OEDGE modeling for the planned tungsten ring experiment on DIII-D
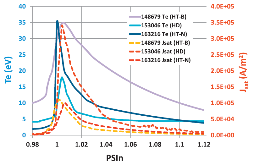
The OEDGE code is used to model tungsten erosion and transport for DIII-D experiments with toroidal rings of high-Z metal tiles. Such modeling is needed for both experimental and diagnostic design to have estimates of the expected core and edge tungsten density and to understand the various factors contributing to the uncertainties in these calculations. OEDGE simulations are performed using the planned experimental magnetic geometries and plasma conditions typical of both L-mode and inter-ELM H-mode discharges in DIII-D. OEDGE plasma reconstruction based on specific representative discharges for similar geometries is used to determine the plasma conditions applied to tungsten plasma impurity simulations. We developed a new model for tungsten erosion in OEDGE which imports charge-state resolved carbon impurity fluxes and impact energies from a separate OEDGE run which models the carbon production, transport and deposition for the same plasma conditions as the tungsten simulations. Furthermore, these values are then used to calculate the gross tungsten physical sputtering due to carbon plasma impurities which is then added to any sputtering by deuterium ions; tungsten self-sputtering is also included. The code results are found to be dependent on the following factors: divertor geometry and closure, the choice of cross-field anomalous transport coefficients, divertor plasma conditions (affecting both tungsten source strength and transport), the choice of tungsten atomic physics data used in the model (in particular sviz(Te) for W-atoms), and the model of the carbon flux and energy used for 2 calculating the tungsten source due to sputtering. The core tungsten density is found to be of order 1015 m-3 (excluding effects of any core transport barrier and with significant variability depending on the other factors mentioned) with density decaying into the scrape off layer.
- Research Organization:
- General Atomics, San Diego, CA (United States); Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Nuclear Energy (NE); USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES); USDOE National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-06OR23100; FC02-04ER54698; AC52007NA27344; FG02-07ER54917; AC05-00OR22725; AC04-94AL85000; AC52-07NA27344; AC52-007NA27344
- OSTI ID:
- 1471775
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1374999; OSTI ID: 1474376; OSTI ID: 1530090
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-752152; S2352179116301983; PII: S2352179116301983
- Journal Information:
- Nuclear Materials and Energy, Journal Name: Nuclear Materials and Energy Vol. 12 Journal Issue: C; ISSN 2352-1791
- Publisher:
- ElsevierCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- Netherlands
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Tungsten–carbon surface evolution and erosion modeling for a small angle slot divertor in DIII-D
Modeling the effect of nitrogen recycling on the erosion and leakage of tungsten impurities from the SAS-VW divertor in DIII-D during nitrogen gas injection