Displacement of WDR5 from Chromatin by a WIN Site Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity
Abstract
The chromatin-associated protein WDR5 is a promising target for pharmacological inhibition in cancer. Drug discovery efforts center on the blockade of the “WIN site” of WDR5, a well-defined pocket that is amenable to small molecule inhibition. Various cancer contexts have been proposed to be targets for WIN site inhibitors, but a lack of understanding of WDR5 target genes and of the primary effects of WIN site inhibitors hampers their utility. Here, by the discovery of potent WIN site inhibitors, we demonstrate that the WIN site links WDR5 to chromatin at a small cohort of loci, including a specific subset of ribosome protein genes. WIN site inhibitors rapidly displace WDR5 from chromatin and decrease the expression of associated genes, causing translational inhibition, nucleolar stress, and p53 induction. Our studies define a mode by which WDR5 engages chromatin and forecast that WIN site blockade could have utility against multiple cancer types.
- Authors:
- more »
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Argonne National Laboratory (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Advanced Photon Source (APS)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC); National Institutes of Health (NIH); Vanderbilt Ingram Cancer Center; Vanderbilt Digestive Disease Research Center; Vanderbilt Vision Research Center; National Cancer Institute (NCI); Robert J. Kleberg, Jr., and Helen C. Kleberg Foundation; Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1547648
- Alternate Identifier(s):
- OSTI ID: 1502226
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-06CH11357; 1S-10RR025677-01; CA68485; DK058404; EY008126; HHSN261200800001E; CA200709; CA211305
- Resource Type:
- Journal Article: Published Article
- Journal Name:
- Cell Reports
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Name: Cell Reports Journal Volume: 26 Journal Issue: 11; Journal ID: ISSN 2211-1247
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- Netherlands
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 59 BASIC BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES; chromatin; WDR5; small molecule inhibitor; ribosomal proteins; cancer; cancer therapy; gene expression; p53; nuclear stress; MLL
Citation Formats
Aho, Erin R., Wang, Jing, Gogliotti, Rocco D., Howard, Gregory C., Phan, Jason, Acharya, Pankaj, Macdonald, Jonathan D., Cheng, Ken, Lorey, Shelly L., Lu, Bin, Wenzel, Sabine, Foshage, Audra M., Alvarado, Joseph, Wang, Feng, Shaw, J. Grace, Zhao, Bin, Weissmiller, April M., Thomas, Lance R., Vakoc, Christopher R., Hall, Matthew D., Hiebert, Scott W., Liu, Qi, Stauffer, Shaun R., Fesik, Stephen W., and Tansey, William P. Displacement of WDR5 from Chromatin by a WIN Site Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity. Netherlands: N. p., 2019.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.047.
Aho, Erin R., Wang, Jing, Gogliotti, Rocco D., Howard, Gregory C., Phan, Jason, Acharya, Pankaj, Macdonald, Jonathan D., Cheng, Ken, Lorey, Shelly L., Lu, Bin, Wenzel, Sabine, Foshage, Audra M., Alvarado, Joseph, Wang, Feng, Shaw, J. Grace, Zhao, Bin, Weissmiller, April M., Thomas, Lance R., Vakoc, Christopher R., Hall, Matthew D., Hiebert, Scott W., Liu, Qi, Stauffer, Shaun R., Fesik, Stephen W., & Tansey, William P. Displacement of WDR5 from Chromatin by a WIN Site Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity. Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.047
Aho, Erin R., Wang, Jing, Gogliotti, Rocco D., Howard, Gregory C., Phan, Jason, Acharya, Pankaj, Macdonald, Jonathan D., Cheng, Ken, Lorey, Shelly L., Lu, Bin, Wenzel, Sabine, Foshage, Audra M., Alvarado, Joseph, Wang, Feng, Shaw, J. Grace, Zhao, Bin, Weissmiller, April M., Thomas, Lance R., Vakoc, Christopher R., Hall, Matthew D., Hiebert, Scott W., Liu, Qi, Stauffer, Shaun R., Fesik, Stephen W., and Tansey, William P. 2019.
"Displacement of WDR5 from Chromatin by a WIN Site Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity". Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.047.
@article{osti_1547648,
title = {Displacement of WDR5 from Chromatin by a WIN Site Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity},
author = {Aho, Erin R. and Wang, Jing and Gogliotti, Rocco D. and Howard, Gregory C. and Phan, Jason and Acharya, Pankaj and Macdonald, Jonathan D. and Cheng, Ken and Lorey, Shelly L. and Lu, Bin and Wenzel, Sabine and Foshage, Audra M. and Alvarado, Joseph and Wang, Feng and Shaw, J. Grace and Zhao, Bin and Weissmiller, April M. and Thomas, Lance R. and Vakoc, Christopher R. and Hall, Matthew D. and Hiebert, Scott W. and Liu, Qi and Stauffer, Shaun R. and Fesik, Stephen W. and Tansey, William P.},
abstractNote = {The chromatin-associated protein WDR5 is a promising target for pharmacological inhibition in cancer. Drug discovery efforts center on the blockade of the “WIN site” of WDR5, a well-defined pocket that is amenable to small molecule inhibition. Various cancer contexts have been proposed to be targets for WIN site inhibitors, but a lack of understanding of WDR5 target genes and of the primary effects of WIN site inhibitors hampers their utility. Here, by the discovery of potent WIN site inhibitors, we demonstrate that the WIN site links WDR5 to chromatin at a small cohort of loci, including a specific subset of ribosome protein genes. WIN site inhibitors rapidly displace WDR5 from chromatin and decrease the expression of associated genes, causing translational inhibition, nucleolar stress, and p53 induction. Our studies define a mode by which WDR5 engages chromatin and forecast that WIN site blockade could have utility against multiple cancer types.},
doi = {10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.047},
url = {https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1547648},
journal = {Cell Reports},
issn = {2211-1247},
number = 11,
volume = 26,
place = {Netherlands},
year = {Fri Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2019},
month = {Fri Mar 01 00:00:00 EST 2019}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
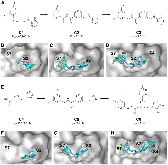 Figure 1: Discovery of Small Molecule WIN Site Inhibitors (A) Elaboration of fragment hit C1 into our firstgeneration chemical probe C3. (B–D) X-ray co-crystal structures of WDR5 bound to (B) the fragment hit C1 (PDB: 6DY7), (C) C2 (PDB: 6E1Y), and (D) C3 (PDB: 6E22). (E) Elaboration of fragment hitmore »
Figure 1: Discovery of Small Molecule WIN Site Inhibitors (A) Elaboration of fragment hit C1 into our firstgeneration chemical probe C3. (B–D) X-ray co-crystal structures of WDR5 bound to (B) the fragment hit C1 (PDB: 6DY7), (C) C2 (PDB: 6E1Y), and (D) C3 (PDB: 6E22). (E) Elaboration of fragment hitmore »
Figures / Tables found in this record: