Could Machine Learning Break the Convection Parameterization Deadlock?
Abstract
Representing unresolved moist convection in coarse-scale climate models remains one of the main bottlenecks of current climate simulations. Many of the biases present with parameterized convection are strongly reduced when convection is explicitly resolved (i.e., in cloud resolving models at high spatial resolution approximately a kilometer or so). We here present a novel approach to convective parameterization based on machine learning, using an aquaplanet with prescribed sea surface temperatures as a proof of concept. A deep neural network is trained with a superparameterized version of a climate model in which convection is resolved by thousands of embedded 2-D cloud resolving models. The machine learning representation of convection, which we call the Cloud Brain (CBRAIN), can skillfully predict many of the convective heating, moistening, and radiative features of superparameterization that are most important to climate simulation, although an unintended side effect is to reduce some of the superparameterization’s inherent variance. Since as few as three months’ high-frequency global training data prove sufficient to provide this skill, the approach presented here opens up a new possibility for a future class of convection parameterizations in climate models that are built “top-down,” that is, by learning salient features of convection from unusually explicit simulations.
- Authors:
-
- Earth and Environmental Engineering, Columbia University, New York NY USA
- Earth System Science, University of California, Irvine CA USA
- Faculty of Physics, LMU Munich, Munich Germany
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Univ. of California, Irvine, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE; National Science Foundation (NSF)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1452657
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1452658; OSTI ID: 1510994
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012548; SC0012152
- Resource Type:
- Published Article
- Journal Name:
- Geophysical Research Letters
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Geophysical Research Letters Journal Volume: 45 Journal Issue: 11; Journal ID: ISSN 0094-8276
- Publisher:
- American Geophysical Union
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 54 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES; 97 MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTING
Citation Formats
Gentine, P., Pritchard, M., Rasp, S., Reinaudi, G., and Yacalis, G. Could Machine Learning Break the Convection Parameterization Deadlock?. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1029/2018GL078202.
Gentine, P., Pritchard, M., Rasp, S., Reinaudi, G., & Yacalis, G. Could Machine Learning Break the Convection Parameterization Deadlock?. United States. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078202
Gentine, P., Pritchard, M., Rasp, S., Reinaudi, G., and Yacalis, G. Tue .
"Could Machine Learning Break the Convection Parameterization Deadlock?". United States. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078202.
@article{osti_1452657,
title = {Could Machine Learning Break the Convection Parameterization Deadlock?},
author = {Gentine, P. and Pritchard, M. and Rasp, S. and Reinaudi, G. and Yacalis, G.},
abstractNote = {Representing unresolved moist convection in coarse-scale climate models remains one of the main bottlenecks of current climate simulations. Many of the biases present with parameterized convection are strongly reduced when convection is explicitly resolved (i.e., in cloud resolving models at high spatial resolution approximately a kilometer or so). We here present a novel approach to convective parameterization based on machine learning, using an aquaplanet with prescribed sea surface temperatures as a proof of concept. A deep neural network is trained with a superparameterized version of a climate model in which convection is resolved by thousands of embedded 2-D cloud resolving models. The machine learning representation of convection, which we call the Cloud Brain (CBRAIN), can skillfully predict many of the convective heating, moistening, and radiative features of superparameterization that are most important to climate simulation, although an unintended side effect is to reduce some of the superparameterization’s inherent variance. Since as few as three months’ high-frequency global training data prove sufficient to provide this skill, the approach presented here opens up a new possibility for a future class of convection parameterizations in climate models that are built “top-down,” that is, by learning salient features of convection from unusually explicit simulations.},
doi = {10.1029/2018GL078202},
journal = {Geophysical Research Letters},
number = 11,
volume = 45,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Jun 12 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Tue Jun 12 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078202
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
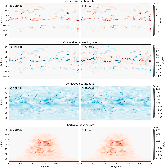 Figure 1: Latitude-longitude snapshot of neural network predictions and the corresponding SP-CAM truth at model level 20 (roughly 700 hPa) for one time step in the validation set.
Figure 1: Latitude-longitude snapshot of neural network predictions and the corresponding SP-CAM truth at model level 20 (roughly 700 hPa) for one time step in the validation set.
Works referenced in this record:
Sensitivity of Coupled Tropical Pacific Model Biases to Convective Parameterization in CESM1
journal, January 2018
- Woelfle, M. D.; Yu, S.; Bretherton, C. S.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 10, Issue 1
The Net is many people's only chance of access
journal, May 2001
- Khan, F. A.
- Nature, Vol. 411, Issue 6837
What favors convective aggregation and why?: WHAT FAVORS CONVECTIVE AGGREGATION
journal, July 2015
- Muller, Caroline; Bony, Sandrine
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 42, Issue 13
Stochastic Behavior of Tropical Convection in Observations and a Multicloud Model
journal, November 2013
- Peters, Karsten; Jakob, Christian; Davies, Laura
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 70, Issue 11
Structure of the Madden–Julian Oscillation in the Superparameterized CAM
journal, November 2009
- Benedict, James J.; Randall, David A.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 66, Issue 11
Deep learning
journal, May 2015
- LeCun, Yann; Bengio, Yoshua; Hinton, Geoffrey
- Nature, Vol. 521, Issue 7553
Forcings and feedbacks on convection in the 2010 Pakistan flood: Modeling extreme precipitation with interactive large-scale ascent: FORCINGS AND FEEDBACKS IN PAKISTAN FLOOD
journal, July 2016
- Nie, Ji; Shaevitz, Daniel A.; Sobel, Adam H.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 8, Issue 3
Representation of daytime moist convection over the semi-arid Tropics by parametrizations used in climate and meteorological models
journal, March 2015
- Couvreux, F.; Roehrig, R.; Rio, C.
- Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, Vol. 141, Issue 691
Increases in tropical rainfall driven by changes in frequency of organized deep convection
journal, March 2015
- Tan, Jackson; Jakob, Christian; Rossow, William B.
- Nature, Vol. 519, Issue 7544
Comparison of PERSIANN and V7 TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) products with rain gauge data over Iran
journal, September 2013
- Moazami, Saber; Golian, Saeed; Kavianpour, M. Reza
- International Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol. 34, Issue 22
Role of Vertical Structure of Convective Heating in MJO Simulation in NCAR CAM5.3
journal, September 2017
- Cao, Guyu; Zhang, Guang J.
- Journal of Climate, Vol. 30, Issue 18
A strategy for representing the effects of convective momentum transport in multiscale models: Evaluation using a new superparameterized version of the Weather Research and Forecast model (SP-WRF): CMT IN SP-WRF
journal, June 2015
- Tulich, S. N.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 7, Issue 2
Precipitation distributions for explicit versus parametrized convection in a large-domain high-resolution tropical case study
journal, March 2012
- Holloway, C. E.; Woolnough, S. J.; Lister, G. M. S.
- Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, Vol. 138, Issue 668
Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search
journal, January 2016
- Silver, David; Huang, Aja; Maddison, Chris J.
- Nature, Vol. 529, Issue 7587
What Are Climate Models Missing?
journal, May 2013
- Stevens, B.; Bony, S.
- Science, Vol. 340, Issue 6136
Water, Energy, and Carbon with Artificial Neural Networks (WECANN): a statistically based estimate of global surface turbulent fluxes and gross primary productivity using solar-induced fluorescence
journal, January 2017
- Alemohammad, Seyed Hamed; Fang, Bin; Konings, Alexandra G.
- Biogeosciences, Vol. 14, Issue 18
Ensemble superparameterization versus stochastic parameterization: A comparison of model uncertainty representation in tropical weather prediction
journal, May 2017
- Subramanian, Aneesh C.; Palmer, Tim N.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 9, Issue 2
Restricting 32-128 km horizontal scales hardly affects the MJO in the Superparameterized Community Atmosphere Model v.3.0 but the number of cloud-resolving grid columns constrains vertical mixing
journal, August 2014
- Pritchard, Michael S.; Bretherton, Christopher S.; DeMott, Charlotte A.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 6, Issue 3
Orogenic Propagating Precipitation Systems over the United States in a Global Climate Model with Embedded Explicit Convection
journal, August 2011
- Pritchard, Michael S.; Moncrieff, Mitchell W.; Somerville, Richard C. J.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 68, Issue 8
Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E and ASCAT microwave observation synergy. Part 1: Satellite data analysis
journal, February 2016
- Kolassa, J.; Gentine, P.; Prigent, C.
- Remote Sensing of Environment, Vol. 173
Toward an estimation of global land surface heat fluxes from multisatellite observations
journal, January 2009
- Jiménez, Carlos; Prigent, Catherine; Aires, Filipe
- Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 114, Issue D6
A stochastic multicloud model for tropical convection
journal, January 2010
- Biello, Joseph; Khouider, Boualem; Majda, Andrew J.
- Communications in Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Using aquaplanets to understand the robust responses of comprehensive climate models to forcing
journal, May 2014
- Medeiros, Brian; Stevens, Bjorn; Bony, Sandrine
- Climate Dynamics, Vol. 44, Issue 7-8
Lung cancer cell identification based on artificial neural network ensembles
journal, January 2002
- Zhou, Zhi-Hua; Jiang, Yuan; Yang, Yu-Bin
- Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, Vol. 24, Issue 1
Mesoscale convective systems
journal, January 2004
- Houze, Robert A.
- Reviews of Geophysics, Vol. 42, Issue 4
Simulations of the Atmospheric General Circulation Using a Cloud-Resolving Model as a Superparameterization of Physical Processes
journal, July 2005
- Khairoutdinov, Marat; Randall, David; DeMott, Charlotte
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 62, Issue 7
Deep Convection Triggering by Boundary Layer Thermals. Part II: Stochastic Triggering Parameterization for the LMDZ GCM
journal, February 2014
- Rochetin, Nicolas; Grandpeix, Jean-Yves; Rio, Catherine
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 71, Issue 2
Intercomparison of methods of coupling between convection and large-scale circulation: 1. Comparison over uniform surface conditions: CONVECTION AND LARGE-SCALE DYNAMICS
journal, October 2015
- Daleu, C. L.; Plant, R. S.; Woolnough, S. J.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Climate goals and computing the future of clouds
journal, January 2017
- Schneider, Tapio; Teixeira, João; Bretherton, Christopher S.
- Nature Climate Change, Vol. 7, Issue 1
Effects of explicit convection on global land-atmosphere coupling in the superparameterized CAM: EXPLICIT CONVECTION ON GLOBAL LAND-ATMOSPHERE COUPLING
journal, August 2016
- Sun, Jian; Pritchard, Michael S.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 8, Issue 3
Development of a Quasi-3D Multiscale Modeling Framework: Motivation, Basic Algorithm and Preliminary results: DEVELOPMENT OF A Q3D MMF
journal, April 2010
- Jung, Joon-Hee; Arakawa, Akio
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 2, Issue 4
Clouds, circulation and climate sensitivity
journal, March 2015
- Bony, Sandrine; Stevens, Bjorn; Frierson, Dargan M. W.
- Nature Geoscience, Vol. 8, Issue 4
Soil moisture retrieval from AMSR-E and ASCAT microwave observation synergy. Part 2: Product evaluation
journal, June 2017
- Kolassa, J.; Gentine, P.; Prigent, C.
- Remote Sensing of Environment, Vol. 195
Deep Neural Networks for Acoustic Modeling in Speech Recognition: The Shared Views of Four Research Groups
journal, November 2012
- Hinton, Geoffrey; Deng, Li; Yu, Dong
- IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, Vol. 29, Issue 6
Effects of explicit atmospheric convection at high CO2
journal, July 2014
- Arnold, N. P.; Branson, M.; Burt, M. A.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 111, Issue 30
Impact of soil moisture on the development of a Sahelian mesoscale convective system: a case-study from the AMMA Special Observing Period
journal, August 2009
- Taylor, Christopher M.; Harris, Phil P.; Parker, Douglas J.
- Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, Vol. 136, Issue S1
Cloud Resolving Modeling of the ARM Summer 1997 IOP: Model Formulation, Results, Uncertainties, and Sensitivities
journal, February 2003
- Khairoutdinov, Marat F.; Randall, David A.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 60, Issue 4
Toward unification of the multiscale modeling of the atmosphere
journal, January 2011
- Arakawa, A.; Jung, J. -H.; Wu, C. -M.
- Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, Vol. 11, Issue 8
Triggering Deep Convection with a Probabilistic Plume Model
journal, November 2014
- D’Andrea, Fabio; Gentine, Pierre; Betts, Alan K.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 71, Issue 11
Large-eddy simulation of maritime deep tropical convection
journal, December 2009
- Khairoutdinov, Marat F.; Krueger, Steve K.; Moeng, Chin-Hoh
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 2
High-Resolution Simulation of Shallow-to-Deep Convection Transition over Land
journal, December 2006
- Khairoutdinov, Marat; Randall, David
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 63, Issue 12
Representing Convective Organization in Prediction Models by a Hybrid Strategy
journal, December 2006
- Moncrieff, Mitchell W.; Liu, Changhai
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 63, Issue 12
The Effects of Explicit versus Parameterized Convection on the MJO in a Large-Domain High-Resolution Tropical Case Study. Part II: Processes Leading to Differences in MJO Development*
journal, July 2015
- Holloway, Christopher E.; Woolnough, Steven J.; Lister, Grenville M. S.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 72, Issue 7
An expert system for detection of breast cancer based on association rules and neural network
journal, March 2009
- Karabatak, Murat; Ince, M. Cevdet
- Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 36, Issue 2
Convective self-aggregation, cold pools, and domain size: AGGREGATION, COLD POOLS, AND DOMAIN SIZE
journal, March 2013
- Jeevanjee, Nadir; Romps, David M.
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 40, Issue 5
Impacts of cloud superparameterization on projected daily rainfall intensity climate changes in multiple versions of the Community Earth System Model
journal, October 2016
- Kooperman, Gabriel J.; Pritchard, Michael S.; Burt, Melissa A.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 8, Issue 4
A Simple Multicloud Parameterization for Convectively Coupled Tropical Waves. Part I: Linear Analysis
journal, April 2006
- Khouider, Boualem; Majda, Andrew J.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 63, Issue 4
Physical mechanisms controlling self-aggregation of convection in idealized numerical modeling simulations: SELF-AGGREGATION MECHANISMS
journal, February 2014
- Wing, Allison A.; Emanuel, Kerry A.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 6, Issue 1
MJO Intensification with Warming in the Superparameterized CESM
journal, April 2015
- Arnold, Nathan P.; Branson, Mark; Kuang, Zhiming
- Journal of Climate, Vol. 28, Issue 7
Assessing the diurnal cycle of precipitation in a multi-scale climate model
journal, October 2009
- Pritchard, Michael S.; Somerville, Richard C. J.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 2
Nonhydrostatic icosahedral atmospheric model (NICAM) for global cloud resolving simulations
journal, March 2008
- Satoh, M.; Matsuno, T.; Tomita, H.
- Journal of Computational Physics, Vol. 227, Issue 7
Evaluation of the PERSIANN-CDR Daily Rainfall Estimates in Capturing the Behavior of Extreme Precipitation Events over China
journal, June 2015
- Miao, Chiyuan; Ashouri, Hamed; Hsu, Kuo-Lin
- Journal of Hydrometeorology, Vol. 16, Issue 3
Beyond deadlock: BEYOND DEADLOCK
journal, November 2013
- Randall, David A.
- Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 40, Issue 22
Context-Dependent Pre-Trained Deep Neural Networks for Large-Vocabulary Speech Recognition
journal, January 2012
- Dahl, G. E.
- IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, Vol. 20, Issue 1
A parameterization of cloud microphysics for long-term cloud-resolving modeling of tropical convection
journal, August 1999
- Grabowski, Wojciech W.
- Atmospheric Research, Vol. 52, Issue 1-2
Spread in model climate sensitivity traced to atmospheric convective mixing
journal, January 2014
- Sherwood, Steven C.; Bony, Sandrine; Dufresne, Jean-Louis
- Nature, Vol. 505, Issue 7481
Modelling the diurnal cycle of deep precipitating convection over land with cloud-resolving models and single-column models
journal, October 2004
- Guichard, F.; Petch, J. C.; Redelsperger, J. -L.
- Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, Vol. 130, Issue 604
Global Effects of Superparameterization on Hydrothermal Land‐Atmosphere Coupling on Multiple Timescales
journal, February 2018
- Qin, Hongchen; Pritchard, Michael S.; Kooperman, Gabriel J.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 10, Issue 2
Coarse-grained stochastic models for tropical convection and climate
journal, September 2003
- Khouider, B.; Majda, A. J.; Katsoulakis, M. A.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 100, Issue 21
Soil moisture retrieval from multi-instrument observations: Information content analysis and retrieval methodology: SOIL MOISTURE RETRIEVAL METHODOLOGY
journal, May 2013
- Kolassa, J.; Aires, F.; Polcher, J.
- Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, Vol. 118, Issue 10
Parameterizing Convective Organization to Escape the Entrainment Dilemma: PARAMETERIZING CONVECTIVE ORGANIZATION
journal, February 2011
- Mapes, Brian; Neale, Richard
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 3, Issue 2
Intercomparison of methods of coupling between convection and large‐scale circulation: 2. Comparison over nonuniform surface conditions
journal, January 2016
- Daleu, C. L.; Plant, R. S.; Woolnough, S. J.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Physical mechanisms controlling the initiation of convective self-aggregation in a General Circulation Model: MECHANISMS OF INITIATION OF AGGREGATION
journal, December 2015
- Coppin, David; Bony, Sandrine
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Convective self-aggregation feedbacks in near-global cloud-resolving simulations of an aquaplanet: AGGREGATION FEEDBACKS IN NEAR-GLOBAL CRM
journal, November 2015
- Bretherton, Christopher S.; Khairoutdinov, Marat F.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Coupling Cloud Processes with the Large-Scale Dynamics Using the Cloud-Resolving Convection Parameterization (CRCP)
journal, May 2001
- Grabowski, Wojciech W.
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 58, Issue 9
Robust effects of cloud superparameterization on simulated daily rainfall intensity statistics across multiple versions of the C ommunity E arth S ystem M odel
journal, February 2016
- Kooperman, Gabriel J.; Pritchard, Michael S.; Burt, Melissa A.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 8, Issue 1
Deep Convection Triggering by Boundary Layer Thermals. Part I: LES Analysis and Stochastic Triggering Formulation
journal, February 2014
- Rochetin, Nicolas; Couvreux, Fleur; Grandpeix, Jean-Yves
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 71, Issue 2
Moist Static Energy Budget of MJO-like Disturbances in the Atmosphere of a Zonally Symmetric Aquaplanet
journal, April 2012
- Andersen, Joseph Allan; Kuang, Zhiming
- Journal of Climate, Vol. 25, Issue 8
Global-scale convective aggregation: Implications for the Madden-Julian Oscillation: GLOBAL-SCALE CONVECTIVE AGGREGATION
journal, October 2015
- Arnold, Nathan P.; Randall, David A.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 7, Issue 4
Simulation, Modeling, and Dynamically Based Parameterization of Organized Tropical Convection for Global Climate Models
journal, May 2017
- Moncrieff, Mitchell W.; Liu, Changhai; Bogenschutz, Peter
- Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, Vol. 74, Issue 5
A Deep Neural Network Modeling Framework to Reduce Bias in Satellite Precipitation Products
journal, March 2016
- Tao, Yumeng; Gao, Xiaogang; Hsu, Kuolin
- Journal of Hydrometeorology, Vol. 17, Issue 3
Deep learning in neural networks: An overview
journal, January 2015
- Schmidhuber, Jürgen
- Neural Networks, Vol. 61
Coupled radiative convective equilibrium simulations with explicit and parameterized convection: COUPLED RCE SIMULATIONS
journal, September 2016
- Hohenegger, Cathy; Stevens, Bjorn
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 8, Issue 3
Toward low-cloud-permitting cloud superparameterization with explicit boundary layer turbulence: LOW-CLOUD ULTRAPARAMETERIZATION
journal, July 2017
- Parishani, Hossein; Pritchard, Michael S.; Bretherton, Christopher S.
- Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, Vol. 9, Issue 3
Global patterns of land-atmosphere fluxes of carbon dioxide, latent heat, and sensible heat derived from eddy covariance, satellite, and meteorological observations
journal, January 2011
- Jung, Martin; Reichstein, Markus; Margolis, Hank A.
- Journal of Geophysical Research, Vol. 116
Merging active and passive microwave observations in soil moisture data assimilation
journal, March 2017
- Kolassa, J.; Reichle, R. H.; Draper, C. S.
- Remote Sensing of Environment, Vol. 191
Multiscale Convective Organization and the YOTC Virtual Global Field Campaign
journal, August 2012
- Moncrieff, Mitchell W.; Waliser, Duane E.; Miller, Martin J.
- Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, Vol. 93, Issue 8
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal