Enhancing Dissociative Adsorption of Water on Cu(111) via Chemisorbed Oxygen
Abstract
We have used X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to study the dehydrogenation of H2O molecules on the clean and oxygenated Cu(111) surfaces. The clean surface does not show reactivity toward H2O dehydrogenation. By contrast, H2O molecules on the oxygenated Cu(111) dissociate into OH species by reacting with chemisorbed oxygen until the complete consumption of the chemisorbed oxygen at which the surface loses its reactivity toward H2O dehydrogenation. Increasing the temperature to 200 °C and above decreases molecularly adsorbed H2O for dehydrogenation, thereby resulting in less loss of chemisorbed O. In conjunction with density-functional theory calculations, a three-step reaction pathway is proposed to account for the chemisorbed O assisted dehydrogenation of H2O molecules and the net loss of surface oxygen. Finally, these results provide insight into understanding the elemental steps of the dehydrogenation of H2O molecules and the controllable conditions for tuning H2O dissociation on metal surfaces.
- Authors:
-
- State Univ. of New York, Binghamton, NY (United States). Dept. of Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science and Engineering Program
- State Univ. of New York, Binghamton, NY (United States). Dept. of Physics, Applied Physics and Astronomy & Materials Science and Engineering Program
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States). Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1438301
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-205656-2018-JAAM
Journal ID: ISSN 1932-7447; TRN: US1900415
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704; CMMI- 1056611; CBET-1264940
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Journal of Physical Chemistry. C
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 121; Journal Issue: 22; Journal ID: ISSN 1932-7447
- Publisher:
- American Chemical Society
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 36 MATERIALS SCIENCE; 37 INORGANIC, ORGANIC, PHYSICAL, AND ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY
Citation Formats
Liu, Qianqian, Li, Jonathan, Tong, Xiao, and Zhou, Guangwen. Enhancing Dissociative Adsorption of Water on Cu(111) via Chemisorbed Oxygen. United States: N. p., 2017.
Web. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b12897.
Liu, Qianqian, Li, Jonathan, Tong, Xiao, & Zhou, Guangwen. Enhancing Dissociative Adsorption of Water on Cu(111) via Chemisorbed Oxygen. United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b12897
Liu, Qianqian, Li, Jonathan, Tong, Xiao, and Zhou, Guangwen. Tue .
"Enhancing Dissociative Adsorption of Water on Cu(111) via Chemisorbed Oxygen". United States. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b12897. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1438301.
@article{osti_1438301,
title = {Enhancing Dissociative Adsorption of Water on Cu(111) via Chemisorbed Oxygen},
author = {Liu, Qianqian and Li, Jonathan and Tong, Xiao and Zhou, Guangwen},
abstractNote = {We have used X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to study the dehydrogenation of H2O molecules on the clean and oxygenated Cu(111) surfaces. The clean surface does not show reactivity toward H2O dehydrogenation. By contrast, H2O molecules on the oxygenated Cu(111) dissociate into OH species by reacting with chemisorbed oxygen until the complete consumption of the chemisorbed oxygen at which the surface loses its reactivity toward H2O dehydrogenation. Increasing the temperature to 200 °C and above decreases molecularly adsorbed H2O for dehydrogenation, thereby resulting in less loss of chemisorbed O. In conjunction with density-functional theory calculations, a three-step reaction pathway is proposed to account for the chemisorbed O assisted dehydrogenation of H2O molecules and the net loss of surface oxygen. Finally, these results provide insight into understanding the elemental steps of the dehydrogenation of H2O molecules and the controllable conditions for tuning H2O dissociation on metal surfaces.},
doi = {10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b12897},
journal = {Journal of Physical Chemistry. C},
number = 22,
volume = 121,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue May 16 00:00:00 EDT 2017},
month = {Tue May 16 00:00:00 EDT 2017}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
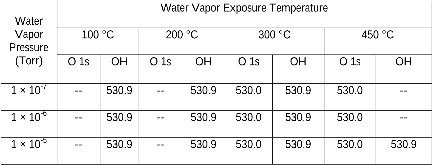 Table 1: Binding energies (eV) of O (1s) and OH spectra at the steady state from the H2O exposure of the oxygenated Cu(111)
Table 1: Binding energies (eV) of O (1s) and OH spectra at the steady state from the H2O exposure of the oxygenated Cu(111)
Works referenced in this record:
Methanol adsorption on Cu(110) and the angular distribution of the reaction products
journal, April 2007
- Demirci, E.; Stettner, J.; Kratzer, M.
- The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 126, Issue 16
Oxygen-assisted cleavage of OH, NH, and CH bonds on transition metal surfaces: bond-order-conservation-Morse-potential analysis
journal, January 1992
- Shustorovich, Evgeny; Bell, Alexis T.
- Surface Science, Vol. 268, Issue 1-3
Reaction pathways in the oxydehydrogenation of ammonia at Cu(110) surfaces
journal, March 1993
- Afsin, B.; Davies, P. R.; Pashusky, A.
- Surface Science, Vol. 284, Issue 1-2
A new approach to the mechanism of heterogeneously catalysed reactions: the oxydehydrogenation of ammonia at a Cu(111) surface
journal, January 1992
- Boronin, A.; Pashusky, A.; Roberts, M. W.
- Catalysis Letters, Vol. 16, Issue 3
A spectroscopic study of the adsorption and reactions of methanol, formaldehyde and methyl formate on clean and oxygenated Cu(110) surfaces
journal, June 1985
- Sexton, B. A.; Hughes, A. E.; Avery, N. R.
- Surface Science, Vol. 155, Issue 1
A First-Principles Analysis for Sulfur Tolerance of CeO 2 in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
journal, July 2007
- Chen, Hsin-Tsung; Choi, YongMan; Liu, Meilin
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 111, Issue 29
The promotion of surface-catalysed reactions by gaseous additives. The role of a surface oxygen transient
journal, January 1987
- Au, Chak-Tong; Roberts, M. Wyn
- Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions 1: Physical Chemistry in Condensed Phases, Vol. 83, Issue 7
Reactions of carboxylic acids on the Pd(111)-(2 × 2)O surface: multiple roles of surface oxygen atoms
journal, October 1991
- Davis, J. L.; Barteau, M. A.
- Surface Science, Vol. 256, Issue 1-2
Oxidation of ethylene on Pd(100); bonding of ethylene and scavenging of dehydrogenation fragments by surface oxygen
journal, September 1985
- Stuve, E. M.; Madix, R. J.
- Surface Science, Vol. 160, Issue 1
The effect of surface oxygen on hydrocarbon reactions catalyzed by platinum crystal surfaces with variable kink concentrations
journal, January 1980
- Davis, S. M.; Somorjai, G. A.
- Surface Science, Vol. 91, Issue 1
Catalytic decomposition of sulfuric acid using metal oxides as the oxygen generating reaction in thermochemical water splitting process
journal, January 1989
- Tagawa, Hiroaki; Endo, Takayuki
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 14, Issue 1
A DFT study of the adsorption of O 2 and H 2 O on Al(111) surfaces
journal, January 2016
- Wei, Xin; Dong, Chaofang; Chen, Zhanghua
- RSC Advances, Vol. 6, Issue 61
Decomposition of H 2 O on clean and oxygen-covered Au (1 0 0) surface: A DFT study
journal, October 2014
- Jiang, Zhao; Li, Mengmeng; Yan, Ting
- Applied Surface Science, Vol. 315
First-Principles Modeling of Direct versus Oxygen-Assisted Water Dissociation on Fe(100) Surfaces
journal, February 2016
- Wang, Wenju; Wang, Guoping; Shao, Minhua
- Catalysts, Vol. 6, Issue 2
Oxygen-assisted water partial dissociation on copper: a model study
journal, January 2015
- Wang, Ying-Qi; Yan, Li-Fen; Wang, Gui-Chang
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 17, Issue 12
Water-gas shift reaction on oxide/Cu(111): Rational catalyst screening from density functional theory
journal, November 2010
- Liu, Ping
- The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 133, Issue 20
Kinetics and mechanism of the water-gas shift reaction catalysed by the clean and Cs-promoted Cu(110) surface: a comparison with Cu(111)
journal, January 1990
- Nakamura, Junji; Campbell, Joseph M.; Campbell, Charles T.
- Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, Vol. 86, Issue 15
Surface science studies of the water–gas shift reaction on a model Cu(111) catalyst
journal, July 1987
- Campbell, Charles T.; Koel, Bruce E.; Daube, K. A.
- Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A: Vacuum, Surfaces, and Films, Vol. 5, Issue 4
On the Mechanism of Low-Temperature Water Gas Shift Reaction on Copper
journal, January 2008
- Gokhale, Amit A.; Dumesic, James A.; Mavrikakis, Manos
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 130, Issue 4
Hydroxyl-Induced Wetting of Metals by Water at Near-Ambient Conditions
journal, June 2007
- Yamamoto, Susumu; Andersson, Klas; Bluhm, Hendrik
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 111, Issue 22
A surface science investigation of the water-gas shift reaction on Cu(111)
journal, March 1987
- Campbell, C.
- Journal of Catalysis, Vol. 104, Issue 1
Oxidation of Cu(111): two new oxygen induced reconstructions
journal, December 1991
- Jensen, F.; Besenbacher, F.; Lægsgaard, E.
- Surface Science, Vol. 259, Issue 3
Two new oxygen induced reconstructions on Cu(111)
journal, May 1992
- Jensen, F.; Besenbacher, F.; Stensgaard, I.
- Surface Science, Vol. 269-270
Scanning tunneling microscopy studies of oxygen adsorption on Cu(111)
journal, January 2001
- Matsumoto, T.; Bennett, R. A.; Stone, P.
- Surface Science, Vol. 471, Issue 1-3
Autocatalytic Reduction of a Cu 2 O/Cu(111) Surface by CO: STM, XPS, and DFT Studies
journal, July 2010
- Yang, Fan; Choi, YongMan; Liu, Ping
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 114, Issue 40
Structurally Accurate Model for the “29”-Structure of Cu x O/Cu(111): A DFT and STM Study
journal, May 2016
- Therrien, Andrew J.; Zhang, Renqin; Lucci, Felicia R.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 120, Issue 20
Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set
journal, October 1996
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 54, Issue 16, p. 11169-11186
Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set
journal, July 1996
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J.
- Computational Materials Science, Vol. 6, Issue 1, p. 15-50
Projector augmented-wave method
journal, December 1994
- Blöchl, P. E.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 50, Issue 24, p. 17953-17979
From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method
journal, January 1999
- Kresse, G.; Joubert, D.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 59, Issue 3, p. 1758-1775
Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations
journal, June 1976
- Monkhorst, Hendrik J.; Pack, James D.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 13, Issue 12, p. 5188-5192
Precursor to the Onset of the Bulk Oxidation of Cu(100)
journal, April 2012
- Li, Liang; Mi, Xi; Shi, Yunfeng
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 108, Issue 17
Oxygen subsurface adsorption on the Cu(110)-c(6×2) surface
journal, September 2013
- Li, Liang; Zhou, Guangwen
- Surface Science, Vol. 615
Density functional theory study of O–H and C–H bond scission of methanol catalyzed by a chemisorbed oxygen layer on Cu(111)
journal, April 2016
- Li, Jonathan; Zhou, Guangwen
- Surface Science, Vol. 646
The onset of sub-surface oxidation induced by defects in a chemisorbed oxygen layer
journal, February 2015
- Li, Jonathan; Li, Liang; Zhou, Guangwen
- The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 142, Issue 8
A climbing image nudged elastic band method for finding saddle points and minimum energy paths
journal, December 2000
- Henkelman, Graeme; Uberuaga, Blas P.; Jónsson, Hannes
- The Journal of Chemical Physics, Vol. 113, Issue 22, p. 9901-9904
VESTA : a three-dimensional visualization system for electronic and structural analysis
journal, May 2008
- Momma, Koichi; Izumi, Fujio
- Journal of Applied Crystallography, Vol. 41, Issue 3
Surface Oxidation and Reduction of CuO and Cu2O Studied Using XPS and XAES
journal, November 1996
- Poulston, S.; Parlett, P. M.; Stone, P.
- Surface and Interface Analysis, Vol. 24, Issue 12
Electronic and optical properties of Cu, CuO and Cu 2 O studied by electron spectroscopy
journal, April 2012
- Tahir, Dahlang; Tougaard, Sven
- Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 24, Issue 17
Insight into -ice adsorption and dissociation on metal surfaces from first-principles simulations
journal, March 2004
- Michaelides, Angelos; Alavi, Ali; King, David A.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 69, Issue 11
Why Au and Cu Are More Selective Than Pt for Preferential Oxidation of CO at Low Temperature
journal, March 2004
- Kandoi, S.; Gokhale, A. A.; Grabow, L. C.
- Catalysis Letters, Vol. 93, Issue 1/2
Identification of General Linear Relationships between Activation Energies and Enthalpy Changes for Dissociation Reactions at Surfaces
journal, April 2003
- Michaelides, Angelos; Liu, Z. -P.; Zhang, C. J.
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 125, Issue 13
The reduction of copper oxide by water vapor visualized by in situ UHV-TEM
journal, June 2001
- Bharadwaj, Mridula D.; Yang, Judith C.
- Scripta Materialia, Vol. 44, Issue 11
The interaction of water with solid surfaces: fundamental aspects revisited
journal, May 2002
- Henderson, M.
- Surface Science Reports, Vol. 46, Issue 1-8
A systematic theoretical study of water dissociation on clean and oxygen-preadsorbed transition metals
journal, November 2006
- Wang, G.; Tao, S.; Bu, X.
- Journal of Catalysis, Vol. 244, Issue 1
A first principles study of water dissociation on small copper clusters
journal, January 2010
- Chen, Lei; Zhang, Qingfan; Zhang, Yunfeng
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 12, Issue 33
Electrolysis of water on (oxidized) metal surfaces
journal, December 2005
- Rossmeisl, J.; Logadottir, A.; Nørskov, J. K.
- Chemical Physics, Vol. 319, Issue 1-3, p. 178-184
Kinetics of oxygen evolution and dissolution on platinum electrodes
journal, July 1966
- Damjanovic, A.; Dey, A.; Bockris, J. O'M.
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 11, Issue 7
General Model for Water Monomer Adsorption on Close-Packed Transition and Noble Metal Surfaces
journal, May 2003
- Michaelides, A.; Ranea, V. A.; de Andres, P. L.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 90, Issue 21
Works referencing / citing this record:
Hydroxylation of ZnO/Cu(1 1 1) inverse catalysts under ambient water vapor and the water–gas shift reaction
journal, August 2019
- Orozco, Ivan; Huang, Erwei; Gutiérrez, Ramón A.
- Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Vol. 52, Issue 45
Molecular Coverage Determines Sliding Wear Behavior of n-Octadecylphosphonic Acid Functionalized Cu–O Coated Steel Disks against Aluminum
text, January 2020
- Prünte, Stephan; Music, Denis; Terziyska, Velislava
- RWTH Aachen University
Surface-reaction induced structural oscillations in the subsurface
journal, January 2020
- Sun, Xianhu; Zhu, Wenhui; Wu, Dongxiang
- Nature Communications, Vol. 11, Issue 1
Molecular Coverage Determines Sliding Wear Behavior of n-Octadecylphosphonic Acid Functionalized Cu–O Coated Steel Disks against Aluminum
journal, January 2020
- Prünte, Stephan; Music, Denis; Terziyska, Velislava L.
- Materials, Vol. 13, Issue 2
Surface-reaction induced structural oscillations in the subsurface
journal, January 2020
- Sun, Xianhu; Zhu, Wenhui; Wu, Dongxiang
- Nature Communications, Vol. 11, Issue 1

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal