Enhancement of Quasistationary Shocks and Heating via Temporal Staging in a Magnetized Laser-Plasma Jet
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France); Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Sorbonne Univ., Paris (France); PSL Research Univ., Paris (France)
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France); Institute of Applied Physics, Nizhny Novgorod (Russia)
- CNRS-UGA-UPS-INSA, Toulouse (France)
- Heinrich-Heine-Univ. Dusseldorf, Dusseldorf (Germany)
- Queen's Univ. Belfast, Belfast (United Kingdom)
- Institute of Applied Physics, Nizhny Novgorod (Russia)
- Joint Institute for High Temperatures, Moscow (Russia); National Research Nuclear Univ. "MEPhl", Moscow (Russia)
- GSI Helmholtzzentrum fur Schweionenforschung GmbH, Darmstadt (Germany)
- INRS-EMT, Varennes, QC (Canada)
- Sorbonne Univ.-UPMC Univ. Paris 06, Ecole Polytechnique, Paris (France)
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France); CEA, DAM, DIF, Arpajon (France)
- Dept. de Fisica de a Univ. de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Paris (France)
- Joint Institute for High Temperatures, Moscow (Russia); M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State Univ., Moscow (Russia)
- Ecole Polytechnique Univ. Paris-Saclay, Sorbonne Univ., Palaiseau Cedex (France)
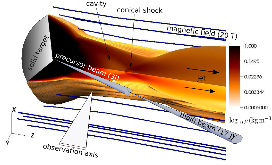
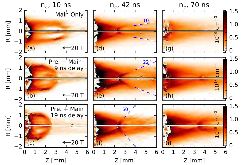
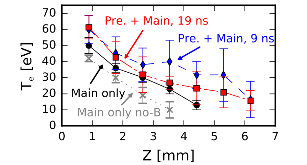
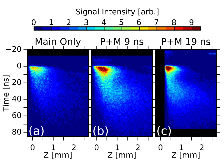
Here, we investigate the formation of a laser-produced magnetized jet under conditions of a varying mass ejection rate and a varying divergence of the ejected plasma flow. This is done by irradiating a solid target placed in a 20 T magnetic field with, first, a collinear precursor laser pulse (1012 W/cm2) and, then, a main pulse (1013 W/cm2) arriving 9–19 ns later. Varying the time delay between the two pulses is found to control the divergence of the expanding plasma, which is shown to increase the strength of and heating in the conical shock that is responsible for jet collimation. These results show that plasma collimation due to shocks against a strong magnetic field can lead to stable, astrophysically relevant jets that are sustained over time scales 100 times the laser pulse duration (i.e., >70 ns), even in the case of strong variability at the source.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344
- OSTI ID:
- 1438720
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1414611
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-733609; PRLTAO; TRN: US1900501
- Journal Information:
- Physical Review Letters, Vol. 119, Issue 25; ISSN 0031-9007
- Publisher:
- American Physical Society (APS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
The influence of the Hall term on the development of magnetized laser-produced plasma jets
|
journal | April 2018 |
Similar Records
Axial plasma jet characterization on a microsecond x-pinch
PALS laser-driven radiative jets for astrophysical and ICF applications