Evidence of high-n hollow-ion emission from Si ions pumped by ultraintense x-rays from relativistic laser plasma
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States). Theoretical Division
- Osaka Univ., Suita (Japan). Inst. for Academic Initiatives
- Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), Moscow (Russian Federation). Joint Institute for High Temperatures; National Research Nuclear University MEPhl, Moscow (Russian Federation)
- Univ. of York (United Kingdom). Dept. of Physics
- Univ. of Strathclyde, Glasglow (United Kingdom). Dept. of Physics
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States). Theoretical Division
- Univ. of Strathclyde, Glasglow (United Kingdom). Dept. of Physics
- Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), Moscow (Russian Federation). Joint Institute for High Temperatures; Osaka Univ., Suita (Japan). Inst. for Academic Initiatives
- Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), Moscow (Russian Federation). Joint Institute for High Temperatures; National Research Nuclear University MEPhl, Moscow (Russian Federation)
- STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, Oxfordshire (United Kingdom)
- Max Born Institute, Berlin (Germany); ELI-ALPS Research Institute, Szeged (Hungary)
- Friedrich Schiller Univ. Jena, Jena (Germany). Inst. für Optik und Quantenelektronic
- Friedrich Schiller Univ. Jena, Jena (Germany). Inst. für Optik und Quantenelektronic
- Osaka Univ., Suita (Japan)
- Univ. of York (United Kingdom). Dept. of Physics
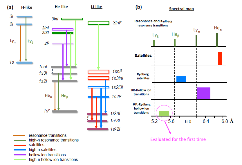
We report on the first observation of high-n hollow ions (ions having no electrons in the K or L shells) produced in Si targets via pumping by ultra-intense x-ray radiation produced in intense laser-plasma interactions reaching the radiation dominant kinetics regime (RDKR). The existence of these new types of hollow ions in high-energy density plasma has been found via observation of highly resolved x-ray emission spectra of silicon plasma. This has been confirmed by plasma kinetics calculations, underscoring the ability of powerful radiation sources to fully strip electrons from the innermost shells of light atoms. Hollow-ions spectral diagnostics provide a unique opportunity to characterize powerful x-ray radiation of laboratory and astrophysical plasmas. With the use of this technique we provide evidence for the existence of the RDKR via observation of asymmetry in the observed radiation of hollow ions from the front and rear sides of the target.
- Research Organization:
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE
- Grant/Contract Number:
- 89233218CNA000001
- OSTI ID:
- 1498043
- Report Number(s):
- LA-UR-16-20472
- Journal Information:
- Europhysics Letters, Vol. 114, Issue 3; ISSN 0295-5075
- Publisher:
- IOP PublishingCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
High resolution X-ray spectra of stainless steel foils irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses with ultra-relativistic intensities
|
journal | January 2017 |
Similar Records
The spectra of the multicharged argon hollow ions: Observation, modeling and using for diagnostics of the early stage of the heating of clusters by a super high contrast femtosecond laser pulses
[Utilizing the ultraintense JanUSP laser at LLNL]. 99-ERD-049 Final LDRD Report