A numerical study of bubble and spike velocities in shock-driven liquid metals
- University of North Carolina, Charlotte, NC (United States)
- Los Alamos National Lab. (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
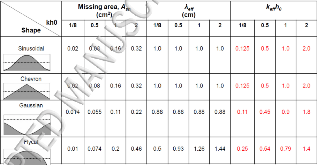
In this study, we use detailed continuum hydrodynamics and molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the dynamics of ejecta that are initialized with large amplitude perturbations and non-sinusoidal shapes. Insights from the simulations are used to suggest a modified expression for the velocity associated with ejected spike structures, whereas a recently suggested model explains the observed bubble velocities. Specifically, we find the asymptotic bubble velocity prediction given by Mikaelian is in excellent agreement with the simulations, when a nonlinear correction for finite amplitudes is used in that model. In contrast, existing models can overpredict observed spike velocities if they do not include the modification of the initial spike growth rates due to nonlinearities. Instead, we find that when potential flow models are corrected with a suitable nonlinear prefactor, this leads to predictions in close agreement with our simulation data. We also propose a simple empirical expression for the nonlinear correction for spike velocities which is able to reproduce results from our simulations and published experimental and simulation data over a wide range of initial conditions and Mach numbers. We discuss extensions of these models to initial interfaces with arbitrary shapes. In particular, for non-sinusoidal shapes, the bubble and spike velocities are still predicted by these models provided we use an effective wavelength λeff which is the wavelength of an equivalent sinusoid that has the same missing area. Lastly, the issues of nonlinearity, non-standard shapes and shock Mach number addressed in this work are relevant to recent experimental campaigns involving twice-shocked targets.
- Research Organization:
- Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL), Los Alamos, NM (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Advanced Research Projects Agency - Energy (ARPA-E)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-06NA25396; AC52-06NA2-5396
- OSTI ID:
- 1479928
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1416841
- Report Number(s):
- LA-UR-17-28876
- Journal Information:
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 123, Issue 2; ISSN 0021-8979
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Molecular dynamics simulations of ejecta production from sinusoidal tin surfaces under supported and unsupported shocks
|
journal | April 2018 |
Peculiarities in breakup and transport process of shock-induced ejecta with surrounding gas
|
journal | May 2019 |
Ejecta velocities in twice-shocked liquid metals under extreme conditions: A hydrodynamic approach
|
journal | July 2019 |
Similar Records
High-resolution simulations and modeling of reshocked single-mode Richtmyer-Meshkov instability. I. Comparison to experimental data and to amplitude growth model predictions
Rarefaction-driven Rayleigh–Taylor instability. Part 2. Experiments and simulations in the nonlinear regime