Architecture for Hard Disk Drives
- International Business and Technology Service, North Oaks, MN (United States)
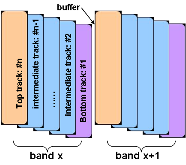
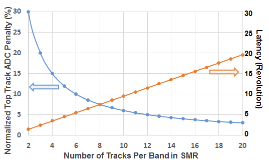
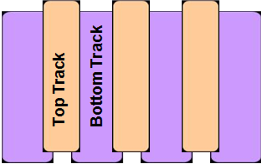
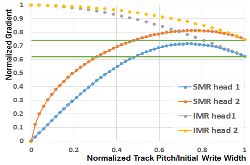
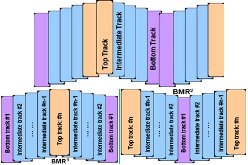
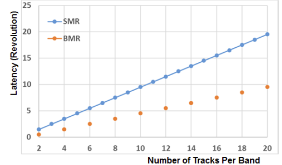
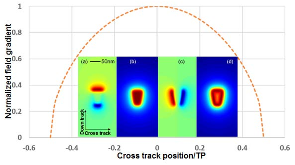
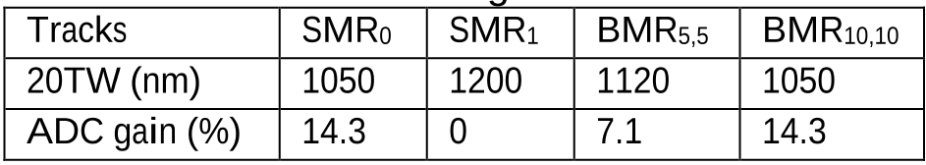
Magnetic data storage has made rapid progress in terms of areal density over the past few decades. Current products have areal density levels that exceed 10(12) bits per square inch, about 1000 times greater than areal densities of the mid-1990s. Five component technologies have become hard-disk-drive industry standards over the past two decades: read heads based on giant magnetoresistance or tunneling magnetoresistance, perpendicular write heads, perpendicular recording media, heaters, and contact detection sensors. At the recording system level, shingled magnetic recording has been implemented by all disk-drive companies, but it has not become a new standard due to the additional penalty in access time (or latency). Here, interlaced magnetic recording and blocked magnetic recording are introduced and compared with conventional and shingled magnetic recording.
- Research Organization:
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-06CH11357
- OSTI ID:
- 1477760
- Journal Information:
- IEEE Magnetics Letters, Vol. 9; ISSN 1949-307X
- Publisher:
- IEEECopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Spinstand demonstration of areal density enhancement using two-dimensional magnetic recording (invited)
Time-resolved scanning Kerr microscopy of flux beam formation in hard disk write heads