Energy-Dispersive X-ray Diffraction: Operando Visualization of Electrochemical Activity of Thick Electrodes
- Stony Brook Univ., Stony Brook, NY (United States)
- Univ. of Massachusetts, Lowell, MA (United States); Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Stony Brook Univ., Stony Brook, NY (United States); The City College of New York, New York, NY (United States)
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States); Muhlenberg College, Allentown, PA (United States)
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Stony Brook Univ., Stony Brook, NY (United States); Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
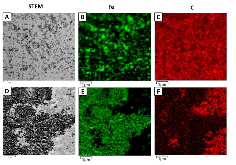
Effective utilization of the electroactive material in thick electrodes could enable Li-based batteries to be developed with higher energy densities while simultaneously reducing the overall cost of the battery. Herein, we explore the lithiation of a multiple electron transfer conversion material, Fe3O4, and report tomographic-like mapping of the electroactive material utilization under operando electrochemical lithiation using energy-dispersive X-ray diffraction. A challenge for thick electrodes is limited Li+ diffusion resulting in an inability to fully access the active material. Our strategy to surmount this obstacle is the deliberate incorporation of acicular carbon nanotubes to the electrode where the design maximized the electron and ion access to the Fe3O4 active material within a thick electrode (~500 μm). Based on whole pattern fitting of the diffraction data, the phase composition was determined with both spatial and temporal resolutions. The data allow identification of the electrochemical conversion products, Li2O and Fe metal, where interestingly, the Li2O crystallites increase in size after initial formation. The observation of increased crystallite size of Li2O after initial formation provides new insight into the time-dependent phenomena of conversion-type active materials and their reversibility. As a result, this investigation contributes to our understanding of Li+ transport in thick electrodes and provides insight into the design of battery electrodes that facilitate electroactive material utilization of energy storage systems crucial for the development of next-generation batteries.
- Research Organization:
- Energy Frontier Research Centers (EFRC) (United States). Center for Mesoscale Transport Properties (m2mt); Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Workforce Development for Teachers and Scientists (WDTS)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704; AC02-06CH113; SC0012673
- OSTI ID:
- 1580219
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-212439-2019-JAAM
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Physical Chemistry. C, Vol. 123, Issue 31; ISSN 1932-7447
- Publisher:
- American Chemical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
High capacity vanadium oxide electrodes: effective recycling through thermal treatment
Electrochemically Induced Phase Evolution of Lithium Vanadium Oxide: Complementary Insights Gained via Ex-Situ, In-Situ, and Operando Experiments and Density Functional Theory