Several Levels of Theory for Description of Isotope Effects in Ozone: Symmetry Effect and Mass Effect
- Marquette Univ., Milwaukee, WI (United States). Dept. of Chemistry; Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States). Theoretical Div. (T-1, MS B221)
- Marquette Univ., Milwaukee, WI (United States). Dept. of Chemistry
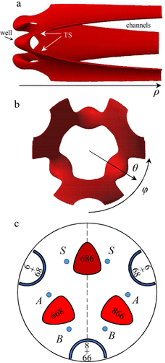
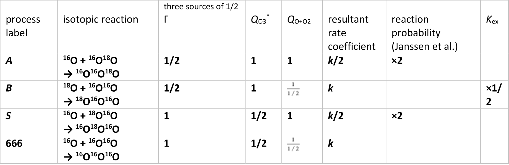
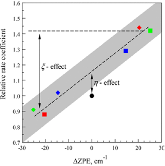
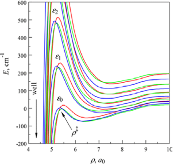
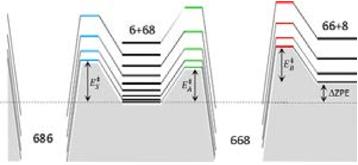
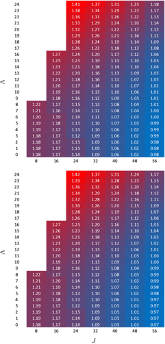
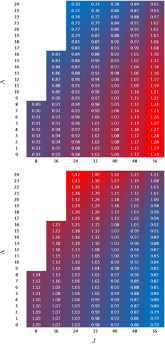
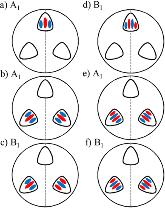
The essential components of theory for the description of isotope effects in recombination reaction that forms ozone are presented, including the introduction of three reaction pathways for symmetric and asymmetric isotopomers, a brief review of relevant experimental data for singly- and doubly substituted isotopologues, the definitions of ζ-effect and η-effect, and the introduction of isotopic enrichment δ. Two levels of theory are developed to elucidate the role of molecular symmetry, atomic masses, vibrational zero-point energies, and rotational excitations in the recombination process. Here, the issue of symmetry is not trivial, since the important factors, such as 1/2 and 2, appear in seven different places in the formalism. It is demonstrated that if all these effects are taken into account properly, then no anomalous isotope effects emerge. At the next level of theory, a model is considered in which one scattering resonance (sitting right at the top of centrifugal barrier) is introduced per ro-vibrational channel. It is found that this approach is equivalent to statistical treatment with partition functions at the transition state. Accurate calculations using hyper-spherical coordinates show that no isotope effects come from difference in the number of states. In contrast, differences in vibrational and rotational energies lead to significant isotope effects. However, those effects appear to be local, found for the rather extreme values of rotational quantum numbers. They largely cancel when rate coefficients are computed for the thermal distribution of rotational excitations. Although large isotope effects (observed in experiments) are not reproduced here, this level of theory can be used as a foundation for more detailed computational treatment, with accurate information about resonance energies and lifetimes computed and included.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States). National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC); Univ. of California, Oakland, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- OSTI ID:
- 1543638
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Physical Chemistry. A, Molecules, Spectroscopy, Kinetics, Environment, and General Theory, Vol. 122, Issue 47; ISSN 1089-5639
- Publisher:
- American Chemical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
On stabilization of scattering resonances in recombination reaction that forms ozone
Theoretical Treatment of the Coriolis Effect Using Hyperspherical Coordinates, with Application to the Ro-Vibrational Spectrum of Ozone