COX-2/sEH Dual Inhibitor PTUPB Potentiates the Antitumor Efficacy of Cisplatin
- Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States). Dept. of Internal Medicine. School of Medicine; Fourth Military Medical Univ., Xi'an (China). Dept. of Urology. Xijing Hospital
- Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States). Dept. of Internal Medicine. School of Medicine
- Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States). Dept. of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine. School of Medicine
- Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States). Dept. of Internal Medicine. School of Medicine; Wuhan Univ. (China). Dept. of Urology. Renmin Hospital
- Univ. of California, Davis, CA (United States). Dept. of Entomology and Nematology
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- The Jackson Lab., Bar Harbor, ME (United States)
- Fourth Military Medical Univ., Xi'an (China). Dept. of Urology. Xijing Hospital
- Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States). Dept. of Urology. School of Medicine. Comprehensive Cancer Center
- Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States). Dept. of Internal Medicine. Dept. of Urology. School of Medicine. Comprehensive Cancer Center; VA Northern California Health Care System, Rancho Cordova, CA (United States)
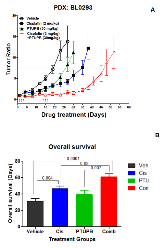
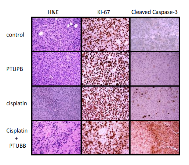
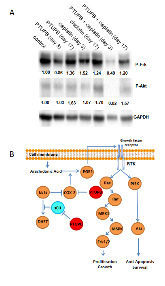
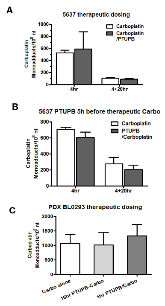
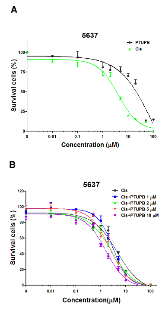
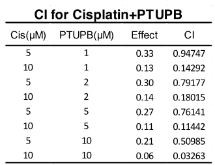
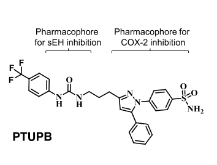
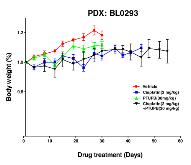
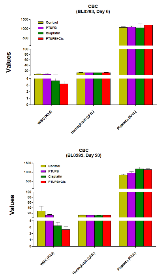
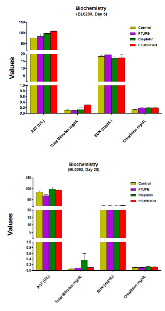
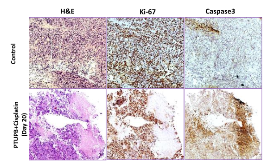
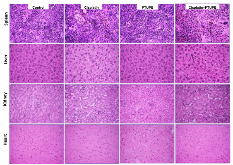
Cisplatin-based therapy is highly toxic, but moderately effective in most cancers. Concurrent inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) results in antitumor activity and has organ-protective effects. The goal of this paper was to determine the antitumor activity of PTUPB, an orally bioavailable COX-2/sEH dual inhibitor, in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine (GC) therapy. NSG mice bearing bladder cancer patient-derived xenografts were treated with vehicle, PTUPB, cisplatin, GC, or combinations thereof. Mouse experiments were performed with two different PDX models. PTUPB potentiated cisplatin and GC therapy, resulting in significantly reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival. PTUPB plus cisplatin was no more toxic than cisplatin single-agent treatment as assessed by body weight, histochemical staining of major organs, blood counts, and chemistry. The combination of PTUPB and cisplatin increased apoptosis and decreased phosphorylation in the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways compared with controls. PTUPB treatment did not alter platinum–DNA adduct levels, which is the most critical step in platinum-induced cell death. The in vitro study using the combination index method showed modest synergy between PTUPB and platinum agents only in 5637 cell line among several cell lines examined. However, PTUPB is very active in vivo by inhibiting angiogenesis. Finally, PTUPB potentiated the antitumor activity of cisplatin-based treatment without increasing toxicity in vivo and has potential for further development as a combination chemotherapy partner.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States); Univ. of California Davis, Sacramento, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE; Dept. of Veterans Affairs (VA) (United States); National Inst. of Health (NIH) (United States)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC52-07NA27344; I01 BX001784; 2 P30 CA 0933730; R01 ES002710; P42 ES04699; HHSN261201200048C; R01 DK103616; U54 NS079202
- OSTI ID:
- 1438685
- Report Number(s):
- LLNL-JRNL-741222
- Journal Information:
- Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, Vol. 17, Issue 2; ISSN 1535-7163
- Publisher:
- American Association for Cancer Research (AACR)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: A review: HASHEMI
|
journal | October 2018 |
Suppression of chemotherapy-induced cytokine/lipid mediator surge and ovarian cancer by a dual COX-2/sEH inhibitor
|
journal | January 2019 |
COX‐2/sEH dual inhibitor PTUPB alleviates bleomycin‐induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice via inhibiting senescence
|
journal | November 2019 |
Curbing Lipids: Impacts ON Cancer and Viral Infection
|
journal | February 2019 |
Radiocarbon Tracers in Toxicology and Medicine: Recent Advances in Technology and Science
|
journal | May 2019 |
Similar Records
Downregulation of COX-2 and CYP 4A signaling by isoliquiritigenin inhibits human breast cancer metastasis through preventing anoikis resistance, migration and invasion
Long-term outcome of concurrent chemotherapy and reirradiation for recurrent and second primary head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma