Impacts of electrode coating irregularities on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell lifetime using quasi in-situ infrared thermography and accelerated stress testing
Abstract
In-line quality control diagnostics for roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing techniques will play a key role in the future commercialization of the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) used in automotive applications. These diagnostics monitor the fabrication of the membrane electrode assembly (MEA), which detect and flag any non-uniformity that may potentially harm PEMFC performance and/or lifetime. This will require quantitative thresholds and a clear distinction between harmful defects and harmless coating irregularities. Thus, novel fuel cell hardware with quasi in-situ infrared (IR) thermography capabilities is utilized to understand how bare spots in the cathode electrode impact MEA lifetime. An accelerated stress test (AST) simulates chemical and mechanical degradation modes seen in vehicular operation. The actual open circuit voltage and rate of change of this voltage are used as in-situ indicators for MEA failure, enabling capture of the progression of failure point development. Bare spot coating irregularities located at the center of the electrode were found to have no impact on MEA lifetime when compared to a pristine MEA. However, MEA lifetime was found to be considerably shortened when these same irregularities are located at the cathode inlet and, especially, the anode inlet regions of the fuel cell.
- Authors:
-
- National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States); Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO (United States)
- National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
- Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), Golden, CO (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Program (EE-3F); USDOE
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1426642
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1496283
- Report Number(s):
- NREL/JA-5900-70934
Journal ID: ISSN 0360-3199
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC36-08GO28308
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 43; Journal Issue: 12; Journal ID: ISSN 0360-3199
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 36 MATERIALS SCIENCE; coating irregularities; PEMFC; manufacturing; infrared thermography; accelerated stress test; defects
Citation Formats
Phillips, Adam, Ulsh, Michael, Neyerlin, K. C., Porter, Jason, and Bender, Guido. Impacts of electrode coating irregularities on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell lifetime using quasi in-situ infrared thermography and accelerated stress testing. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.050.
Phillips, Adam, Ulsh, Michael, Neyerlin, K. C., Porter, Jason, & Bender, Guido. Impacts of electrode coating irregularities on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell lifetime using quasi in-situ infrared thermography and accelerated stress testing. United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.050
Phillips, Adam, Ulsh, Michael, Neyerlin, K. C., Porter, Jason, and Bender, Guido. Fri .
"Impacts of electrode coating irregularities on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell lifetime using quasi in-situ infrared thermography and accelerated stress testing". United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.050. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1426642.
@article{osti_1426642,
title = {Impacts of electrode coating irregularities on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell lifetime using quasi in-situ infrared thermography and accelerated stress testing},
author = {Phillips, Adam and Ulsh, Michael and Neyerlin, K. C. and Porter, Jason and Bender, Guido},
abstractNote = {In-line quality control diagnostics for roll-to-roll (R2R) manufacturing techniques will play a key role in the future commercialization of the polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) used in automotive applications. These diagnostics monitor the fabrication of the membrane electrode assembly (MEA), which detect and flag any non-uniformity that may potentially harm PEMFC performance and/or lifetime. This will require quantitative thresholds and a clear distinction between harmful defects and harmless coating irregularities. Thus, novel fuel cell hardware with quasi in-situ infrared (IR) thermography capabilities is utilized to understand how bare spots in the cathode electrode impact MEA lifetime. An accelerated stress test (AST) simulates chemical and mechanical degradation modes seen in vehicular operation. The actual open circuit voltage and rate of change of this voltage are used as in-situ indicators for MEA failure, enabling capture of the progression of failure point development. Bare spot coating irregularities located at the center of the electrode were found to have no impact on MEA lifetime when compared to a pristine MEA. However, MEA lifetime was found to be considerably shortened when these same irregularities are located at the cathode inlet and, especially, the anode inlet regions of the fuel cell.},
doi = {10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.050},
journal = {International Journal of Hydrogen Energy},
number = 12,
volume = 43,
place = {United States},
year = {Fri Mar 02 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Fri Mar 02 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
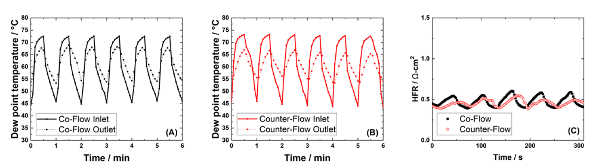 Figure 1: Relative dew point temperatures of the anode during humidification cycling for (A) coflow and (B) counter-flow operation under AST operating conditions. The (C) HFR under AST operating conditions in a H2/N2 environment for co-flow and counter-flow operation.
Figure 1: Relative dew point temperatures of the anode during humidification cycling for (A) coflow and (B) counter-flow operation under AST operating conditions. The (C) HFR under AST operating conditions in a H2/N2 environment for co-flow and counter-flow operation.
Works referenced in this record:
Morphological features (defects) in fuel cell membrane electrode assemblies
journal, July 2006
- Kundu, S.; Fowler, M. W.; Simon, L. C.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 157, Issue 2
Utilizing a Segmented Fuel Cell to Study the Effects of Electrode Coating Irregularities on PEM Fuel Cell Initial Performance
journal, April 2017
- Phillips, A.; Ulsh, M.; Porter, J.
- Fuel Cells, Vol. 17, Issue 3
The degradation mitigation effect of cerium oxide in polymer electrolyte membranes in extended fuel cell durability tests
journal, March 2013
- Pearman, Benjamin P.; Mohajeri, Nahid; Brooker, R. Paul
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 225
Comparison between two PEM fuel cell durability tests performed at constant current and under solicitations linked to transport mission profile
journal, December 2007
- Wahdame, B.; Candusso, D.; Francois, X.
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 32, Issue 17
Aspects of the Chemical Degradation of PFSA Ionomers used in PEM Fuel Cells
journal, April 2005
- Healy, J.; Hayden, C.; Xie, T.
- Fuel Cells, Vol. 5, Issue 2
A degradation study of Nafion proton exchange membrane of PEM fuel cells
journal, June 2007
- Tang, Haolin; Peikang, Shen; Jiang, San Ping
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 170, Issue 1, p. 85-92
Scientific Aspects of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Durability and Degradation
journal, October 2007
- Borup, Rod; Meyers, Jeremy; Pivovar, Bryan
- Chemical Reviews, Vol. 107, Issue 10
A review of PEM fuel cell durability: Degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies
journal, September 2008
- Wu, Jinfeng; Yuan, Xiao Zi; Martin, Jonathan J.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 184, Issue 1, p. 104-119
Understanding and approaches for the durability issues of Pt-based catalysts for PEM fuel cell
journal, September 2007
- Shao, Yuyan; Yin, Geping; Gao, Yunzhi
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 171, Issue 2, p. 558-566
Review: Durability and Degradation Issues of PEM Fuel Cell Components
journal, February 2008
- de Bruijn, F. A.; Dam, V. A. T.; Janssen, G. J. M.
- Fuel Cells, Vol. 8, Issue 1
500h Continuous aging life test on PBI/H3PO4 high-temperature PEMFC
journal, October 2006
- Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Y.
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 31, Issue 13
A review of accelerated stress tests of MEA durability in PEM fuel cells
journal, January 2009
- Zhang, S.; Yuan, X.; Wang, H.
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 34, Issue 1
A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell durability test protocols
journal, November 2011
- Yuan, Xiao-Zi; Li, Hui; Zhang, Shengsheng
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 196, Issue 22
Accelerated stress test procedures for PEM fuel cells under actual load constraints: State-of-art and proposals
journal, September 2015
- Petrone, R.; Hissel, D.; Péra, M. C.
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 40, Issue 36
Investigation of MEA degradation in PEM fuel cell by on/off cyclic operation under different humid conditions
journal, January 2011
- Seo, Dongho; Lee, Junghyun; Park, Sangsun
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 36, Issue 2
Accelerated life-time test protocols for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells operated at high temperature
journal, February 2015
- Jeon, Yukwon; Na, Heeso; Hwang, Hyoungkwon
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 40, Issue 7
Characterization of MEA degradation for an open air cathode PEM fuel cell
journal, April 2012
- Silva, R. A.; Hashimoto, T.; Thompson, G. E.
- International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 37, Issue 8
Accelerated Testing of Carbon Corrosion and Membrane Degradation in PEM Fuel Cells
journal, March 2013
- Mukundan, R.; James, G.; Ayotte, D.
- ECS Transactions, Vol. 50, Issue 2
Accelerated Testing Validation
conference, January 2011
- Mukundan, Rangachary; James, Greg; Davey, John
- 220th ECS Meeting, ECS Transactions
Degradation analysis and modeling of reinforced catalyst coated membranes operated under OCV conditions
journal, September 2008
- Kundu, Sumit; Fowler, Michael W.; Simon, Leonardo C.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 183, Issue 2
Phenomenon Analysis of PEFC for Automotive Use(1) Membrane Degradation Behavior During OCV Hold Test
journal, October 2006
- Ohma, Atsushi; Suga, Sohei; Yamamoto, Shinji
- ECS Transactions, Vol. 3, Issue 1
Gas crossover and membrane degradation in polymer electrolyte fuel cells
journal, August 2006
- Inaba, Minoru; Kinumoto, Taro; Kiriake, Masayuki
- Electrochimica Acta, Vol. 51, Issue 26
Application of a thermally conductive pyrolytic graphite sheet to thermal management of a PEM fuel cell
journal, March 2008
- Wen, Chih-Yung; Huang, Guo-Wei
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 178, Issue 1
The impact of channel path length on PEMFC flow-field design
journal, September 2006
- Shimpalee, S.; Greenway, S.; Van Zee, J. W.
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 160, Issue 1
Defect Detection in Fuel Cell Gas Diffusion Electrodes Using Infrared Thermography
journal, March 2016
- Ulsh, M.; Porter, J. M.; Bittinat, D. C.
- Fuel Cells, Vol. 16, Issue 2
Reactive impinging-flow technique for polymer-electrolyte-fuel-cell electrode-defect detection
journal, November 2016
- Zenyuk, Iryna V.; Englund, Nicholas; Bender, Guido
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 332
Understanding Membrane Failure in PEMFC: Comparison of Diagnostic Tools at Different Observation Scales
journal, March 2012
- De Moor, G.; Bas, C.; Charvin, N.
- Fuel Cells, Vol. 12, Issue 3
In Situ Quantification of Electronic Short Circuits in PEM Fuel Cell Stacks
journal, August 2015
- De Moor, G.; Charvin, N.; Bas, C.
- IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Vol. 62, Issue 8
Detecting and localizing failure points in proton exchange membrane fuel cells using IR thermography
journal, May 2014
- Bender, Guido; Felt, Wyatt; Ulsh, Michael
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 253
Membrane Degradation at Catalyst Layer Edges in PEMFC MEAs
journal, January 2007
- Sompalli, Bhaskar; Litteer, Brian A.; Gu, Wenbin
- Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 154, Issue 12
Determination of Catalyst Unique Parameters for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in a PEMFC
journal, January 2006
- Neyerlin, K. C.; Gu, Wenbin; Jorne, Jacob
- Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 153, Issue 10
Applying infrared thermography as a quality-control tool for the rapid detection of polymer-electrolyte-membrane-fuel-cell catalyst-layer-thickness variations
journal, August 2012
- Aieta, Niccolo V.; Das, Prodip K.; Perdue, Andrew
- Journal of Power Sources, Vol. 211, p. 4-11
Works referencing / citing this record:
In Situ and Operando Characterization of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
journal, August 2019
- Meyer, Quentin; Zeng, Yachao; Zhao, Chuan
- Advanced Materials, Vol. 31, Issue 40

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal