Enhancement of Quasistationary Shocks and Heating via Temporal Staging in a Magnetized Laser-Plasma Jet
Abstract
Here, we investigate the formation of a laser-produced magnetized jet under conditions of a varying mass ejection rate and a varying divergence of the ejected plasma flow. This is done by irradiating a solid target placed in a 20 T magnetic field with, first, a collinear precursor laser pulse (1012 W/cm2) and, then, a main pulse (1013 W/cm2) arriving 9–19 ns later. Varying the time delay between the two pulses is found to control the divergence of the expanding plasma, which is shown to increase the strength of and heating in the conical shock that is responsible for jet collimation. These results show that plasma collimation due to shocks against a strong magnetic field can lead to stable, astrophysically relevant jets that are sustained over time scales 100 times the laser pulse duration (i.e., >70 ns), even in the case of strong variability at the source.
- Authors:
-
more »
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France); Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Sorbonne Univ., Paris (France); PSL Research Univ., Paris (France)
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France); Institute of Applied Physics, Nizhny Novgorod (Russia)
- CNRS-UGA-UPS-INSA, Toulouse (France)
- Heinrich-Heine-Univ. Dusseldorf, Dusseldorf (Germany)
- Queen's Univ. Belfast, Belfast (United Kingdom)
- Institute of Applied Physics, Nizhny Novgorod (Russia)
- Joint Institute for High Temperatures, Moscow (Russia); National Research Nuclear Univ. "MEPhl", Moscow (Russia)
- GSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schweionenforschung GmbH, Darmstadt (Germany)
- INRS-EMT, Varennes, QC (Canada)
- Sorbonne Univ.-UPMC Univ. Paris 06, Ecole Polytechnique, Paris (France)
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France); CEA, DAM, DIF, Arpajon (France)
- Dept. de Fisica de a Univ. de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Paris (France)
- Joint Institute for High Temperatures, Moscow (Russia); M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State Univ., Moscow (Russia)
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1438720
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1414611
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-733609
Journal ID: ISSN 0031-9007; PRLTAO; TRN: US1900501
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Physical Review Letters
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 119; Journal Issue: 25; Journal ID: ISSN 0031-9007
- Publisher:
- American Physical Society (APS)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 70 PLASMA PHYSICS AND FUSION
Citation Formats
Higginson, D. P., Khiar, B., Revet, G., Beard, J., Blecher, M., Borghesi, M., Burdonov, K., Chen, S. N., Filippov, E., Khaghani, D., Naughton, K., Pepin, H., Pikuz, S., Portugall, O., Riconda, C., Riquier, R., Rodriguez, R., Ryazantsev, S. N., Skobelev, I. Yu., Soloviev, A., Starodubtsev, M., Vinci, T., Willi, O., Ciardi, A., and Fuchs, J. Enhancement of Quasistationary Shocks and Heating via Temporal Staging in a Magnetized Laser-Plasma Jet. United States: N. p., 2017.
Web. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.255002.
Higginson, D. P., Khiar, B., Revet, G., Beard, J., Blecher, M., Borghesi, M., Burdonov, K., Chen, S. N., Filippov, E., Khaghani, D., Naughton, K., Pepin, H., Pikuz, S., Portugall, O., Riconda, C., Riquier, R., Rodriguez, R., Ryazantsev, S. N., Skobelev, I. Yu., Soloviev, A., Starodubtsev, M., Vinci, T., Willi, O., Ciardi, A., & Fuchs, J. Enhancement of Quasistationary Shocks and Heating via Temporal Staging in a Magnetized Laser-Plasma Jet. United States. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.255002
Higginson, D. P., Khiar, B., Revet, G., Beard, J., Blecher, M., Borghesi, M., Burdonov, K., Chen, S. N., Filippov, E., Khaghani, D., Naughton, K., Pepin, H., Pikuz, S., Portugall, O., Riconda, C., Riquier, R., Rodriguez, R., Ryazantsev, S. N., Skobelev, I. Yu., Soloviev, A., Starodubtsev, M., Vinci, T., Willi, O., Ciardi, A., and Fuchs, J. Fri .
"Enhancement of Quasistationary Shocks and Heating via Temporal Staging in a Magnetized Laser-Plasma Jet". United States. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.255002. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1438720.
@article{osti_1438720,
title = {Enhancement of Quasistationary Shocks and Heating via Temporal Staging in a Magnetized Laser-Plasma Jet},
author = {Higginson, D. P. and Khiar, B. and Revet, G. and Beard, J. and Blecher, M. and Borghesi, M. and Burdonov, K. and Chen, S. N. and Filippov, E. and Khaghani, D. and Naughton, K. and Pepin, H. and Pikuz, S. and Portugall, O. and Riconda, C. and Riquier, R. and Rodriguez, R. and Ryazantsev, S. N. and Skobelev, I. Yu. and Soloviev, A. and Starodubtsev, M. and Vinci, T. and Willi, O. and Ciardi, A. and Fuchs, J.},
abstractNote = {Here, we investigate the formation of a laser-produced magnetized jet under conditions of a varying mass ejection rate and a varying divergence of the ejected plasma flow. This is done by irradiating a solid target placed in a 20 T magnetic field with, first, a collinear precursor laser pulse (1012 W/cm2) and, then, a main pulse (1013 W/cm2) arriving 9–19 ns later. Varying the time delay between the two pulses is found to control the divergence of the expanding plasma, which is shown to increase the strength of and heating in the conical shock that is responsible for jet collimation. These results show that plasma collimation due to shocks against a strong magnetic field can lead to stable, astrophysically relevant jets that are sustained over time scales 100 times the laser pulse duration (i.e., >70 ns), even in the case of strong variability at the source.},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.255002},
journal = {Physical Review Letters},
number = 25,
volume = 119,
place = {United States},
year = {Fri Dec 22 00:00:00 EST 2017},
month = {Fri Dec 22 00:00:00 EST 2017}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
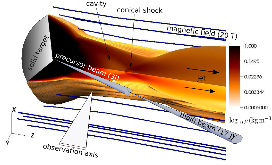 Figure 1: Schematic of the experimental setup and 3D MHD simulations of the overall plasma dynamics. The volume rendering shows the simulated mass density at 22 ns, for the case of a single 17 J pulse, with 1/4 of the volume removed to show the internal flow structure. Two co-linearmore »
Figure 1: Schematic of the experimental setup and 3D MHD simulations of the overall plasma dynamics. The volume rendering shows the simulated mass density at 22 ns, for the case of a single 17 J pulse, with 1/4 of the volume removed to show the internal flow structure. Two co-linearmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Transformation of Observed Radiances into Radial Distribution of the Emission of a Plasma*
journal, January 1961
- Bockasten, Kjell
- Journal of the Optical Society of America, Vol. 51, Issue 9
Modeling Extragalactic jets
journal, September 1998
- Ferrari, Attilio
- Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Vol. 36, Issue 1
X‐Rays from the Vicinity of the Protostar L1551 IRS 5: Reflection or Fast Shocks?
journal, February 2003
- Bally, John; Feigelson, Eric; Reipurth, Bo
- The Astrophysical Journal, Vol. 584, Issue 2
Pulsed-power-driven cylindrical liner implosions of laser preheated fuel magnetized with an axial field
journal, May 2010
- Slutz, S. A.; Herrmann, M. C.; Vesey, R. A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 17, Issue 5
Fusion Yield Enhancement in Magnetized Laser-Driven Implosions
journal, July 2011
- Chang, P. Y.; Fiksel, G.; Hohenberger, M.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 107, Issue 3
Random Phasing of High-Power Lasers for Uniform Target Acceleration and Plasma-Instability Suppression
journal, September 1984
- Kato, Y.; Mima, K.; Miyanaga, N.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 53, Issue 11
Magnetic Fields in Astrophysical Jets: From Launch to Termination
journal, June 2012
- Pudritz, Ralph E.; Hardcastle, Martin J.; Gabuzda, Denise C.
- Space Science Reviews, Vol. 169, Issue 1-4
Critical Magnetic Field Strength for Suppression of the Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability in Plasmas
journal, November 2013
- Sano, Takayoshi; Inoue, Tsuyoshi; Nishihara, Katsunobu
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 111, Issue 20
Laboratory unraveling of matter accretion in young stars
journal, November 2017
- Revet, Guilhem; Chen, Sophia N.; Bonito, Rosaria
- Science Advances, Vol. 3, Issue 11
Radiative Jet Experiments of Astrophysical Interest Using Intense Lasers
journal, September 1999
- Farley, D. R.; Estabrook, K. G.; Glendinning, S. G.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 83, Issue 10
Plasma jets produced in a single laser beam interaction with a planar target
journal, June 2006
- Nicolaï, Ph.; Tikhonchuk, V. T.; Kasperczuk, A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 13, Issue 6
Quenching of the Nonlocal Electron Heat Transport by Large External Magnetic Fields in a Laser-Produced Plasma Measured with Imaging Thomson Scattering
journal, March 2007
- Froula, D.; Ross, J.; Pollock, B.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 98, Issue 13
Fluid and kinetic simulation of inertial confinement fusion plasmas
journal, July 2005
- Atzeni, S.; Schiavi, A.; Califano, F.
- Computer Physics Communications, Vol. 169, Issue 1-3
Experimental results from magnetized-jet experiments executed at the Jupiter Laser Facility
journal, December 2015
- Manuel, M. J. -E.; Kuranz, C. C.; Rasmus, A. M.
- High Energy Density Physics, Vol. 17
Discovery of X-ray emission from the protostellar jet L1551 IRS5 (HH 154)
journal, April 2002
- Favata, F.; Fridlund, C. V. M.; Micela, G.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 386, Issue 1
The mitigating effect of magnetic fields on Rayleigh-Taylor unstable inertial confinement fusion plasmas
journal, May 2013
- Srinivasan, Bhuvana; Tang, Xian-Zhu
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 5
Astrophysics of Magnetically Collimated Jets Generated from Laser-Produced Plasmas
journal, January 2013
- Ciardi, A.; Vinci, T.; Fuchs, J.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 110, Issue 2
Detailed characterization of laser-produced astrophysically-relevant jets formed via a poloidal magnetic nozzle
journal, June 2017
- Higginson, D. P.; Revet, G.; Khiar, B.
- High Energy Density Physics, Vol. 23
Experimental Demonstration of an Inertial Collimation Mechanism in Nested Outflows
journal, April 2014
- Yurchak, R.; Ravasio, A.; Pelka, A.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 112, Issue 15
Laboratory formation of a scaled protostellar jet by coaligned poloidal magnetic field
journal, October 2014
- Albertazzi, B.; Ciardi, A.; Nakatsutsumi, M.
- Science, Vol. 346, Issue 6207
Stable dense plasma jets produced at laser power densities around 1014W∕cm2
journal, June 2006
- Kasperczuk, A.; Pisarczyk, T.; Borodziuk, S.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 13, Issue 6
Use of external magnetic fields in hohlraum plasmas to improve laser-coupling
journal, January 2015
- Montgomery, D. S.; Albright, B. J.; Barnak, D. H.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 22, Issue 1
High-Gain Magnetized Inertial Fusion
journal, January 2012
- Slutz, Stephen A.; Vesey, Roger A.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 108, Issue 2
X-ray generation mechanisms in three-dimensional simulations of wire array Z-pinches
journal, November 2004
- Chittenden, J. P.; Lebedev, S. V.; Jennings, C. A.
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 46, Issue 12B
Diagnostics of laser-produced plasmas based on the analysis of intensity ratios of He-like ions X-ray emission
journal, December 2016
- Ryazantsev, S. N.; Skobelev, I. Yu.; Faenov, A. Ya.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 23, Issue 12
Herbig-Haro Flows: Probes of Early Stellar Evolution
journal, September 2001
- Reipurth, Bo; Bally, John
- Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Vol. 39, Issue 1
The evolution of magnetic tower jets in the laboratory
journal, May 2007
- Ciardi, A.; Lebedev, S. V.; Frank, A.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 14, Issue 5
Formation of X-ray emitting stationary shocks in magnetized protostellar jets
journal, December 2016
- Ustamujic, S.; Orlando, S.; Bonito, R.
- Astronomy & Astrophysics, Vol. 596
Two-dimensional simulations of thermonuclear burn in ignition-scale inertial confinement fusion targets under compressed axial magnetic fields
journal, July 2013
- Perkins, L. J.; Logan, B. G.; Zimmerman, G. B.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 20, Issue 7
Production of large volume, strongly magnetized laser-produced plasmas by use of pulsed external magnetic fields
journal, April 2013
- Albertazzi, B.; Béard, J.; Ciardi, A.
- Review of Scientific Instruments, Vol. 84, Issue 4
Works referencing / citing this record:
The influence of the Hall term on the development of magnetized laser-produced plasma jets
journal, April 2018
- Hamlin, N. D.; Seyler, C. E.; Khiar, B.
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 25, Issue 4
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal