Pellet fueling experiments in Wendelstein 7-X
- Max-Planck Inst. fuer Plasmaphysik IPP, Greifswald (Germany)
- CIEMAT, Madrid (Spain)
- LPP-ERM/KMS, Brussels (Belgium)
- Max-Planck Inst. fuer Plasmaphysik IPP, Garching (Germany)
- Atominstitut TU Wien, Vienna (Austria)
- Wigner Research Centre for Physiks, Budapest (Hungary)
- Princeton Plasma Physics Lab. (PPPL), Princeton, NJ (United States)
- Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison, WI (United States)
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
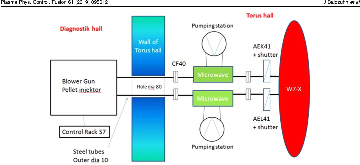
During the two most recent experimental campaigns in the advanced stellarator Wendelstein 7-X (W7-X) (Klinger et al 2017 Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 59 014018; Bosch et al 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 116015; Wolf et al 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 102020; Pedersen et al 2017 Phys. Plasmas 24 0555030) hydrogen ice pellet injection was performed for the first time. In order to investigate the potential of pellet fueling in W7-X and to study the particle deposition in a large stellarator, a blower-gun system was installed with 40 pellets capability. The experience gained with this system will be used for the specification of a future steady-state pellet injector system. One important motivation for a pellet injector (Dibon 2014 Master-Thesis Technical University Munich, Max-Planck Institut IPP) on W7-X is the mitigation of hollow density profiles expected in case of predominant neoclassical transport. For long-pulse operation of up to 30 min, only electron cyclotron resonance heating is available on W7-X. Hence, pellet injection will be the only source for deep particle fueling. Deep particle fueling by pellets in tokamaks is supported by a grad-B drift, if the pellets are injected from the magnetic high-field-side. This approach was tested in W7-X, as well. The injection of series of pellets was also tested. Here, deep fueling is supported for later pellets in the series by the plasma cooling following the initial pellets in the same series. As in earlier experiments in the heliotron LHD (Takeiri et al 2017 Nucl. Fusion 57 102023), deep and rapid fueling could be achieved successfully in W7-X.
- Research Organization:
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- Foreign Funding; USDOE
- Contributing Organization:
- Wendelstein 7-X Team
- Grant/Contract Number:
- 89233218CNA000001
- OSTI ID:
- 1569618
- Report Number(s):
- LA-UR-19-23947; TRN: US2100273
- Journal Information:
- Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, Vol. 61, Issue 9; ISSN 0741-3335
- Publisher:
- IOP ScienceCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Ion temperature clamping in Wendelstein 7-X electron cyclotron heated plasmas
Enhanced energy confinement after series of pellets in Wendelstein 7-X