Bulk viscosity of strongly interacting matter in the relaxation time approximation
Abstract
Here, we show how thermal mean field effects can be incorporated consistently in the hydrodynamical modeling of heavy-ion collisions. The nonequilibrium correction to the distribution function resulting from a temperature-dependent mass is obtained in a procedure which automatically satisfies the Landau matching condition and is thermodynamically consistent. The physics of the bulk viscosity is studied here for Boltzmann and Bose-Einstein gases within the Chapman-Enskog and 14-moment approaches in the relaxation time approximation. Constant and temperature-dependent masses are considered in turn. It is shown that, in the small mass limit, both methods lead to the same value of the ratio of the bulk viscosity to its relaxation time. The inclusion of a temperature-dependent mass leads to the emergence of the βλ function in that ratio, and it is of the expected parametric form for the Boltzmann gas, while for the Bose-Einstein case it is affected by the infrared cutoff. This suggests that the relaxation time approximation may be too crude to obtain a reliable form of ς/τR for gases obeying Bose-Einstein statistics.
- Authors:
-
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada); Jan Kochanowski Univ., Kielce (Poland)
- McGill Univ., Montreal, QC (Canada)
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Nuclear Physics (NP)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1454832
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1434403
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-205755-2018-JAAM
Journal ID: ISSN 2469-9985; PRVCAN; TRN: US1901164
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Physical Review C
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 97; Journal Issue: 4; Journal ID: ISSN 2469-9985
- Publisher:
- American Physical Society (APS)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 73 NUCLEAR PHYSICS AND RADIATION PHYSICS
Citation Formats
Czajka, Alina, Hauksson, Sigtryggur, Shen, Chun, Jeon, Sangyong, and Gale, Charles. Bulk viscosity of strongly interacting matter in the relaxation time approximation. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.97.044914.
Czajka, Alina, Hauksson, Sigtryggur, Shen, Chun, Jeon, Sangyong, & Gale, Charles. Bulk viscosity of strongly interacting matter in the relaxation time approximation. United States. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.97.044914
Czajka, Alina, Hauksson, Sigtryggur, Shen, Chun, Jeon, Sangyong, and Gale, Charles. Tue .
"Bulk viscosity of strongly interacting matter in the relaxation time approximation". United States. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.97.044914. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1454832.
@article{osti_1454832,
title = {Bulk viscosity of strongly interacting matter in the relaxation time approximation},
author = {Czajka, Alina and Hauksson, Sigtryggur and Shen, Chun and Jeon, Sangyong and Gale, Charles},
abstractNote = {Here, we show how thermal mean field effects can be incorporated consistently in the hydrodynamical modeling of heavy-ion collisions. The nonequilibrium correction to the distribution function resulting from a temperature-dependent mass is obtained in a procedure which automatically satisfies the Landau matching condition and is thermodynamically consistent. The physics of the bulk viscosity is studied here for Boltzmann and Bose-Einstein gases within the Chapman-Enskog and 14-moment approaches in the relaxation time approximation. Constant and temperature-dependent masses are considered in turn. It is shown that, in the small mass limit, both methods lead to the same value of the ratio of the bulk viscosity to its relaxation time. The inclusion of a temperature-dependent mass leads to the emergence of the βλ function in that ratio, and it is of the expected parametric form for the Boltzmann gas, while for the Bose-Einstein case it is affected by the infrared cutoff. This suggests that the relaxation time approximation may be too crude to obtain a reliable form of ς/τR for gases obeying Bose-Einstein statistics.},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevC.97.044914},
journal = {Physical Review C},
number = 4,
volume = 97,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Apr 24 00:00:00 EDT 2018},
month = {Tue Apr 24 00:00:00 EDT 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
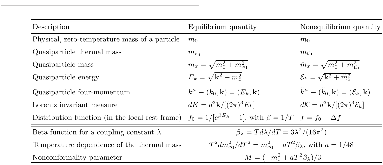 Table I: The quantities characterizing the equilibrium and nonequilibrium dynamics of a gas with Bose-Einstein statistics. For a classical gas with Boltzmann statistics, some of these quantities have different values or forms, and whenever there is a need to distinguish them we add the subscript $c: m_{eq,c,} f_{0,c} = e^{−βE_k}more »
Table I: The quantities characterizing the equilibrium and nonequilibrium dynamics of a gas with Bose-Einstein statistics. For a classical gas with Boltzmann statistics, some of these quantities have different values or forms, and whenever there is a need to distinguish them we add the subscript $c: m_{eq,c,} f_{0,c} = e^{−βE_k}more »
Works referenced in this record:
Transport coefficients of bulk viscous pressure in the 14-moment approximation
journal, August 2014
- Denicol, G. S.; Jeon, S.; Gale, C.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 90, Issue 2
Relativistic viscous hydrodynamics, conformal invariance, and holography
journal, April 2008
- Baier, Rudolf; Romatschke, Paul; Son, Dam Thanh
- Journal of High Energy Physics, Vol. 2008, Issue 04
New theories of relativistic hydrodynamics in the LHC era
journal, February 2018
- Florkowski, Wojciech; Heller, Michal P.; Spaliński, Michał
- Reports on Progress in Physics, Vol. 81, Issue 4
Bulk viscosity, particle spectra, and flow in heavy-ion collisions
journal, April 2012
- Dusling, Kevin; Schäfer, Thomas
- Physical Review C, Vol. 85, Issue 4
Bulk viscous corrections to photon production in the quark–gluon plasma
journal, August 2017
- Hauksson, Sigtryggur; Shen, Chun; Jeon, Sangyong
- Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings, Vol. 289-290
A relativistic relaxation-time model for the Boltzmann equation
journal, June 1974
- Anderson, J. L.; Witting, H. R.
- Physica, Vol. 74, Issue 3
Frontiers of finite temperature lattice QCD
journal, January 2017
- Borsányi, Szabolcs
- EPJ Web of Conferences, Vol. 137
Erratum: Derivation of transient relativistic fluid dynamics from the Boltzmann equation [Phys. Rev. D 85 , 114047 (2012)]
journal, February 2015
- Denicol, G. S.; Niemi, H.; Molnár, E.
- Physical Review D, Vol. 91, Issue 3
Relativistic (lattice) Boltzmann equation with nonideal equation of state
journal, March 2012
- Romatschke, Paul
- Physical Review D, Vol. 85, Issue 6
Effects of bulk viscosity and hadronic rescattering in heavy ion collisions at energies available at the BNL Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider and at the CERN Large Hadron Collider
journal, March 2018
- Ryu, Sangwook; Paquet, Jean-François; Shen, Chun
- Physical Review C, Vol. 97, Issue 3
Strongly Interacting Low-Viscosity Matter Created in Relativistic Nuclear Collisions
journal, October 2006
- Csernai, Laszlo P.; Kapusta, Joseph I.; McLerran, Larry D.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 97, Issue 15
Kubo formulas for the shear and bulk viscosity relaxation times and the scalar field theory shear calculation
journal, June 2017
- Czajka, Alina; Jeon, Sangyong
- Physical Review C, Vol. 95, Issue 6
Bulk viscosity and relaxation time of causal dissipative relativistic fluid dynamics
journal, February 2011
- Huang, Xu-Guang; Kodama, Takeshi; Koide, Tomoi
- Physical Review C, Vol. 83, Issue 2
Spectral sum rules for the quark-gluon plasma
journal, September 2009
- Romatschke, P.; Son, D. T.
- Physical Review D, Vol. 80, Issue 6
Transport Coefficients of Hadronic Matter Near
journal, October 2009
- Noronha-Hostler, Jacquelyn; Noronha, Jorge; Greiner, Carsten
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 103, Issue 17
Lectures on hydrodynamic fluctuations in relativistic theories
journal, November 2012
- Kovtun, Pavel
- Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical, Vol. 45, Issue 47
Shear Viscosity Coefficient and Relaxation Time of Causal Dissipative Hydrodynamics in QCD
journal, July 2009
- Koide, T.; Nakano, E.; Kodama, T.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 103, Issue 5
Transient relativistic thermodynamics and kinetic theory
journal, April 1979
- Israel, W.; Stewart, J. M.
- Annals of Physics, Vol. 118, Issue 2
Importance of the Bulk Viscosity of QCD in Ultrarelativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions
journal, September 2015
- Ryu, S.; Paquet, J. -F.; Shen, C.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 115, Issue 13
Transport coefficients in high temperature gauge theories (I): leading-log results
journal, November 2000
- Arnold, Peter; Moore, Guy David; Yaffe, Laurence G.
- Journal of High Energy Physics, Vol. 2000, Issue 11
Dissipative Relativistic Fluid Dynamics: A New Way to Derive the Equations of Motion from Kinetic Theory
journal, October 2010
- Denicol, G. S.; Koide, T.; Rischke, D. H.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 105, Issue 16
Effect of bulk viscosity on elliptic flow near the QCD phase transition
journal, December 2009
- Denicol, G. S.; Kodama, T.; Koide, T.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 80, Issue 6
Extracting the QGP viscosity from RHIC data—a status report from viscous hydrodynamics
journal, May 2009
- Song, Huichao; Heinz, Ulrich
- Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vol. 36, Issue 6
Quasiparticle theory of shear and bulk viscosities of hadronic matter
journal, January 2011
- Chakraborty, P.; Kapusta, J. I.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 83, Issue 1
The QCD equation of state at finite density from analytical continuation
journal, November 2017
- Guenther, J. N.; Bellwied, R.; Borsányi, S.
- Nuclear Physics A, Vol. 967
Effect of bulk viscosity on interferometry correlations in ultrarelativistic heavy-ion collisions
journal, May 2017
- Bożek, Piotr
- Physical Review C, Vol. 95, Issue 5
Transport Coefficients of a Gluon Plasma
journal, February 2005
- Nakamura, Atsushi; Sakai, Sunao
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 94, Issue 7
Bulk viscosity of high-temperature QCD
journal, October 2006
- Arnold, Peter; Doğan, Çağlar; Moore, Guy D.
- Physical Review D, Vol. 74, Issue 8
Production of photons in relativistic heavy-ion collisions
journal, April 2016
- Paquet, Jean-François; Shen, Chun; Denicol, Gabriel S.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 93, Issue 4
Relativistic quantum transport coefficients for second-order viscous hydrodynamics
journal, May 2015
- Florkowski, Wojciech; Jaiswal, Amaresh; Maksymiuk, Ewa
- Physical Review C, Vol. 91, Issue 5
Quasiparticle second-order viscous hydrodynamics from kinetic theory
journal, March 2017
- Tinti, Leonardo; Jaiswal, Amaresh; Ryblewski, Radoslaw
- Physical Review D, Vol. 95, Issue 5
Bulk viscosity in quasiparticle models
journal, May 2009
- Sasaki, Chihiro; Redlich, Krzysztof
- Physical Review C, Vol. 79, Issue 5
Transport coefficients for bulk viscous evolution in the relaxation-time approximation
journal, October 2014
- Jaiswal, Amaresh; Ryblewski, Radoslaw; Strickland, Michael
- Physical Review C, Vol. 90, Issue 4
Collective Flow and Viscosity in Relativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions
journal, October 2013
- Heinz, Ulrich; Snellings, Raimond
- Annual Review of Nuclear and Particle Science, Vol. 63, Issue 1
Shear and bulk viscosities of the gluon plasma in a quasiparticle description
journal, August 2011
- Bluhm, M.; Kämpfer, B.; Redlich, K.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 84, Issue 2
Introduction to hydrodynamics
journal, October 2015
- Jeon, Sangyong; Heinz, Ulrich
- International Journal of Modern Physics E, Vol. 24, Issue 10
Hydrodynamic transport coefficients in relativistic scalar field theory
journal, September 1995
- Jeon, Sangyong
- Physical Review D, Vol. 52, Issue 6
The effect of shear and bulk viscosities on elliptic flow
journal, August 2010
- Denicol, G. S.; Kodama, T.; Koide, T.
- Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vol. 37, Issue 9
Phenomenological consequences of enhanced bulk viscosity near the QCD critical point
journal, March 2017
- Monnai, Akihiko; Mukherjee, Swagato; Yin, Yi
- Physical Review C, Vol. 95, Issue 3
On the kinetic theory of rarefied gases
journal, December 1949
- Grad, Harold
- Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, Vol. 2, Issue 4
Complete second-order dissipative fluid dynamics
journal, May 2009
- Betz, B.; Henkel, D.; Rischke, D. H.
- Journal of Physics G: Nuclear and Particle Physics, Vol. 36, Issue 6
Derivation of fluid dynamics from kinetic theory with the 14-moment approximation
journal, November 2012
- Denicol, G. S.; Molnár, E.; Niemi, H.
- The European Physical Journal A, Vol. 48, Issue 11
New Developments in Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics
journal, January 2010
- Romatschke, Paul
- International Journal of Modern Physics E, Vol. 19, Issue 01
Phenomenological constraints on the bulk viscosity of QCD
journal, November 2017
- Paquet, Jean-François; Shen, Chun; Denicol, Gabriel
- Nuclear Physics A, Vol. 967
Derivation of transient relativistic fluid dynamics from the Boltzmann equation
journal, June 2012
- Denicol, G. S.; Niemi, H.; Molnár, E.
- Physical Review D, Vol. 85, Issue 11
Rational Chebyshev Approximations for the Bickley Functions Ki n (x)
journal, July 1978
- Blair, J. M.; Edwards, C. A.; Johnson, J. H.
- Mathematics of Computation, Vol. 32, Issue 143
Transport coefficients in high temperature gauge theories, 2. Beyond leading log
journal, May 2003
- Arnold, Peter; Moore, Guy D.; Yaffe, Laurence G.
- Journal of High Energy Physics, Vol. 2003, Issue 05
From quantum field theory to hydrodynamics: Transport coefficients and effective kinetic theory
journal, May 1996
- Jeon, Sangyong; Yaffe, Laurence G.
- Physical Review D, Vol. 53, Issue 10
Anisotropic flow of thermal photons as a quark-gluon plasma viscometer
journal, February 2015
- Shen, Chun; Heinz, Ulrich; Paquet, Jean-François
- Physical Review C, Vol. 91, Issue 2
3D Relativistic Hydrodynamic Computations Using Lattice-QCD-Inspired Equations of State
journal, August 2006
- Hama, Yogiro; Andrade, Rone P. G.; Grassi, Frédérique
- Nuclear Physics A, Vol. 774
Origin of the relaxation time in dissipative fluid dynamics
journal, April 2011
- Denicol, Gabriel S.; Noronha, Jorge; Niemi, Harri
- Physical Review D, Vol. 83, Issue 7
Universal properties of bulk viscosity near the QCD phase transition
journal, May 2008
- Karsch, Frithjof; Kharzeev, Dmitri; Tuchin, Kirill
- Physics Letters B, Vol. 663, Issue 3
Bulk viscosity from hydrodynamic fluctuations with relativistic hydrokinetic theory
journal, February 2018
- Akamatsu, Yukinao; Mazeliauskas, Aleksas; Teaney, Derek
- Physical Review C, Vol. 97, Issue 2
Quasiparticle Anisotropic Hydrodynamics for Ultrarelativistic Heavy-Ion Collisions
journal, July 2017
- Alqahtani, Mubarak; Nopoush, Mohammad; Ryblewski, Radoslaw
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 119, Issue 4
Effective kinetic theory for high temperature gauge theories
journal, January 2003
- Arnold, Peter B.; Moore, Guy D.; Yaffe, Laurence G.
- Journal of High Energy Physics, Vol. 2003, Issue 01
Hydrodynamic Modeling of Heavy-Ion Collisions
journal, April 2013
- Gale, Charles; Jeon, Sangyong; Schenke, BjÖRn
- International Journal of Modern Physics A, Vol. 28, Issue 11
Quasiparticle theory of transport coefficients for hadronic matter at finite temperature and baryon density
journal, January 2016
- Albright, M.; Kapusta, J. I.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 93, Issue 1
Departure from equilibrium of the quasiparticle distribution functions in high-energy nuclear collisions
journal, January 2017
- Chakraborty, P.; Kapusta, J. I.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 95, Issue 1
Photon emission from a momentum-anisotropic quark-gluon plasma
journal, January 2015
- Shen, Chun; Paquet, Jean-François; Heinz, Ulrich
- Physical Review C, Vol. 91, Issue 1

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal