Tolerance Factor and Cooperative Tilting Effects in Vacancy-Ordered Double Perovskite Halides
- Department of Chemistry, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado 80523-1872, United States
- Kathleen Lonsdale Materials Chemistry, Department of Chemistry, University College London, 20 Gordon Street, London WC1H 0AJ, United Kingdom, Diamond Light Source Ltd., Diamond House, Harwell Science and Innovation Campus, Didcot, Oxfordshire OX11 0DE, United Kingdom, Thomas Young Centre, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, United Kingdom
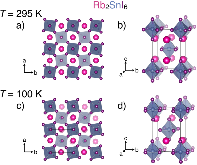
Lattice dynamics and structural instabilities are strongly implicated in dictating the electronic properties of perovskite halide semiconductors. We present a study of the vacancy-ordered double perovskite Rb2SnI6 and correlate dynamic and cooperative octahedral tilting with changes in electronic behavior compared to those of Cs2SnI6. Though both compounds exhibit native n-type semiconductivity, Rb2SnI6 exhibits carrier mobilities that are reduced by a factor of ~50 relative to Cs2SnI6. From synchrotron powder X-ray diffraction, we find that Rb2SnI6 adopts the tetragonal vacancy-ordered double perovskite structure at room temperature and undergoes a phase transition to a lower-symmetry monoclinic structure upon cooling, characterized by cooperative octahedral tilting of the [SnI6] octahedra. X-ray and neutron pair distribution function analyses reveal that the local coordination environment of Rb2SnI6 is consistent with the monoclinic structure at all temperatures; we attribute this observation to dynamic octahedral rotations that become frozen in to yield the low-temperature monoclinic structure. In contrast, Cs2SnI6 adopts the cubic vacancy-ordered double perovskite structure at all temperatures. Density functional calculations show that static octahedral tilting in Rb2SnI6 results in marginally increased carrier effective masses, which alone are insufficient to account for the experimental electronic behavior. Rather, the larger number of low-frequency phonons introduced by the lower symmetry of the Rb2SnI6 structure yield stronger electron–phonon coupling interactions that produce larger electron effective masses and reduced carrier mobilities relative to Cs2SnI6. Further, we discuss the results for Rb2SnI6 in the context of other vacancy-ordered double perovskite semiconductors, in order to demonstrate that the electron–phonon coupling characteristics can be predicted using the geometric perovskite tolerance factor. This study represents an important step in designing perovskite halide semiconductors with desired charge transport properties for optoelectronic applications.
- Research Organization:
- Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins, CO (United States); Univ. College London (United Kingdom)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES); Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-06CH11357; SC0016083; EP/L000202; EP/N01572X/1; EP/L015862/1
- OSTI ID:
- 1457590
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1499116
- Journal Information:
- Chemistry of Materials, Journal Name: Chemistry of Materials Vol. 30 Journal Issue: 11; ISSN 0897-4756
- Publisher:
- American Chemical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Anharmonicity and Octahedral Tilting in Hybrid Vacancy-Ordered Double Perovskites
Anion Distribution, Structural Distortion, and Symmetry-Driven Optical Band Gap Bowing in Mixed Halide Cs2SnX6 Vacancy Ordered Double Perovskites