Low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect and excellent mechanical properties in a NiMn-based multiferroic alloy
Abstract
Multiferroic magnetic shape memory alloys with first-order magntostructural transformation exhibit much enhanced magnetocaloric effect which incorporates the latent heat associated with the phase transformation itself, but they suffer from the drawbacks of large hysteresis and transformation interval and consequently too high critical field to actuate the magnetocaloric effect, greatly impeding their applications. Here, by generating a kind of specific stacking-mediated structure of martensite through minor Al substitution to improve the geometric compatibility between martensite and austenite in the Ni40Co10Mn40Sn9Al1 alloy, we greatly reduced the thermal hysteresis and transformation temperature interval while conserving the large magnetization difference between the two phases. Consequently, a low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect with isothermal entropy change of 23 J kg–1 K–1 for a field change from 0 to 2 T, which is among the highest values reported heretofore for all magnetocaloric materials, was successfully achieved. Meanwhile, with minor Al substitution, the present single-phase multiferroic alloy that is intermetallic in nature exhibits superior mechanical properties, including excellent compressive properties over a wide temperature range and a relatively high fracture toughness, which are quite beneficial for practical applications. Lastly, by incorporating the advantages of low cost, environment friendliness and easy fabrication, this alloy shows great potential for magnetocaloricmore »
- Authors:
-
- Univ. of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing (People's Republic of China)
- Normandie Univ., Caen (France)
- Institut Neel, Grenoble Cedex (France)
- Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing (People's Republic of China)
- Northeastern Univ., Shenyang (People's Republic of China)
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States)
- Univ. of Duisburg-Essen, Duisburg (Germany)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities; Agence Nationale de la recherche (ANR); Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), State Key Laboratory for Advanced Metals and Materials; USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1466371
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-06CH11357
- Resource Type:
- Journal Article: Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Acta Materialia
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 146; Journal Issue: C; Journal ID: ISSN 1359-6454
- Publisher:
- Elsevier
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 36 MATERIALS SCIENCE; hysteresis; magnetic shape memory alloy; magnetocaloric effect; magnetostructural transformation; martensitic transformation
Citation Formats
Cong, D. Y., Huang, L., Hardy, V., Bourgault, D., Sun, X. M., Nie, Z. H., Wang, M. G., Ren, Y., Entel, P., and Wang, Y. D. Low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect and excellent mechanical properties in a NiMn-based multiferroic alloy. United States: N. p., 2018.
Web. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2017.12.047.
Cong, D. Y., Huang, L., Hardy, V., Bourgault, D., Sun, X. M., Nie, Z. H., Wang, M. G., Ren, Y., Entel, P., & Wang, Y. D. Low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect and excellent mechanical properties in a NiMn-based multiferroic alloy. United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.12.047
Cong, D. Y., Huang, L., Hardy, V., Bourgault, D., Sun, X. M., Nie, Z. H., Wang, M. G., Ren, Y., Entel, P., and Wang, Y. D. 2018.
"Low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect and excellent mechanical properties in a NiMn-based multiferroic alloy". United States. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2017.12.047. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1466371.
@article{osti_1466371,
title = {Low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect and excellent mechanical properties in a NiMn-based multiferroic alloy},
author = {Cong, D. Y. and Huang, L. and Hardy, V. and Bourgault, D. and Sun, X. M. and Nie, Z. H. and Wang, M. G. and Ren, Y. and Entel, P. and Wang, Y. D.},
abstractNote = {Multiferroic magnetic shape memory alloys with first-order magntostructural transformation exhibit much enhanced magnetocaloric effect which incorporates the latent heat associated with the phase transformation itself, but they suffer from the drawbacks of large hysteresis and transformation interval and consequently too high critical field to actuate the magnetocaloric effect, greatly impeding their applications. Here, by generating a kind of specific stacking-mediated structure of martensite through minor Al substitution to improve the geometric compatibility between martensite and austenite in the Ni40Co10Mn40Sn9Al1 alloy, we greatly reduced the thermal hysteresis and transformation temperature interval while conserving the large magnetization difference between the two phases. Consequently, a low-field-actuated giant magnetocaloric effect with isothermal entropy change of 23 J kg–1 K–1 for a field change from 0 to 2 T, which is among the highest values reported heretofore for all magnetocaloric materials, was successfully achieved. Meanwhile, with minor Al substitution, the present single-phase multiferroic alloy that is intermetallic in nature exhibits superior mechanical properties, including excellent compressive properties over a wide temperature range and a relatively high fracture toughness, which are quite beneficial for practical applications. Lastly, by incorporating the advantages of low cost, environment friendliness and easy fabrication, this alloy shows great potential for magnetocaloric applications.},
doi = {10.1016/j.actamat.2017.12.047},
url = {https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1466371},
journal = {Acta Materialia},
issn = {1359-6454},
number = C,
volume = 146,
place = {United States},
year = {Tue Jan 09 00:00:00 EST 2018},
month = {Tue Jan 09 00:00:00 EST 2018}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
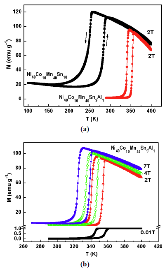 Fig. 1: (a) $M(T)$ curves recorded under 2 T for Ni40Co10Mn40Sn10 and Ni40Co10Mn40Sn9Al1, respectively. (b) M(T) curves recorded under 0.01 T, 2 T, 4 T and 7 T, respectively, for Ni40Co10Mn40Sn9Al1.
Fig. 1: (a) $M(T)$ curves recorded under 2 T for Ni40Co10Mn40Sn10 and Ni40Co10Mn40Sn9Al1, respectively. (b) M(T) curves recorded under 0.01 T, 2 T, 4 T and 7 T, respectively, for Ni40Co10Mn40Sn9Al1.
Works referenced in this record:
Giant Magnetocaloric Effect in
journal, June 1997
- Pecharsky, V. K.; Gschneidner, Jr., K. A.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 78, Issue 23, p. 4494-4497
Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications
journal, January 2002
- Tegus, O.; Brück, E.; Buschow, K. H. J.
- Nature, Vol. 415, Issue 6868
Magnetic refrigerants with continuous phase transitions: Amorphous and nanostructured materials
journal, September 2012
- Franco, V.; Conde, A.
- Scripta Materialia, Vol. 67, Issue 6
Caloric materials near ferroic phase transitions
journal, April 2014
- Moya, X.; Kar-Narayan, S.; Mathur, N. D.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 13, Issue 5
Magnetocaloric materials: The search for new systems
journal, September 2012
- Sandeman, Karl G.
- Scripta Materialia, Vol. 67, Issue 6
Inverse magnetocaloric effect in ferromagnetic Ni–Mn–Sn alloys
journal, May 2005
- Krenke, Thorsten; Duman, Eyüp; Acet, Mehmet
- Nature Materials, Vol. 4, Issue 6
On the determination of the magnetic entropy change in materials with first-order transitions
journal, November 2009
- Caron, L.; Ou, Z. Q.; Nguyen, T. T.
- Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, Vol. 321, Issue 21
Recent Progress in Exploring Magnetocaloric Materials
journal, December 2009
- Shen, B. G.; Sun, J. R.; Hu, F. X.
- Advanced Materials, Vol. 21, Issue 45
Developments in magnetocaloric refrigeration
journal, November 2005
- Brück, Ekkes
- Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Vol. 38, Issue 23
Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials
journal, May 2005
- Gschneidner, K. A.; Pecharsky, V. K.; Tsokol, A. O.
- Reports on Progress in Physics, Vol. 68, Issue 6, p. 1479-1539
The Magnetocaloric Effect and Magnetic Refrigeration Near Room Temperature: Materials and Models
journal, August 2012
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J. S.; Ingale, B.
- Annual Review of Materials Research, Vol. 42, Issue 1
The magnetocaloric effect, magnetic refrigeration and ductile intermetallic compounds
journal, January 2009
- Gschneidner, K. A.
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 57, Issue 1
Caloric Effects in Ferroic Materials: New Concepts for Cooling
journal, November 2011
- Fähler, Sebastian; Rößler, Ulrich K.; Kastner, Oliver
- Advanced Engineering Materials, Vol. 14, Issue 1-2
A review on Mn based materials for magnetic refrigeration: Structure and properties
journal, August 2008
- Brück, E.; Tegus, O.; Cam Thanh, D. T.
- International Journal of Refrigeration, Vol. 31, Issue 5
Materials Challenges for High Performance Magnetocaloric Refrigeration Devices
journal, September 2012
- Smith, Anders; Bahl, Christian R. H.; Bjørk, Rasmus
- Advanced Energy Materials, Vol. 2, Issue 11
Novel Design of La(Fe,Si)13 Alloys Towards High Magnetic Refrigeration Performance
journal, August 2010
- Lyubina, Julia; Schäfer, Rudolf; Martin, Norbert
- Advanced Materials, Vol. 22, Issue 33
Taming the First-Order Transition in Giant Magnetocaloric Materials
journal, February 2014
- Guillou, François; Porcari, Giacomo; Yibole, Hargen
- Advanced Materials, Vol. 26, Issue 17
Direct Measurement of the “Giant” Adiabatic Temperature Change in
journal, September 1999
- Giguère, A.; Foldeaki, M.; Ravi Gopal, B.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 83, Issue 11
Enhanced magnetocaloric effects and tunable thermal hysteresis in transition metal pnictides
journal, September 2012
- Brück, E.; Trung, N. T.; Ou, Z. Q.
- Scripta Materialia, Vol. 67, Issue 6
Metamagnetism Seeded by Nanostructural Features of Single-Crystalline Gd 5 Si 2 Ge 2
journal, October 2009
- Moore, James D.; Morrison, Kelly; Perkins, Garry K.
- Advanced Materials, Vol. 21, Issue 37
Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation
journal, February 2006
- Kainuma, R.; Imano, Y.; Ito, W.
- Nature, Vol. 439, Issue 7079
Giant magnetocaloric effect driven by structural transitions
journal, May 2012
- Liu, Jian; Gottschall, Tino; Skokov, Konstantin P.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 11, Issue 7
Giant magnetic refrigeration capacity near room temperature in Ni 40 Co 10 Mn 40 Sn 10 multifunctional alloy
journal, March 2014
- Huang, L.; Cong, D. Y.; Suo, H. L.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 104, Issue 13
Magnetic Field-Induced Phase Transformation in NiMnCoIn Magnetic Shape-Memory Alloys-A New Actuation Mechanism with Large Work Output
journal, April 2009
- Karaca, Haluk E.; Karaman, Ibrahim; Basaran, Burak
- Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 19, Issue 7
Lattice dynamics in magnetic superelastic Ni-Mn-In alloys: Neutron scattering and ultrasonic experiments
journal, June 2009
- Moya, Xavier; González-Alonso, David; Mañosa, Lluís
- Physical Review B, Vol. 79, Issue 21
Observation of large magnetoresistance of magnetic Heusler alloy Ni50Mn36Sn14 in high magnetic fields
journal, October 2006
- Koyama, Keiichi; Okada, Hironari; Watanabe, Kazuo
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 89, Issue 18
Magnetic superelasticity and inverse magnetocaloric effect in Ni-Mn-In
journal, March 2007
- Krenke, Thorsten; Duman, Eyüp; Acet, Mehmet
- Physical Review B, Vol. 75, Issue 10
Large elastocaloric effect in a Ni–Co–Mn–Sn magnetic shape memory alloy
journal, February 2016
- Yang, Z.; Cong, D. Y.; Huang, L.
- Materials & Design, Vol. 92
Giant solid-state barocaloric effect in the Ni–Mn–In magnetic shape-memory alloy
journal, April 2010
- Mañosa, Lluís; González-Alonso, David; Planes, Antoni
- Nature Materials, Vol. 9, Issue 6
Large Exchange Bias after Zero-Field Cooling from an Unmagnetized State
journal, February 2011
- Wang, B. M.; Liu, Y.; Ren, P.
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 106, Issue 7
Direct measurements of the magnetocaloric effect in pulsed magnetic fields: The example of the Heusler alloy Ni 50 Mn 35 In 15
journal, February 2015
- Ghorbani Zavareh, M.; Salazar Mejía, C.; Nayak, A. K.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 106, Issue 7
Magnetic properties and structural transformations in Ni–Co–Mn–Sn multifunctional alloys
journal, August 2012
- Cong, D. Y.; Roth, S.; Schultz, L.
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 60, Issue 13-14
Enhanced reversibility and unusual microstructure of a phase-transforming material
journal, October 2013
- Song, Yintao; Chen, Xian; Dabade, Vivekanand
- Nature, Vol. 502, Issue 7469
Combinatorial search of thermoelastic shape-memory alloys with extremely small hysteresis width
journal, March 2006
- Cui, Jun; Chu, Yong S.; Famodu, Olugbenga O.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 5, Issue 4
Critical examination of heat capacity measurements made on a Quantum Design physical property measurement system
journal, June 2003
- Lashley, J. C.; Hundley, M. F.; Migliori, A.
- Cryogenics, Vol. 43, Issue 6
Calorimetric investigation of the magnetocaloric effect in Ni 45 Co 5 Mn 37.5 In 12.5
journal, June 2012
- Guillou, F.; Courtois, P.; Porcar, L.
- Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Vol. 45, Issue 25
The “colossal” magnetocaloric effect in Mn1−xFexAs: What are we really measuring?
journal, August 2009
- Balli, Mohamed; Fruchart, Daniel; Gignoux, Damien
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 95, Issue 7
Effect of Co and Cu substitution on the magnetic entropy change in Ni 46 Mn 43 Sn 11 alloy
journal, April 2011
- Das, Rahul; Sarma, S.; Perumal, A.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 109, Issue 7
Ambient pressure colossal magnetocaloric effect tuned by composition in Mn1−xFe x As
journal, September 2006
- de Campos, Ariana; Rocco, Daniel L.; Carvalho, Alexandre Magnus G.
- Nature Materials, Vol. 5, Issue 10
Influence of Ni/Mn concentration on the structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties in Ni 50− x Mn 37+ x Sn 13 Heusler alloys
journal, October 2010
- Muthu, S. Esakki; Rao, N. V. Rama; Raja, M. Manivel
- Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, Vol. 43, Issue 42
Evaluation of Ni–Mn–In–Si Alloys for Magnetic Refrigerant Application
journal, October 2011
- Das, Rahul; Perumal, A.; Srinivasan, A.
- IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, Vol. 47, Issue 10
The effect of microstructure on fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth behavior in γ-titanium aluminide based intermetallics
journal, March 1999
- Campbell, J. P.; Ritchie, R. O.; Venkateswara Rao, K. T.
- Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, Vol. 30, Issue 3
Microstructures and fracture toughness of Ti–(43–48)Al–2Cr–2Nb prepared by electromagnetic cold crucible directional solidification
journal, December 2014
- Wang, Yongzhe; Ding, Hongsheng; Zhang, Hailong
- Materials & Design, Vol. 64
On the fracture and fatigue properties of Mo-Mo3Si-Mo5SiB2 refractory intermetallic alloys at ambient to elevated temperatures (25 °C to 1300 °C)
journal, February 2003
- Choe, H.; Schneibel, J. H.; Ritchie, R. O.
- Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, Vol. 34, Issue 2
Microstructure and mechanical properties of MoSi2 single crystals and directionally solidified MoSi2-Based alloys
journal, January 1997
- Ito, Kazuhiro; Yano, Takayuki; Nakamoto, Takayuki
- Progress in Materials Science, Vol. 42, Issue 1-4
Solidification processing of high temperature intermetallic eutectic-based alloys
journal, February 1995
- Bewlay, B. P.; Lipsitt, H. A.; Jackson, M. R.
- Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 192-193
Elastic and mechanical properties of Nb(Cr,V)2 C15 Laves phases
journal, December 1997
- Thoma, D. J.; Chu, F.; Peralta, P.
- Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 239-240
Microstructural and mechanical characterization of Nb-based in situ composites from Nb–Si–Ti ternary system
journal, November 2007
- Li, Z.; Peng, L. M.
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 55, Issue 19
Thermomagnetic irreversibility in shape-memory alloy
journal, June 2008
- Chatterjee, S.; Giri, S.; Majumdar, S.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 77, Issue 22
In-situ studies of stress- and magnetic-field-induced phase transformation in a polymer-bonded Ni–Co–Mn–In composite
journal, June 2010
- Liu, D. M.; Nie, Z. H.; Wang, G.
- Materials Science and Engineering: A, Vol. 527, Issue 15
Energy barriers and hysteresis in martensitic phase transformations
journal, September 2009
- Zhang, Zhiyong; James, Richard D.; Müller, Stefan
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 57, Issue 15, p. 4332-4352
Identification of Quaternary Shape Memory Alloys with Near-Zero Thermal Hysteresis and Unprecedented Functional Stability
journal, May 2010
- Zarnetta, Robert; Takahashi, Ryota; Young, Marcus L.
- Advanced Functional Materials, Vol. 20, Issue 12
Transmission electron microscopy study of phase compatibility in low hysteresis shape memory alloys
journal, January 2010
- Delville, Rémi; Kasinathan, Sakthivel; Zhang, Zhiyong
- Philosophical Magazine, Vol. 90, Issue 1-4
Microstructure in the cubic to monoclinic transition in titanium–nickel shape memory alloys
journal, July 1999
- Hane, K. F.; Shield, T. W.
- Acta Materialia, Vol. 47, Issue 9
Hysteresis of the martensitic phase transition in magnetocaloric-effect Ni-Mn-Sn alloys
journal, April 2009
- Shamberger, P. J.; Ohuchi, F. S.
- Physical Review B, Vol. 79, Issue 14
Transformation intervals and elastic strain energies of B2-B19′ martensitic transformation of NiTi
journal, December 2010
- Meng, Qinglin; Yang, Hong; Liu, Yinong
- Intermetallics, Vol. 18, Issue 12
Elastic micro-strain energy of austenite–martensite interface in NiTi
journal, January 2012
- Stupkiewicz, S.; Maciejewski, G.; Petryk, H.
- Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, Vol. 20, Issue 3
Influence of stacking-fault energy on high temperature creep of alpha titanium alloys
journal, June 2006
- Guo, Z.; Miodownik, A. P.; Saunders, N.
- Scripta Materialia, Vol. 54, Issue 12
Ferroelastic phase transitions: structure and microstructure
journal, December 2004
- Salje, Ekhard K. H.; Hayward, Stuart A.; Lee, William T.
- Acta Crystallographica Section A Foundations of Crystallography, Vol. 61, Issue 1
Domain boundary-dominated systems: adaptive structures and functional twin boundaries
journal, July 2014
- Viehland, Dwight D.; Salje, Ekhard K. H.
- Advances in Physics, Vol. 63, Issue 4
Works referencing / citing this record:
Magnetocaloric effect near room temperature in quintenary and sextenary Heusler alloys
journal, October 2019
- White, B. D.; Barabash, R. I.; Barabash, O. M.
- Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 126, Issue 16
Tuning the Reversible Magnetocaloric Effect in Ni–Mn–In‐Based Alloys through Co and Cu Co‐Doping
journal, February 2019
- Li, Zongbin; Yang, Jiajing; Li, Dong
- Advanced Electronic Materials
Giant tensile superelasticity originating from two-step phase transformation in a Ni-Mn-Sn-Fe magnetic microwire
journal, September 2018
- Li, F. Q.; Qu, Y. H.; Yan, H. L.
- Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 113, Issue 11
Effect of Si substitution in ferromagnetic Pr 2 Fe 17 : a magnetocaloric material with zero thermal expansion operative at high temperature
journal, January 2019
- Dan, Shovan; Mukherjee, S.; Mazumdar, Chandan
- Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Vol. 21, Issue 5
Prediction of magnetocaloric effect and spontaneous magnetization in Cu-doped MnCoGe system
journal, September 2018
- Si, Xiaodong; Zhou, Keyi; Zhang, Rui
- Materials Research Express, Vol. 5, Issue 12
Universal curve and long-range ferromagnetic order in the intermetallic compound Mn 0.92 Sn 0.08 CoGe
journal, July 2018
- Si, Xiaodong; Zhou, Keyi; Zhang, Rui
- Materials Research Express, Vol. 5, Issue 8
Figures / Tables found in this record: