Naturally occurring 32Si and low-background silicon dark matter detectors
Abstract
Here, the naturally occurring radioisotope 32Si represents a potentially limiting background in future dark matter direct-detection experiments. We investigate sources of 32Si and the vectors by which it comes to reside in silicon crystals used for fabrication of radiation detectors. We infer that the 32Si concentration in commercial single-crystal silicon is likely variable, dependent upon the specific geologic and hydrologic history of the source (or sources) of silicon “ore” and the details of the silicon-refinement process. The silicon production industry is large, highly segmented by refining step, and multifaceted in terms of final product type, from which we conclude that production of 32Si-mitigated crystals requires both targeted silicon material selection and a dedicated refinement-through-crystal-production process. We review options for source material selection, including quartz from an underground source and silicon isotopically reduced in 32Si. To quantitatively evaluate the 32Si content in silicon metal and precursor materials, we propose analytic methods employing chemical processing and radiometric measurements. Ultimately, it appears feasible to produce silicon detectors with low levels of 32Si, though significant assay method development is required to validate this claim and thereby enable a quality assurance program during an actual controlled silicon-detector production cycle.
- Authors:
-
- Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), Richland, WA (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), High Energy Physics (HEP)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1420890
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1548746
- Report Number(s):
- PNNL-SA-127795
Journal ID: ISSN 0927-6505; PII: S0927650517302529; TRN: US1801504
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-76RL01830
- Resource Type:
- Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Astroparticle Physics
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 99; Journal ID: ISSN 0927-6505
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 79 ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS; Dark matter; Direct detection; Silicon; 32Si assay
Citation Formats
Orrell, John L., Arnquist, Isaac J., Bliss, Mary, Bunker, Raymond, and Finch, Zachary S. Naturally occurring 32Si and low-background silicon dark matter detectors. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.astropartphys.2018.02.005.
Orrell, John L., Arnquist, Isaac J., Bliss, Mary, Bunker, Raymond, & Finch, Zachary S. Naturally occurring 32Si and low-background silicon dark matter detectors. United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.astropartphys.2018.02.005
Orrell, John L., Arnquist, Isaac J., Bliss, Mary, Bunker, Raymond, and Finch, Zachary S. Sat .
"Naturally occurring 32Si and low-background silicon dark matter detectors". United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.astropartphys.2018.02.005. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1420890.
@article{osti_1420890,
title = {Naturally occurring 32Si and low-background silicon dark matter detectors},
author = {Orrell, John L. and Arnquist, Isaac J. and Bliss, Mary and Bunker, Raymond and Finch, Zachary S.},
abstractNote = {Here, the naturally occurring radioisotope 32Si represents a potentially limiting background in future dark matter direct-detection experiments. We investigate sources of 32Si and the vectors by which it comes to reside in silicon crystals used for fabrication of radiation detectors. We infer that the 32Si concentration in commercial single-crystal silicon is likely variable, dependent upon the specific geologic and hydrologic history of the source (or sources) of silicon “ore” and the details of the silicon-refinement process. The silicon production industry is large, highly segmented by refining step, and multifaceted in terms of final product type, from which we conclude that production of 32Si-mitigated crystals requires both targeted silicon material selection and a dedicated refinement-through-crystal-production process. We review options for source material selection, including quartz from an underground source and silicon isotopically reduced in 32Si. To quantitatively evaluate the 32Si content in silicon metal and precursor materials, we propose analytic methods employing chemical processing and radiometric measurements. Ultimately, it appears feasible to produce silicon detectors with low levels of 32Si, though significant assay method development is required to validate this claim and thereby enable a quality assurance program during an actual controlled silicon-detector production cycle.},
doi = {10.1016/j.astropartphys.2018.02.005},
journal = {Astroparticle Physics},
number = ,
volume = 99,
place = {United States},
year = {Sat Feb 10 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Sat Feb 10 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
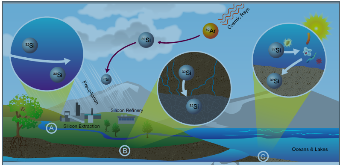 Figure 1: Conjectured transport and accumulation of cosmogenically created 32Si in the terrestrial environment. Cosmic rays interact with 40Ar in the atmosphere to spallate 32Si that is then transported into the terrestrial environment via precipitation, leading to accumulation of 32Si in: A) streams and settling ponds that may be sourcesmore »
Figure 1: Conjectured transport and accumulation of cosmogenically created 32Si in the terrestrial environment. Cosmic rays interact with 40Ar in the atmosphere to spallate 32Si that is then transported into the terrestrial environment via precipitation, leading to accumulation of 32Si in: A) streams and settling ponds that may be sourcesmore »
Works referenced in this record:
From Metallurgical-Grade to Solar-Grade Silicon: An Overview
journal, April 2017
- Chigondo, Fidelis
- Silicon, Vol. 10, Issue 3
Cosmogenic Activation of Materials Used in Rare Event Search Experiments
text, January 2016
- Zhang, C.; Mei, D. -M.; Kudryavtsev, V. A.
- arXiv
Coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering
journal, May 2015
- Scholberg, Kate
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 606
Low-Radioactivity Background Techniques
journal, December 1995
- Heusser, G.
- Annual Review of Nuclear and Particle Science, Vol. 45, Issue 1
Erratum: Reliability of usual assumptions in the calculation of and spectra [Phys. Rev. C 91 , 055504 (2015)]
journal, November 2015
- Mougeot, X.
- Physical Review C, Vol. 92, Issue 5
Neutral current coherent cross-sections — Implications on detecting SN and earth neutrinos with gaseous spherical TPC’s
journal, January 2017
- Vergados, J. D.; Giomataris, Y.
- International Journal of Modern Physics E, Vol. 26, Issue 01n02
Large-mass ultralow noise germanium detectors: performance and applications in neutrino and astroparticle physics
journal, September 2007
- Barbeau, P. S.; Collar, J. I.; Tench, O.
- Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 2007, Issue 09
Spur im Kristall: Erstmals Spur eines einzelnen hochenergetischen schweren Ions in Halbleiter beobachtet/Silizium-28-Einkristall für die metrologische Forschung/Hochtemperatur-Supraleiter: Ihr Potential für technische Anwendungen/Weltrekord im HLRZ/KASCAD
journal, January 1993
- Dreisigacker, E.; Seyfried, P.; Härtwich, P.
- Physik Journal, Vol. 49, Issue 1
Nuclear Data Sheets for A = 28
journal, October 2013
- Shamsuzzoha Basunia, M.
- Nuclear Data Sheets, Vol. 114, Issue 10
Silicon-32 as a tool for dating the recent past
journal, October 2009
- Fifield, L. Keith; Morgenstern, Uwe
- Quaternary Geochronology, Vol. 4, Issue 5
Precision determination of weak charge of $^{133}$Cs from atomic parity violation
text, January 2010
- Porsev, S. G.; Beloy, K.; Derevianko, A.
- arXiv
Limits on Spin-Independent Interactions of Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with Nucleons from the Two-Tower Run of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search
journal, January 2006
- Akerib, D. S.; Attisha, M. J.; Bailey, C. N.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 96, Issue 1
Review of mathematics, numerical factors, and corrections for dark matter experiments based on elastic nuclear recoil
journal, December 1996
- Lewin, J. D.; Smith, P. F.
- Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 6, Issue 1
Measurement of the cosmogenic activation of germanium detectors in EDELWEISS-III
journal, May 2017
- Armengaud, E.; Arnaud, Q.; Augier, C.
- Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 91
Radiopurity of CaWO4 crystals for direct dark matter search with CRESST and EURECA
journal, May 2014
- Münster, A.; Sivers, M. v.; Angloher, G.
- Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 2014, Issue 05
Cosmogenic radionuclide production in NaI(Tl) crystals
journal, February 2015
- Amaré, J.; Cebrián, S.; Cuesta, C.
- Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 2015, Issue 02
Measurement of radioactive contamination in the high-resistivity silicon CCDs of the DAMIC experiment
journal, August 2015
- Aguilar-Arevalo, A.; Amidei, D.; Bertou, X.
- Journal of Instrumentation, Vol. 10, Issue 08
Large-mass ultralow noise germanium detectors: performance and applications in neutrino and astroparticle physics
journal, September 2007
- Barbeau, P. S.; Collar, J. I.; Tench, O.
- Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 2007, Issue 09
Cosmogenic activation of materials
journal, October 2017
- Cebrián, Susana
- International Journal of Modern Physics A, Vol. 32, Issue 30
Limits on Sensitivity of Large Silicon Bolometers for Solar Neutrino Detection
journal, July 1987
- Martoff, C. J.
- Science, Vol. 237, Issue 4814
Silicon for ultra-low-level detectors and 32Si
journal, November 1991
- Plaga, R.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 309, Issue 3
‘Dating’ Ground Waters of Ages Younger than 1,000–1,500 Years Using Natural Silicon-32
journal, April 1966
- Nijampurkar, V. N.; Amin, B. S.; Kharkar, D. P.
- Nature, Vol. 210, Issue 5035
Low-Radioactivity Background Techniques
journal, December 1995
- Heusser, G.
- Annual Review of Nuclear and Particle Science, Vol. 45, Issue 1
Searching for the cosmion by scattering in Si detectors
journal, September 1990
- Caldwell, D.; Magnusson, B.; Witherell, M.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 65, Issue 11
Cosmic-Ray-ProducedSi 32
journal, October 1959
- Lal, Devendra; Goldberg, Edward D.; Koide, Minoru
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 3, Issue 8
An overview of five decades of studies of cosmic ray produced nuclides in oceans
journal, September 1999
- Lal, D.
- Science of The Total Environment, Vol. 237-238
Cosmic ray labeling of erosion surfaces: in situ nuclide production rates and erosion models
journal, June 1991
- Lal, D.
- Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 104, Issue 2-4
Terrestrial in situ cosmogenic nuclides: theory and application
journal, August 2001
- Gosse, John C.; Phillips, Fred M.
- Quaternary Science Reviews, Vol. 20, Issue 14
Paradox lost: silicon 32 and the global ocean silica cycle
journal, February 2000
- Craig, H.; Somayajulu, B. L. K.; Turekian, K. K.
- Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 175, Issue 3-4
Twin cosmogenic radiotracer studies of phosphorus recycling and chemical fluxes in the upper ocean
journal, January 1988
- Lal, D.; Chung, Y.; Platt, T.
- Limnology and Oceanography, Vol. 33, Issue 6_part_2
Nuclear Data Sheets for A = 32
journal, September 2011
- Ouellet, Christian; Singh, Balraj
- Nuclear Data Sheets, Vol. 112, Issue 9
Silica in soil Solutions: ii. the Adsorption of Monosilicic acid by soil and by Other Substances
journal, January 1963
- McKeague, J. A.; Cline, M. G.
- Canadian Journal of Soil Science, Vol. 43, Issue 1
The chemistry of silica surfaces
journal, January 1955
- Holt, P. F.; King, D. T.
- Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed)
New processes for the production of solar-grade polycrystalline silicon: A review
journal, April 2008
- Braga, A. F. B.; Moreira, S. P.; Zampieri, P. R.
- Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, Vol. 92, Issue 4
Development of fluidized bed reactors for silicon production
journal, December 2010
- Filtvedt, W. O.; Javidi, M.; Holt, A.
- Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, Vol. 94, Issue 12
Czochralski growth of silicon
journal, December 1983
- Zulehner, W.
- Journal of Crystal Growth, Vol. 65, Issue 1-3
Simulation of large-scale silicon melt flow in magnetic Czochralski growth
journal, August 2002
- Savolainen, V.; Heikonen, J.; Ruokolainen, J.
- Journal of Crystal Growth, Vol. 243, Issue 2
Growth in global materials use, GDP and population during the 20th century
journal, August 2009
- Krausmann, Fridolin; Gingrich, Simone; Eisenmenger, Nina
- Ecological Economics, Vol. 68, Issue 10
32Si in limestone aquifers
journal, February 1995
- Morgenstern, U.; Gellermann, R.; Hebert, D.
- Chemical Geology, Vol. 120, Issue 1-2
Geant4—a simulation toolkit
journal, July 2003
- Agostinelli, S.; Allison, J.; Amako, K.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 506, Issue 3
Geant4 developments and applications
journal, February 2006
- Allison, J.; Amako, K.; Apostolakis, J.
- IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, Vol. 53, Issue 1
Extension of the Liège Intra Nuclear Cascade model to light ion-induced collisions for medical and space applications
journal, March 2013
- Leray, S.; Mancusi, D.; Kaitaniemi, P.
- Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 420
Cosmogenic activation of materials used in rare event search experiments
journal, November 2016
- Zhang, C.; Mei, D. -M.; Kudryavtsev, V. A.
- Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 84
Measurement of the flux and energy spectrum of cosmic-ray induced neutrons on the ground
journal, December 2004
- Gordon, M. S.; Goldhagen, P.; Rodbell, K. P.
- IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, Vol. 51, Issue 6
Fully depleted, back-illuminated charge-coupled devices fabricated on high-resistivity silicon
journal, January 2003
- Holland, S. E.; Groom, D. E.; Palaio, N. P.
- IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, Vol. 50, Issue 1
Cryogenic Dark Matter Search detector fabrication process and recent improvements
journal, February 2015
- Jastram, A.; Harris, H. R.; Mahapatra, R.
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment, Vol. 772
Atomic weights of the elements. Review 2000 (IUPAC Technical Report)
journal, January 2003
- de Laeter, John R.; Böhlke, John Karl; De Bièvre, P.
- Pure and Applied Chemistry, Vol. 75, Issue 6
The silicon-28 path to the Avogadro constant-first experiments and outlook
journal, April 1995
- Becker, P.; Bettin, H.; De Bievre, P.
- IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, Vol. 44, Issue 2
Realization of the kilogram by the XRCD method
journal, September 2016
- Fujii, Kenichi; Bettin, Horst; Becker, Peter
- Metrologia, Vol. 53, Issue 5
Direct determination of the mass of28Si as a contribution to a new definition of the kilogram
journal, October 1993
- Jertz, R.; Beck, D.; Bollen, G.
- Physica Scripta, Vol. 48, Issue 4
Enrichment of silicon for a better kilogram
journal, January 2010
- Becker, P.; Pohl, H. -J.; Riemann, H.
- physica status solidi (a), Vol. 207, Issue 1
Purity of 28Si-Enriched Silicon Material Used for the Determination of the Avogadro Constant
journal, June 2016
- D’Agostino, Giancarlo; Di Luzio, Marco; Mana, Giovanni
- Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 88, Issue 13
Mass Spectrometric Investigation of Silicon Extremely Enriched in 28Si: From 28SiF4 (Gas Phase IRMS) to 28Si Crystals (MC-ICP-MS)
journal, May 2016
- Pramann, Axel; Rienitz, Olaf
- Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 88, Issue 11
Large-scale production of highly enriched28Si for the precise determination of the Avogadro constant
journal, June 2006
- Becker, P.; Schiel, D.; Pohl, H-J
- Measurement Science and Technology, Vol. 17, Issue 7
Probing the homogeneity of the isotopic composition and molar mass of the ‘Avogadro’-crystal
journal, October 2015
- Pramann, Axel; Lee, Kyoung-Seok; Noordmann, Janine
- Metrologia, Vol. 52, Issue 6
Measurement background and the sediment age-dating reach of 32Si
journal, November 2015
- Keillor, Martin E.; Aalseth, Craig E.; Arrigo, Leah M.
- Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 307, Issue 3
Toward sufficient reduction of radio-impurities for 32Si sediment age dating
journal, December 2015
- Finch, Z. S.; Seiner, B. N.; Arrigo, L. M.
- Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 307, Issue 3
Silicon-32 as a tool for dating the recent past
journal, October 2009
- Fifield, L. Keith; Morgenstern, Uwe
- Quaternary Geochronology, Vol. 4, Issue 5
32Si dating of sediments from Lake Baikal
journal, May 2013
- Morgenstern, U.; Ditchburn, R. G.; Vologina, E. G.
- Journal of Paleolimnology, Vol. 50, Issue 3
The half life of32Si determined from a varved Gulf of California sediment core
journal, June 1980
- Demaster, David J.
- Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 48, Issue 1
Measurement of Cosmogenic 32P and 33P Activities in Rainwater and Seawater
journal, January 1998
- Benitez-Nelson, Claudia R.; Buesseler, Ken O.
- Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 70, Issue 1
An interlaboratory comparison for the measurement of biogenic silica in sediments
journal, December 1998
- Conley, Daniel J.
- Marine Chemistry, Vol. 63, Issue 1-2
Determination of Impurities in Silicon by Neutron Activation Analysis
journal, December 1956
- Kant, Arthur.; Cali, J. P.; Thompson, H. D.
- Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 28, Issue 12
Study on the Mechanism of Silicon Etching in HNO3-Rich HF/HNO3 Mixtures
journal, January 2007
- Steinert, M.; Acker, J.; Oswald, S.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, Vol. 111, Issue 5
Chemical Etching of Silicon
journal, January 1961
- Schwartz, B.; Robbins, H.
- Journal of The Electrochemical Society, Vol. 108, Issue 4
The design, construction, and initial characterization of an ultra-low-background gas-proportional counting system
journal, August 2012
- Seifert, A.; Aalseth, C. E.; Day, A. R.
- Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 296, Issue 2
Determination of phosphorus and arsenic in trichlorosilane by electrothermal vaporization-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with prior concentration by cuprous chloride
journal, January 1995
- Wei, Wen-Ching; Yang, Mo-Hsiung
- Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, Vol. 353, Issue 2
Vacuum Refining of Molten Silicon
journal, September 2012
- Safarian, Jafar; Tangstad, Merete
- Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, Vol. 43, Issue 6
Phosphorus Removal from Silicon by Vacuum Refining and Directional Solidification
journal, October 2013
- Jiang, Dachuan; Ren, Shiqiang; Shi, Shuang
- Journal of Electronic Materials, Vol. 43, Issue 2
Evaporation Behavior of Phosphorus from Metallurgical Grade Silicon via Calcium-Based Slag Treatment and Hydrochloric Acid Leaching
journal, November 2015
- Huang, Liuqing; Lai, Huixian; Lu, Chenghao
- Journal of Electronic Materials, Vol. 45, Issue 1
A network of neutral current spherical TPCs for dedicated supernova detection
journal, March 2006
- Giomataris, Y.; Vergados, J. D.
- Physics Letters B, Vol. 634, Issue 1
Model-independent form factors for spin-independent neutralino–nucleon scattering from elastic electron scattering data
journal, April 2007
- Dūda, Gintaras; Kemper, Ann; Gondolo, Paolo
- Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 2007, Issue 04
The ground-state charge distribution of the silicon isotopes and the excited states of28Si,30Si
journal, June 1977
- Brain, S. W.; Johnston, A.; Gillespie, W. A.
- Journal of Physics G: Nuclear Physics, Vol. 3, Issue 6
Nuclear Data Sheets for A = 28
journal, October 2013
- Shamsuzzoha Basunia, M.
- Nuclear Data Sheets, Vol. 114, Issue 10
A model of nuclear recoil scintillation efficiency in noble liquids
journal, August 2008
- Mei, D. -M.; Yin, Z. -B.; Stonehill, L. C.
- Astroparticle Physics, Vol. 30, Issue 1
32Si in precipitation: evaluation of temporal and spatial variation and as dating tool for glacial ice
journal, October 1996
- Morgenstern, U.; Taylor, C. B.; Parrat, Y.
- Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 144, Issue 1-2
Advances in separation methods for large-scale production of silicon isotopes
journal, February 2015
- Wang, Caijiao; Bai, Peng; Guo, Xianghai
- Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, Vol. 304, Issue 3
Monoisotopic varieties of silicon and germanium with a high chemical and isotopic purity
journal, February 2013
- Churbanov, M. F.; Gusev, A. V.; Bulanov, A. D.
- Russian Chemical Bulletin, Vol. 62, Issue 2
Figures / Tables found in this record:

 Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal
Search WorldCat to find libraries that may hold this journal