Characteristics of the fourth order resonance in high intensity linear accelerators
Abstract
For the 4σ = 360° space-charge resonance in high intensity linear accelerators, the emittance growth is surveyed for input Gaussian beams, as a function of the depressed phase advance per cell σ and the initial tune depression (σo – σ). For each data point, the linac lattice is designed such that the fourth order resonance dominates over the envelope instability. Additionally, the data show that the maximum emittance growth takes place at σ ≈ 87° over a wide range of the tune depression (or beam current), which confirms that the relevant parameter for the emittance growth is σ and that for the bandwidth is σo – σ. An interesting four-fold phase space structure is observed that cannot be explained with the fourth order resonance terms alone. Analysis attributes this effect to a small negative sixth order detuning term as the beam is redistributed by the resonance. Analytical studies show that the tune increases monotonically for the Gaussian beam which prevents the resonance for σ > 90°. Lastly, frequency analysis indicates that the four-fold structure observed for input Kapchinskij-Vladmirskij beams when σ < 90°, is not the fourth order resonance but a fourth order envelope instability because the 1/4 = 90°/360°more »
- Authors:
-
- Institute for Basic Science, Daejeon (South Korea)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1436155
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1364184
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Physics of Plasmas
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 24; Journal Issue: 6; Journal ID: ISSN 1070-664X
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 43 PARTICLE ACCELERATORS
Citation Formats
Jeon, D., and Hwang, Kyung Ryun. Characteristics of the fourth order resonance in high intensity linear accelerators. United States: N. p., 2017.
Web. doi:10.1063/1.4985685.
Jeon, D., & Hwang, Kyung Ryun. Characteristics of the fourth order resonance in high intensity linear accelerators. United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4985685
Jeon, D., and Hwang, Kyung Ryun. Mon .
"Characteristics of the fourth order resonance in high intensity linear accelerators". United States. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4985685. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1436155.
@article{osti_1436155,
title = {Characteristics of the fourth order resonance in high intensity linear accelerators},
author = {Jeon, D. and Hwang, Kyung Ryun},
abstractNote = {For the 4σ = 360° space-charge resonance in high intensity linear accelerators, the emittance growth is surveyed for input Gaussian beams, as a function of the depressed phase advance per cell σ and the initial tune depression (σo – σ). For each data point, the linac lattice is designed such that the fourth order resonance dominates over the envelope instability. Additionally, the data show that the maximum emittance growth takes place at σ ≈ 87° over a wide range of the tune depression (or beam current), which confirms that the relevant parameter for the emittance growth is σ and that for the bandwidth is σo – σ. An interesting four-fold phase space structure is observed that cannot be explained with the fourth order resonance terms alone. Analysis attributes this effect to a small negative sixth order detuning term as the beam is redistributed by the resonance. Analytical studies show that the tune increases monotonically for the Gaussian beam which prevents the resonance for σ > 90°. Lastly, frequency analysis indicates that the four-fold structure observed for input Kapchinskij-Vladmirskij beams when σ < 90°, is not the fourth order resonance but a fourth order envelope instability because the 1/4 = 90°/360° component is missing in the frequency spectrum.},
doi = {10.1063/1.4985685},
journal = {Physics of Plasmas},
number = 6,
volume = 24,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Jun 19 00:00:00 EDT 2017},
month = {Mon Jun 19 00:00:00 EDT 2017}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
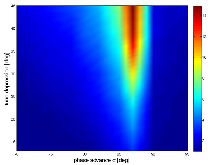 FIG. 1: 2D plot of emittance growth factor (= εfinal / εinitial) by the 4σ= 360° space-charge resonance as a function of the initial tune depression (σ° - σ) and depressed phase advance per cell σ. Regardless of the tune depression (or beam current), maximum emittance growth happens at σmore »
FIG. 1: 2D plot of emittance growth factor (= εfinal / εinitial) by the 4σ= 360° space-charge resonance as a function of the initial tune depression (σ° - σ) and depressed phase advance per cell σ. Regardless of the tune depression (or beam current), maximum emittance growth happens at σmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Experimental evidence of space charge driven resonances in high intensity linear accelerators
journal, January 2016
- Jeon, Dong-O
- Physical Review Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 19, Issue 1
Evidence of a halo formation mechanism in the Spallation Neutron Source linac
journal, April 2013
- Jeon, Dong-O
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 16, Issue 4
Interplay of space-charge fourth order resonance and envelope instability
journal, October 2016
- Jeon, D.; Jang, J. H.; Jin, H.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 832
Practical transverse matching of the high-intensity SNS Linac
journal, August 2009
- Jeon, D.; Chu, C. M.; Stovall, J.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 607, Issue 3
Core-halo issues for a very high intensity beam
journal, February 2014
- Nghiem, P. A. P.; Chauvin, N.; Simeoni, W.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 104, Issue 7
Self-consistent study of space-charge-driven coupling resonances
journal, May 2006
- Hofmann, I.; Franchetti, G.
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 9, Issue 5
Particle-core model for transverse dynamics of beam halo
journal, December 1998
- Wangler, T. P.; Crandall, K. R.; Ryne, R.
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 1, Issue 8
The IFMIF-EVEDA challenges in beam dynamics and their treatment
journal, October 2011
- Nghiem, P. A. P.; Chauvin, N.; Comunian, M.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 654, Issue 1
On halo formation from space-charge dominated beams
journal, June 1994
- Lagniel, Jean-Michel
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 345, Issue 1
Steady-State Transport of High-Current Beams in a Focused Channel
journal, May 1979
- Haber, I.; Maschke, A. W.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 42, Issue 22
Effects of resonances on halo formation in high-intensity storage rings
journal, December 1999
- Jeon, D.; Holmes, J. A.; Danilov, V. V.
- Physical Review E, Vol. 60, Issue 6
RMS Envelope Equations with Space Charge
journal, January 1971
- Sacherer, Frank J.
- IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, Vol. 18, Issue 3
Possible Emittance Increase through Filamentation Due to Space Charge in Continuous Beams
journal, January 1971
- Lapostolle, P. M.
- IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, Vol. 18, Issue 3
Fourth order resonance of a high intensity linear accelerator
journal, May 2009
- Jeon, D.; Groening, L.; Franchetti, G.
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 12, Issue 5
Analytic Model for Halo Formation in High Current Ion Linacs
journal, August 1994
- Gluckstern, Robert L.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 73, Issue 9
Experimental Evidence of the 90° Stop Band in the GSI UNILAC
journal, June 2009
- Groening, L.; Barth, W.; Bayer, W.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 102, Issue 23
Formation and mitigation of halo particles in the Spallation Neutron Source linac
journal, September 2002
- Jeon, D.; Stovall, J.; Aleksandrov, A.
- Physical Review Special Topics - Accelerators and Beams, Vol. 5, Issue 9
Space-Charge Structural Instabilities and Resonances in High-Intensity Beams
journal, November 2015
- Hofmann, Ingo; Boine-Frankenheim, Oliver
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 115, Issue 20
The Spallation Neutron Source accelerator system design
journal, November 2014
- Henderson, S.; Abraham, W.; Aleksandrov, A.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 763
Beam Dynamics for High-Power Superconducting Heavy-Ion Linear Accelerator of RAON
journal, April 2016
- Hwang, Ji-Gwang; Kim, Eun-San; Kim, Hye-Jin
- IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, Vol. 63, Issue 2
Design of the RAON accelerator systems
journal, October 2014
- Jeon, D.; Hong, I. S.; Kim, H. J.
- Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 65, Issue 7
Sixth-Order Resonance of High-Intensity Linear Accelerators
journal, May 2015
- Jeon, Dong-O; Hwang, Kyung Ryun; Jang, Ji-Ho
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 114, Issue 18
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal