Axial magnetic field injection in magnetized liner inertial fusion
- Univ. of Rochester, Rochester, NY (United States)
- Cornell Univ., Ithaca, NY (United States)
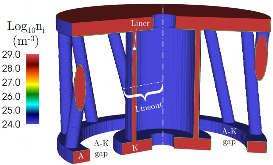
MagLIF is a fusion concept using a Z-pinch implosion to reach thermonuclear fusion. In current experiments, the implosion is driven by the Z-machine using 19 MA of electrical current with a rise time of 100 ns. MagLIF requires an initial axial magnetic field of 30 T to reduce heat losses to the liner wall during compression and to confine alpha particles during fusion burn. This field is generated well before the current ramp starts and needs to penetrate the transmission lines of the pulsed-power generator, as well as the liner itself. Consequently, the axial field rise time must exceed hundreds of microseconds. Any coil capable of being submitted to such a field for that length of time is inevitably bulky. The space required to fit the coil near the liner, increases the inductance of the load. In turn, the total current delivered to the load decreases since the voltage is limited by driver design. Yet, the large amount of current provided by the Z-machine can be used to produce the required 30 T field by tilting the return current posts surrounding the liner, eliminating the need for a separate coil. However, the problem now is the field penetration time, across the liner wall. This paper discusses why skin effect arguments do not hold in the presence of resistivity gradients. Numerical simulations show that fields larger than 30 T can diffuse across the liner wall in less than 60 ns, demonstrating that external coils can be replaced by return current posts with optimal helicity.
- Research Organization:
- Univ. of Rochester, NY (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Advanced Research Projects Agency - Energy (ARPA-E)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0016252; AR000056
- OSTI ID:
- 1515030
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1406140
- Journal Information:
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 24, Issue 10; ISSN 1070-664X
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
The generation of mega-gauss fields on the Cornell beam research accelerator
|
journal | September 2018 |
Enhancing cylindrical compression by reducing plasma ablation in pulsed-power drivers
|
journal | April 2019 |
Design of dynamic screw pinch experiments for magnetized liner inertial fusion
|
journal | October 2019 |
Similar Records
Auto-magnetizing liners for magnetized inertial fusion
Three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic modeling of auto-magnetizing liner implosions on the Z accelerator