Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Cd, In and Sn Effects on a 15%Co/Al2O3 Catalyst
- Univ. of Kentucky, Lexington, KY (United States)
- Univ. of Kentucky, Lexington, KY (United States); Univ. of Texas at San Antonio, TX (United States)
- Univ. of Kentucky, Lexington, KY (United States); Asbury Univ., Wilmore, KY (United States)
- NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, OH (United States)
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
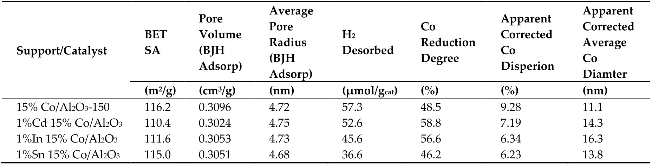
The effects of 1% of Cd, In and Sn additives on the physicochemical properties and Fischer-Tropsch synthesis (FTS) performance of a 15% Co/Al2O3 catalyst were investigated. The fresh and spent catalysts were characterized by BET, temperature programmed reduction (TPR), H2-chemisorption, NH3 temperature programmed desorption (TPD), X-ray absorption near edge spectroscopy (XANES), and X ray diffraction (XRD). The catalysts were tested in a 1 L continuously stirred tank reactor (CSTR) at 220 °C, 2.2 MPa, H2/CO = 2.1 and 20–55% CO conversion. Addition of 1% of Cd or In enhanced the reduction degree of 15%Co/Al2O3 by ~20%, while addition of 1% Sn slightly hindered it. All three additives adversely impacted Co dispersion by 22–32% by increasing apparent Co cluster size based on the H2-chemisorption measurements. However, the decreased Co active site density resulting from the additives did not result in a corresponding activity loss; instead, the additives decreased the activity of the Co catalysts to a much greater extent than expected, i.e., 82–93%. The additional detrimental effect on catalyst activity likely indicates that the Cd, In and Sn additives migrated to and covered active sites during reaction and/or provided an electronic effect. XANES results showed that oxides of the additives were present during the reaction, but that a fraction of metal was also likely present based on the TPR and reaction testing results. This is in contrast to typical promoters that become metallic at or below ~350 °C, such as noble metal promoters (e.g., Pt, Ru) and Group 11 promoters (e.g., Ag, Au) on Co catalysts in earlier studies. In the current work, all three additives remarkably increased CH4 and CO2 selectivities and decreased C5+ selectivity, with the Sn and In additives having a greater effect. Interestingly, the Cd, In, or Sn additives were found to influence hydrogenation and isomerization activities. At a similar conversion level (i.e., in the range of 40–50%), the additives significantly increased 2-C4 olefin content from 3.8 to 10.6% and n-C4 paraffin from 50 to 61% accompanied by decreases in 1-C4 olefin content from 48 to 30%. The Sn contributed the greatest impact on the secondary reactions of 1-olefins, followed by the In and Cd. NH3-TPD results suggest enhanced acid sites on cobalt catalysts resulting from the additives, which likely explains the change in selectivities for the different catalysts.
- Research Organization:
- Brookhaven National Lab. (BNL), Upton, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0012704
- OSTI ID:
- 1571413
- Report Number(s):
- BNL-212223-2019-JAAM; CATACJ; TRN: US2001124
- Journal Information:
- Catalysts, Vol. 9, Issue 10; ISSN 2073-4344
- Publisher:
- MDPICopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Editorial: Cobalt and Iron Catalysis
|
journal | December 2019 |
Similar Records
Mo-Fe catalysts supported on activated carbon for synthesis of liquid fuels by the Fischer-Tropsch process: effect of Mo addition on reducibility, activity, and hydrocarbon selectivity
Effect of basic additives on Pt/Al{sub 2}O{sub 3} for CO and propylene oxidation under oxygen-deficient conditions