nuclear quadrupole resonance as a microscopic probe in the Te-doped correlated semimetal : Emergence of electronic Griffith phase, magnetism, and metallic behavior
Abstract
121,123Sb nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) was applied to Fe(Sb1-xTex)2 in the low doping regime (x = 0 , 0.01, and 0.05) as a microscopic zero field probe to study the evolution of 3d magnetism and the emergence of metallic behavior. Whereas the NQR spectra itself reflects the degree of local disorder via the width of the individual NQR lines, the spin lattice relaxation rate (SLRR) 1/T1 (T) probes the fluctuations at the Sb site. The fluctuations originate either from conduction electrons or from magnetic moments. In contrast to the semimetal FeSb2 with a clear signature of the charge and spin gap formation in 1/T1(T)T[~exp/(ΔkBT)] , the 1% Te-doped system exhibits almost metallic conductivity and the SLRR nicely confirms that the gap is almost filled. A weak divergence of the SLRR coefficient 1/T1(T)T ~ T-n ~ T-0.2 points towards the presence of electronic correlations towards low temperatures. This is supported by the electronic specific heat coefficient γ = (Cel/T) showing a power-law divergence γ (T) ~ T-m ~ (1/T1T)1/2 ~ T-n/2 ~ Cel/T which is expected in the renormalized Landau Fermi liquid theory for correlated electrons. In contrast to that the 5% Te-doped sample exhibits a much larger divergence in themore »
- Authors:
-
- Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Dresden (Germany); M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (Russia). Faculty of Physics
- M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (Russia). Faculty of Physics
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States). Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science Department
- Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids, Dresden (Germany)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1430876
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1420201
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-203432-2018-JAAM
Journal ID: ISSN 2469-9950; PRBMDO; TRN: US1802629
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Physical Review B
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 97; Journal Issue: 7; Journal ID: ISSN 2469-9950
- Publisher:
- American Physical Society (APS)
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 75 CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS, SUPERCONDUCTIVITY AND SUPERFLUIDITY
Citation Formats
Gippius, A. A., Zhurenko, S. V., Hu, R., Petrovic, Cedomir, and Baenitz, M. Sb121,123 nuclear quadrupole resonance as a microscopic probe in the Te-doped correlated semimetal FeSb2 : Emergence of electronic Griffith phase, magnetism, and metallic behavior. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.97.075118.
Gippius, A. A., Zhurenko, S. V., Hu, R., Petrovic, Cedomir, & Baenitz, M. Sb121,123 nuclear quadrupole resonance as a microscopic probe in the Te-doped correlated semimetal FeSb2 : Emergence of electronic Griffith phase, magnetism, and metallic behavior. United States. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.075118
Gippius, A. A., Zhurenko, S. V., Hu, R., Petrovic, Cedomir, and Baenitz, M. Mon .
"Sb121,123 nuclear quadrupole resonance as a microscopic probe in the Te-doped correlated semimetal FeSb2 : Emergence of electronic Griffith phase, magnetism, and metallic behavior". United States. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.97.075118. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1430876.
@article{osti_1430876,
title = {Sb121,123 nuclear quadrupole resonance as a microscopic probe in the Te-doped correlated semimetal FeSb2 : Emergence of electronic Griffith phase, magnetism, and metallic behavior},
author = {Gippius, A. A. and Zhurenko, S. V. and Hu, R. and Petrovic, Cedomir and Baenitz, M.},
abstractNote = {121,123Sb nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) was applied to Fe(Sb1-xTex)2 in the low doping regime (x = 0 , 0.01, and 0.05) as a microscopic zero field probe to study the evolution of 3d magnetism and the emergence of metallic behavior. Whereas the NQR spectra itself reflects the degree of local disorder via the width of the individual NQR lines, the spin lattice relaxation rate (SLRR) 1/T1 (T) probes the fluctuations at the Sb site. The fluctuations originate either from conduction electrons or from magnetic moments. In contrast to the semimetal FeSb2 with a clear signature of the charge and spin gap formation in 1/T1(T)T[~exp/(ΔkBT)] , the 1% Te-doped system exhibits almost metallic conductivity and the SLRR nicely confirms that the gap is almost filled. A weak divergence of the SLRR coefficient 1/T1(T)T ~ T-n ~ T-0.2 points towards the presence of electronic correlations towards low temperatures. This is supported by the electronic specific heat coefficient γ = (Cel/T) showing a power-law divergence γ (T) ~ T-m ~ (1/T1T)1/2 ~ T-n/2 ~ Cel/T which is expected in the renormalized Landau Fermi liquid theory for correlated electrons. In contrast to that the 5% Te-doped sample exhibits a much larger divergence in the SLRR coefficient showing 1/T1(T)T ~ T-0.72 . According to the specific heat divergence a power law with n = 2 m = 0.56 is expected for the SLRR. This dissimilarity originates from admixed critical magnetic fluctuations in the vicinity of antiferromagnetic long range order with 1/T1(T)T ~ T-3/4 behavior. Furthermore Te-doped FeSb2 as a disordered paramagnetic metal might be a platform for the electronic Griffith phase scenario. NQR evidences a substantial asymmetric broadening of the 121,123Sb NQR spectrum for the 5% sample. Lastly, this has a predominant electronic origin in agreement with the electronic Griffith phase and stems probably from an enhanced Sb-Te bond polarization and electronic density shift towards the Te atom inside Sb-Te dumbbell.},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevB.97.075118},
journal = {Physical Review B},
number = 7,
volume = 97,
place = {United States},
year = {Mon Feb 12 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Mon Feb 12 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
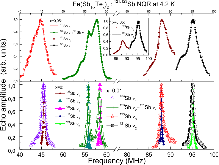 FIG. 1. : (color online). 121,123$Sb$ spectra measured at 4.2 K in $Fe$($Sb$1−x$Te$$x$)2 compounds with $x$ = 0.01 (lower panel) and 0.05 (upper panel). For comparison, the same $Sb$ NQR lines for the undoped $FeSb$2 measured at 10 K and retrieved from [19] are presented (lower panel). The intensities ofmore »
FIG. 1. : (color online). 121,123$Sb$ spectra measured at 4.2 K in $Fe$($Sb$1−x$Te$$x$)2 compounds with $x$ = 0.01 (lower panel) and 0.05 (upper panel). For comparison, the same $Sb$ NQR lines for the undoped $FeSb$2 measured at 10 K and retrieved from [19] are presented (lower panel). The intensities ofmore »
Works referenced in this record:
Quantum Griffiths Phase in the Weak Itinerant Ferromagnetic Alloy
journal, February 2010
- Ubaid-Kassis, Sara; Vojta, Thomas; Schroeder, Almut
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 104, Issue 6
Logarithmic Fermi-Liquid Breakdown in
journal, July 2008
- Brando, M.; Duncan, W. J.; Moroni-Klementowicz, D.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 101, Issue 2
Non-Fermi-liquid behavior in - and -electron metals
journal, October 2001
- Stewart, G. R.
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 73, Issue 4
Paramagnetic Excited State of FeSi
journal, August 1967
- Jaccarino, V.; Wertheim, G. K.; Wernick, J. H.
- Physical Review, Vol. 160, Issue 3
Ferromagnetic instability in a doped band gap semiconductor FeGa
journal, October 2012
- Umeo, K.; Hadano, Y.; Narazu, S.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 86, Issue 14
Non-Fermi Liquid Behavior and Griffiths Phase in -Electron Compounds
journal, October 1998
- Castro Neto, A. H.; Castilla, G.; Jones, B. A.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 81, Issue 16
Kondo insulator description of spin state transition in FeSb2
journal, July 2005
- Petrovic, C.; Lee, Y.; Vogt, T.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 72, Issue 4
Quantum Phase Transitions and Multicriticality in Ta(Fe 1− x V x ) 2
journal, August 2016
- Brando, Manuel; Kerkau, Alexander; Todorova, Adriana
- Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, Vol. 85, Issue 8
Interplay between localized and itinerant magnetism in Co-substituted FeGa
journal, March 2014
- Gippius, A. A.; Verchenko, V. Yu.; Tkachev, A. V.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Non-Fermi-liquid behavior in U and Ce alloys: Criticality, disorder, dissipation, and Griffiths-McCoy singularities
journal, December 2000
- Castro Neto, A. H.; Jones, B. A.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 62, Issue 22
Metallic quantum ferromagnets
journal, May 2016
- Brando, M.; Belitz, D.; Grosche, F. M.
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 88, Issue 2
Magnetic properties of Ta(Fe 1− x T x ) 2 with T =V, Cr, Mn, Co and Ni
journal, January 2010
- Horie, Yuki; Kawashima, Shun-ichi; Yamada, Yoshihiro
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 200, Issue 3
Magnetic spin-lattice relaxation in nuclear quadrupole resonance: the eta not=0 case
journal, October 1991
- Chepin, J.; Ross, J. H.
- Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 3, Issue 41
Fermi-liquid instabilities at magnetic quantum phase transitions
journal, August 2007
- Löhneysen, Hilbert v.; Rosch, Achim; Vojta, Matthias
- Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol. 79, Issue 3
Evidence for spiral magnetic order in the heavy fermion material
journal, September 2000
- Curro, N. J.; Hammel, P. C.; Pagliuso, P. G.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 62, Issue 10
Disorder-driven non-Fermi liquid behaviour of correlated electrons
journal, August 2005
- Miranda, E.; Dobrosavljević, V.
- Reports on Progress in Physics, Vol. 68, Issue 10
Towards ferromagnetic quantum criticality in NQR as a zero-field microscopic probe
journal, February 2016
- Majumder, M.; Wagner-Reetz, M.; Cardoso-Gil, R.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 93, Issue 6
Large anomalous Hall effect in a silicon-based magnetic semiconductor
journal, March 2004
- Manyala, Ncholu; Sidis, Yvan; DiTusa, John F.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 3, Issue 4
Intermetallic solid solution Fe1−xCoxGa3: Synthesis, structure, NQR study and electronic band structure calculations
journal, October 2012
- Verchenko, V. Yu.; Likhanov, M. S.; Kirsanova, M. A.
- Journal of Solid State Chemistry, Vol. 194
Quantum criticality in heavy-fermion metals
journal, March 2008
- Gegenwart, Philipp; Si, Qimiao; Steglich, Frank
- Nature Physics, Vol. 4, Issue 3
Magnetism and metal-insulator transition in
journal, February 2009
- Hu, Rongwei; Mitrović, V. F.; Petrovic, C.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 79, Issue 6
Nonanalytic Behavior Above the Critical Point in a Random Ising Ferromagnet
journal, July 1969
- Griffiths, Robert B.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 23, Issue 1
Kondo-Cluster-Glass State near a Ferromagnetic Quantum Phase Transition
journal, May 2009
- Westerkamp, T.; Deppe, M.; Küchler, R.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 102, Issue 20
Field-tuned critical fluctuations in YFe Al : Evidence from magnetization, Al NMR, and NQR investigations
journal, December 2012
- Khuntia, P.; Strydom, A. M.; Wu, L. S.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 86, Issue 22
Heavy Fermions and Quantum Phase Transitions
journal, September 2010
- Si, Q.; Steglich, F.
- Science, Vol. 329, Issue 5996
Sb Magnetic Resonance as a Local Probe for the Gap Formation in the Correlated Semimetal FeSb2
journal, September 2014
- Gippius, A. A.; Baenitz, M.; Okhotnikov, K. S.
- Applied Magnetic Resonance, Vol. 45, Issue 11
Quantum Griffiths Effects and Smeared Phase Transitions in Metals: Theory and Experiment
journal, August 2010
- Vojta, Thomas
- Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 161, Issue 1-2
Spin Fluctuations in Itinerant Electron Magnetism
book, January 1985
- Moriya, Tôru
- Springer Series in Solid-State Sciences
Effect of a nonzero temperature on quantum critical points in itinerant fermion systems
journal, September 1993
- Millis, A. J.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 48, Issue 10
Contiguous and Magnetism: Strongly Correlated Electrons in
journal, November 2014
- Khuntia, P.; Peratheepan, P.; Strydom, A. M.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 113, Issue 21
Electronic Griffiths Phase in the Te-Doped Semiconductor
journal, December 2012
- Hu, Rongwei; Wang, Kefeng; Ryu, Hyejin
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 109, Issue 25
Crystal growth, electronic structure, and properties of Ni-substituted FeGa
journal, April 2016
- Likhanov, Maxim S.; Verchenko, Valeriy Yu.; Bykov, Mikhail A.
- Journal of Solid State Chemistry, Vol. 236
Thermodynamics of FeSi
journal, February 1995
- Mandrus, D.; Sarrao, J. L.; Migliori, A.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 51, Issue 8
Phenomenological theory of non-Fermi-liquid heavy-fermion alloys
journal, October 1993
- Tsvelik, A. M.; Reizer, M.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 48, Issue 13
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal