Hydrogen retention in lithium on metallic walls from “in vacuo” analysis in LTX and implications for high-Z plasma-facing components in NSTX-U
- Princeton Plasma Physics Lab. (PPPL), Princeton, NJ (United States)
- Univ. of Illinois, Urbana, IL (United States). Dept. of Nuclear, Plasma, & Radiological Engineering
- The College of New Jersey, Ewing, NJ (United States). Dept. of Physics
- Princeton Univ., NJ (United States). Dept. of Chemical & Biological Engineering
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
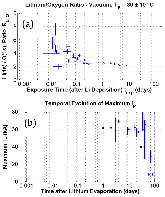
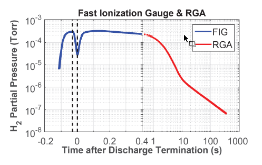
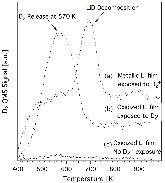
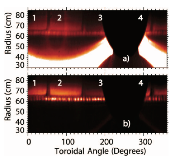
The application of lithium to plasma-facing components (PFCs) has long been used as a technique for wall conditioning in magnetic confinement devices to improve plasma performance. Determining the characteristics of PFCs at the time of exposure to the plasma, however, is difficult because they can only be analyzed after venting the vacuum vessel and removing them at the end of an operational period. The Materials Analysis and Particle Probe (MAPP) addresses this problem here by enabling PFC samples to be exposed to plasmas, and then withdrawn into an analysis chamber without breaking vacuum. The MAPP system was used to introduce samples that matched the metallic PFCs of the Lithium Tokamak Experiment (LTX). Lithium that was subsequently evaporated onto the walls also covered the MAPP samples, which were then subject to LTX discharges. In vacuo extraction and analysis of the samples indicated that lithium oxide formed on the PFCs, but improved plasma performance persisted in LTX. The reduced recycling this suggests is consistent with separate surface science experiments that demonstrated deuterium retention in the presence of lithium oxide films. Since oxygen decreases the thermal stability of the deuterium in the film, the release of deuterium was observed below the lithium deuteride dissociation temperature. This may explain what occurred when lithium was applied to the surface of the NSTX Liquid Lithium Divertor (LLD). The LLD had segments with individual heaters, and the deuterium-alpha emission was clearly lower in the cooler regions. The plan for NSTX-U is to replace the graphite tiles with high-Z PFCs, and apply lithium to their surfaces with lithium evaporation. Experiments with lithium coatings on such PFCs suggest that deuterium could still be retained if lithium compounds form, but limiting their surface temperatures may be necessary.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), Princeton, NJ (United States); Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, IL (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Fusion Energy Sciences (FES)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344; AC02-09CH11466; SC0010717
- OSTI ID:
- 1512618
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1416200
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-771458; 960989
- Journal Information:
- Fusion Engineering and Design, Vol. 117; ISSN 0920-3796
- Publisher:
- ElsevierCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Material Surface Characteristics and Plasma Performance in the Lithium Tokamak Experiment
The impact of lithium wall coatings on NSTX discharges and the engineering of the Lithium Tokamak eXperiment (LTX)