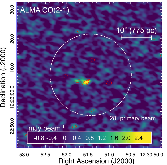
ALMA observation of the disruption of molecular gas in M87
- Inst. of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), Sagamihara, Kanagawa (Japan)
- Yale Univ., New Haven, CT (United States). Dept. of Physics and Yale Center for Astronomy & Astrophysics; Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, Cambridge, MA (United States)
- MTA-Eotvos Lorand Univ. Lendulet, Budapest (Hungary); Masaryk Univ., Brno (Czech Republic). Dept. of Theoretical Physics and Astrophysics, Faculty of Science; Hiroshima Univ., Higashi-Hiroshima (Japan)
- Stanford Univ., CA (United States). KIPAC; Stanford Univ., CA (United States). Dept. of Physics
- Stanford Univ., CA (United States). KIPAC; Stanford Univ., CA (United States). Dept. of Physics; SLAC National Accelerator Lab., Menlo Park, CA (United States)
- ASTRON, Netherlands Inst. for Radio Astronomy, Dwingeloo (the Netherlands)
We present the results from Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) observations centred 40 arcsec (3 kpc in projection) south-east of the nucleus of M87. Here, we report the detection of extended CO (2–1) line emission with a total flux of (5.5 ± 0.6) × 10-18 erg s-1 cm-2 and corresponding molecular gas mass M$$H{_2}$$=(4.7±0.4)×105M⊙, assuming a Galactic CO to H2 conversion factor. ALMA data indicate a line-of-sight velocity of -129 ± 3 km s-1, in good agreement with measurements based on the [C II] and H α+[N II] lines, and a velocity dispersion of σ = 27 ± 3 km s-1. The CO (2–1) emission originates only outside the radio lobe of the active galactic nucleus (AGN) seen in the 6 cm Very Large Array image, while the filament prolongs further inwards at other wavelengths. The molecular gas in M87 appears to be destroyed or excited by AGN activity, either by direct interaction with the radio plasma, or by the shock driven by the lobe into the X-ray emitting atmosphere. This is an important piece of the puzzle in understanding the impact of the central AGN on the amount of the coldest gas from which star formation can proceed.
- Research Organization:
- SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory (SLAC), Menlo Park, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE; Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-76SF00515
- OSTI ID:
- 1436082
- Journal Information:
- Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 475, Issue 3; ISSN 0035-8711
- Publisher:
- Royal Astronomical SocietyCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
ALMA IMAGING OF THE CO (6-5) LINE EMISSION IN NGC 7130
SERENDIPITOUS ALMA DETECTION OF A DISTANT CO-EMITTING X-RAY BRIGHT GALAXY