, Issue 10
Fast estimation of polarization power spectra using correlation functions
journal, May 2004
- Chon, Gayoung; Challinor, Anthony; Prunet, Simon
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 350, Issue 3
Bayesian methods for cosmological parameter estimation from cosmic microwave background measurements
journal, June 2001
- Christensen, Nelson; Meyer, Renate; Knox, Lloyd
- Classical and Quantum Gravity, Vol. 18, Issue 14
THE ATACAMA COSMOLOGY TELESCOPE: A MEASUREMENT OF THE COSMIC MICROWAVE BACKGROUND POWER SPECTRUM AT 148 AND 218 GHz FROM THE 2008 SOUTHERN SURVEY
journal, February 2011
- Das, Sudeep; Marriage, Tobias A.; Ade, Peter A. R.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 729, Issue 1
Detection of the Power Spectrum of Cosmic Microwave Background Lensing by the Atacama Cosmology Telescope
journal, July 2011
- Das, Sudeep; Sherwin, Blake D.; Aguirre, Paula
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 107, Issue 2
CMB temperature lensing power reconstruction
journal, February 2011
- Hanson, Duncan; Challinor, Anthony; Efstathiou, George
- Physical Review D, Vol. 83, Issue 4
Measurements of the Temperature and E-mode Polarization of the CMB from 500 Square Degrees of SPTpol Data
journal, January 2018
- Henning, J. W.; Sayre, J. T.; Reichardt, C. L.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 852, Issue 2
KiDS-450: cosmological parameter constraints from tomographic weak gravitational lensing
journal, November 2016
- Hildebrandt, H.; Viola, M.; Heymans, C.
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 465, Issue 2
Mass Reconstruction with Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization
journal, August 2002
- Hu, Wayne; Okamoto, Takemi
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 574, Issue 2
CFHTLenS revisited: assessing concordance with Planck including astrophysical systematics
journal, October 2016
- Joudaki, Shahab; Blake, Chris; Heymans, Catherine
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 465, Issue 2
A Measurement of the Damping tail of the Cosmic Microwave Background Power Spectrum with the South pole Telescope
journal, November 2011
- Keisler, R.; Reichardt, C. L.; Aird, K. A.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 743, Issue 1
Lensing reconstruction with CMB temperature and polarization
journal, June 2003
- Kesden, Michael; Cooray, Asantha; Kamionkowski, Marc
- Physical Review D, Vol. 67, Issue 12
SEVEN-YEAR WILKINSON MICROWAVE ANISOTROPY PROBE ( WMAP ) OBSERVATIONS: COSMOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION
journal, January 2011
- Komatsu, E.; Smith, K. M.; Dunkley, J.
- The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, Vol. 192, Issue 2
Cosmological parameters from CMB and other data: A Monte Carlo approach
journal, November 2002
- Lewis, Antony; Bridle, Sarah
- Physical Review D, Vol. 66, Issue 10
Weak gravitational lensing of the CMB
journal, June 2006
- Lewis, A.; Challinor, A.
- Physics Reports, Vol. 429, Issue 1
Efficient Computation of Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropies in Closed Friedmann‐Robertson‐Walker Models
journal, August 2000
- Lewis, Antony; Challinor, Anthony; Lasenby, Anthony
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 538, Issue 2
Bias-hardened CMB lensing
journal, February 2013
- Namikawa, Toshiya; Hanson, Duncan; Takahashi, Ryuichi
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 431, Issue 1
Cosmic microwave background lensing reconstruction on the full sky
journal, April 2003
- Okamoto, Takemi; Hu, Wayne
- Physical Review D, Vol. 67, Issue 8
A 2500 deg 2 CMB Lensing Map from Combined South Pole Telescope and Planck Data
journal, November 2017
- Omori, Y.; Chown, R.; Simard, G.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 849, Issue 2
Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters
journal, October 2014
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Armitage-Caplan, C.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 571
Planck 2013 results. XVII. Gravitational lensing by large-scale structure
journal, October 2014
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Armitage-Caplan, C.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 571
Planck 2015 results : XIII. Cosmological parameters
journal, September 2016
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
Planck 2015 results : XV. Gravitational lensing
journal, September 2016
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Polarization Lensing Power Spectrum with the POLARBEAR Experiment
journal, July 2014
- Ade, P. A. R.; Akiba, Y.; Anthony, A. E.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 113, Issue 2
Joint analysis of CMB temperature and lensing-reconstruction power spectra
journal, September 2013
- Schmittfull, Marcel M.; Challinor, Anthony; Hanson, Duncan
- Physical Review D, Vol. 88, Issue 6
Evidence for Dark Energy from the Cosmic Microwave Background Alone Using the Atacama Cosmology Telescope Lensing Measurements
journal, July 2011
- Sherwin, Blake D.; Dunkley, Joanna; Das, Sudeep
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 107, Issue 2
Two-season Atacama Cosmology Telescope polarimeter lensing power spectrum
journal, June 2017
- Sherwin, Blake D.; van Engelen, Alexander; Sehgal, Neelima
- Physical Review D, Vol. 95, Issue 12
Cosmological information from lensed CMB power spectra
journal, December 2006
- Smith, Kendrick M.; Hu, Wayne; Kaplinghat, Manoj
- Physical Review D, Vol. 74, Issue 12
Detection of gravitational lensing in the cosmic microwave background
journal, August 2007
- Smith, Kendrick M.; Zahn, Oliver; Doré, Olivier
- Physical Review D, Vol. 76, Issue 4
Gravitational lensing of cosmic microwave background anisotropies and cosmological parameter estimation
journal, February 1999
- Stompor, R.; Efstathiou, G.
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 302, Issue 4
A Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Gravitational Lensing Potential from 100 Square Degrees of Sptpol data
journal, August 2015
- Story, K. T.; Hanson, D.; Ade, P. A. R.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 810, Issue 1
A Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Damping tail from the 2500-Square-Degree Spt-Sz Survey
journal, November 2013
- Story, K. T.; Reichardt, C. L.; Hou, Z.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 779, Issue 1
Fast Cosmic Microwave Background Analyses via Correlation Functions
journal, February 2001
- Szapudi, István; Prunet, Simon; Pogosyan, Dmitry
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 548, Issue 2
Cmb Lensing Power Spectrum Biases from Galaxies and Clusters Using High-Angular Resolution Temperature maps
journal, April 2014
- van Engelen, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sehgal, N.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 786, Issue 1
A Measurement of Gravitational Lensing of the Microwave Background Using South pole Telescope data
journal, August 2012
- van Engelen, A.; Keisler, R.; Zahn, O.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 756, Issue 2
Reconstructing projected matter density power spectrum from cosmic microwave background
journal, May 1999
- Zaldarriaga, Matias; Seljak, Uroš
- Physical Review D, Vol. 59, Issue 12
Planck 2015 results : XI. CMB power spectra, likelihoods, and robustness of parameters
journal, September 2016
- Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.; Ashdown, M.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
Planck 2015 results : XXIII. The thermal Sunyaev-Zeldovich effect-cosmic infrared background correlation
journal, September 2016
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Arnaud, M.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
Two-season Atacama Cosmology Telescope polarimeter lensing power spectrum
text, January 2017
- Sherwin, Blake; Van Engelen, A.; Sehgal, N.
- Apollo - University of Cambridge Repository
Planck 2015 results : X. Diffuse component separation: Foreground maps
journal, September 2016
- Adam, R.; Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
Planck 2015 results : XVI. Isotropy and statistics of the CMB
journal, September 2016
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Akrami, Y.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
Planck 2015 results : XXVI. The Second
journal, September 2016
- Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.; Argüeso, F.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 594
The Atacama Cosmology Telescope: A Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Power Spectrum at 148 and 218 GHz from the 2008 Southern Survey
text, January 2010
- Das, Sudeep; Marriage, Tobias A.; Ade, Peter A. R.
- arXiv
Detection of the Power Spectrum of Cosmic Microwave Background Lensing by the Atacama Cosmology Telescope
text, January 2011
- Das, Sudeep; Sherwin, Blake D.; Aguirre, Paula
- arXiv
Evidence for dark energy from the cosmic microwave background alone using the Atacama Cosmology Telescope lensing measurements
text, January 2011
- Sherwin, Blake D.; Dunkley, Joanna; Das, Sudeep
- arXiv
A Measurement of the Damping Tail of the Cosmic Microwave Background Power Spectrum with the South Pole Telescope
text, January 2011
- Keisler, R.; Reichardt, C. L.; Aird, K. A.
- arXiv
Bias-Hardened CMB Lensing
text, January 2012
- Namikawa, Toshiya; Hanson, Duncan; Takahashi, Ryuichi
- arXiv
Planck 2013 results. XVI. Cosmological parameters
text, January 2013
- Collaboration, Planck; Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.
- arXiv
On the joint analysis of CMB temperature and lensing-reconstruction power spectra
text, January 2013
- Schmittfull, Marcel M.; Challinor, Anthony; Hanson, Duncan
- arXiv
Neutrino Physics from the Cosmic Microwave Background and Large Scale Structure
text, January 2013
- Abazajian, K. N.; Arnold, K.; Austermann, J.
- arXiv
CMB Lensing Power Spectrum Biases from Galaxies and Clusters using High-angular Resolution Temperature Maps
text, January 2013
- van Engelen, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sehgal, N.
- arXiv
Planck 2015 results. XIII. Cosmological parameters
text, January 2015
- Collaboration, Planck; Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.
- arXiv
Planck 2015 results. XV. Gravitational lensing
text, January 2015
- Collaboration, Planck; Ade, P. A. R.; Aghanim, N.
- arXiv
CFHTLenS revisited: assessing concordance with Planck including astrophysical systematics
text, January 2016
- Joudaki, Shahab; Blake, Chris; Heymans, Catherine
- arXiv
A bias to CMB lensing measurements from the bispectrum of large-scale structure
text, January 2016
- Böhm, Vanessa; Schmittfull, Marcel; Sherwin, Blake D.
- arXiv
KiDS-450: Cosmological parameter constraints from tomographic weak gravitational lensing
text, January 2016
- Hildebrandt, H.; Viola, M.; Heymans, C.
- arXiv
Measurements of the Temperature and E-Mode Polarization of the CMB from 500 Square Degrees of SPTpol Data
text, January 2017
- Henning, J. W.; Sayre, J. T.; Reichardt, C. L.
- arXiv
Cosmological parameters from CMB and other data: a Monte-Carlo approach
text, January 2002
- Lewis, Antony; Bridle, Sarah
- arXiv
Fast estimation of polarization power spectra using correlation functions
text, January 2003
- Chon, Gayoung; Challinor, Anthony; Prunet, Simon
- arXiv
Works referencing / citing this record:
CMB lensing reconstruction biases in cross-correlation with large-scale structure probes
journal, October 2019
- Fabbian, Giulio; Lewis, Antony; Beck, Dominic
- Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 2019, Issue 10
Dark Energy Survey Year 1 results: constraints on intrinsic alignments and their colour dependence from galaxy clustering and weak lensing
journal, August 2019
- Samuroff, S.; Blazek, J.; Troxel, M. A.
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 489, Issue 4
Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the 500 deg 2 SPTPOL Lensing Power Spectrum
journal, January 2020
- Bianchini, F.; Wu, W. L. K.; Ade, P. A. R.
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 888, Issue 2
Maps of the Southern Millimeter-wave Sky from Combined 2500 deg 2 SPT-SZ and Planck Temperature Data
journal, November 2018
- Chown, R.; Omori, Y.; Aylor, K.
- The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, Vol. 239, Issue 1
On the effect of non-Gaussian lensing deflections on CMB lensing measurements
text, January 2018
- Böhm, Vanessa; Sherwin, Blake D.; Liu, Jia
- arXiv
Dark Energy Survey Year 1 Results: Constraints on Intrinsic Alignments and their Colour Dependence from Galaxy Clustering and Weak Lensing
text, January 2018
- Samuroff, S.; Blazek, J.; Troxel, M. A.
- arXiv
Constraints on Cosmological Parameters from the 500 deg$^2$ SPTpol Lensing Power Spectrum
text, January 2019
- Bianchini, F.; Wu, W. L. K.; Ade, P. A. R.
- arXiv
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal