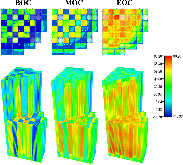
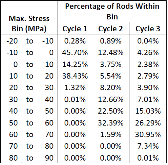
Pellet-clad mechanical interaction screening using VERA applied to Watts Bar Unit 1, Cycles 1–3
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States)
- Sandia National Lab. (SNL-NM), Albuquerque, NM (United States)
- Idaho National Lab. (INL), Idaho Falls, ID (United States)
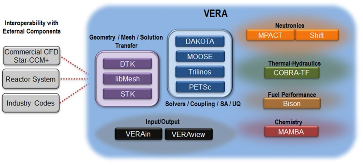
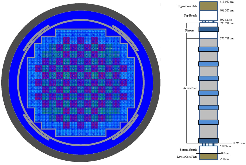
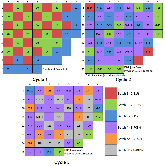
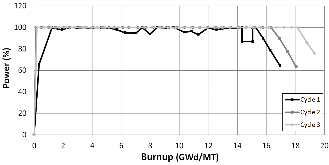
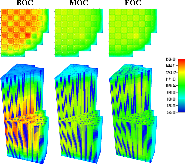
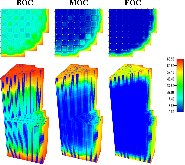
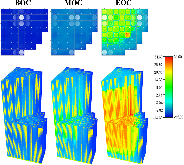
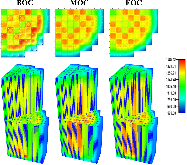
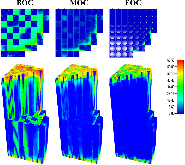
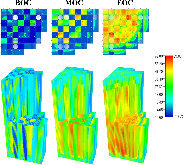
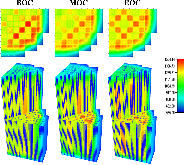
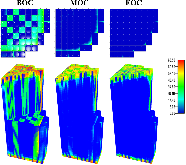
The Consortium for Advanced Simulation of Light Water Reactors (CASL) aims to provide high-fidelity multiphysics simulations of light water nuclear reactors. To accomplish this, CASL is developing the Virtual Environment for Reactor Applications (VERA), which is a suite of code packages for thermal hydraulics, neutron transport, fuel performance, and coolant chemistry. As VERA continues to grow and expand, there has been an increased focus on incorporating fuel performance analysis methods. One of the primary goals of CASL is to estimate local cladding failure probability through pellet-clad interaction, which consists of both pellet-clad mechanical interaction (PCMI) and stress corrosion cracking. Estimating clad failure is important to preventing release of fission products to the primary system and accurate estimates could prove useful in establishing less conservative power ramp rates or when considering load-follow operations.While this capability is being pursued through several different approaches, the procedure presented in this article focuses on running independent fuel performance calculations with BISON using a file-based one-way coupling based on multicycle output data from high fidelity, pin-resolved coupled neutron transport–thermal hydraulics simulations. This type of approach is consistent with traditional fuel performance analysis methods, which are typically separate from core simulation analyses. A more tightly coupled approach is currently being developed, which is the ultimate target application in CASL.Recent work simulating 12 cycles of Watts Bar Unit 1 with VERA core simulator are capitalized upon, and quarter-core BISON results for parameters of interest to PCMI (maximum centerline fuel temperature, maximum clad hoop stress, and minimum gap size) are presented for Cycles 1–3. In conclusion, based on these results, this capability demonstrates its value and how it could be used as a screening tool for gathering insight into PCMI, singling out limiting rods for further, more detailed analysis.
- Research Organization:
- Oak Ridge National Lab. (ORNL), Oak Ridge, TN (United States). Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC); USDOE Office of Nuclear Energy (NE)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC05-00OR22725; AC07-05ID14517
- OSTI ID:
- 1429216
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1549000
- Journal Information:
- Nuclear Engineering and Design, Vol. 327, Issue C; ISSN 0029-5493
- Publisher:
- ElsevierCopyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
The technological challenge for current generation nuclear reactors
|
journal | September 2019 |
Similar Records
Assessing pellet-clad interaction with VERA: WBN1, cycles 6-7
Demonstration of Load-Follow Operations with Standalone BISON through VERA