Reaction rate for carbon burning in massive stars
Journal Article
·
· Physical Review C
more »
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Physics Division
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Physics Division; Louisiana State Univ., Baton Rouge, LA (United States). Dept. of Physics and Astronomy
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Physics Division; Florida State Univ., Tallahassee, FL (United States). Dept. of Physics
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Physics Division; Univ. of Connecticut, Storrs, CT (United States)
- Argonne National Lab. (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States). Physics Division; Univ. of Maryland, College Park, MD (United States). Dept. of Chemistry and Biochemistry
- Univ. de Strasbourg, Strasbourg (France)
- Univ. de Strasbourg, Strasbourg (France); Univ. of Strasbourg Inst. for Advanced Study (USIAS), Strasbourg (France)
- Univ. of York, Heslington, York (United Kingdom). Dept. of Physics
- Univ. Paris-Sud, Orsay (France)
- TRIUMF, Vancouver, BC (Canada)
- Sun Yat-Sen Univ., Zhuhai, (China). Sino-French Inst. of Nuclear Engineering and Technology
- Inst. of Modern Physics, Lanzhou (China)
- Lawrence Livermore National Lab. (LLNL), Livermore, CA (United States)
- Louisiana State Univ., Baton Rouge, LA (United States). Dept. of Physics and Astronomy
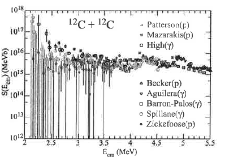
Carbon burning is a critical phase for nucleosynthesis in massive stars. The conditions for igniting this burning stage, and the subsequent isotope composition of the resulting ashes, depend strongly on the reaction rate for 12C+12C fusion at very low energies. Results for the cross sections for this reaction are influenced by various backgrounds encountered in measurements at such energies. In this paper, we report on a new measurement of 12C+12C fusion cross sections where these backgrounds have been minimized. It is found that the astrophysical S factor exhibits a maximum around Ecm=3.5–4.0 MeV, which leads to a reduction of the previously predicted astrophysical reaction rate.
- Research Organization:
- Argonne National Laboratory (ANL), Argonne, IL (United States); University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC (United States); Duke Univ., Durham, NC (United States). Triangle Universities Nuclear Laboratory
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Nuclear Physics (NP)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-06CH11357; FG02-96ER40978; FG02-97ER41041; FG02-97ER41033
- OSTI ID:
- 1425275
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1416458; OSTI ID: 1658909; OSTI ID: 1658933
- Journal Information:
- Physical Review C, Vol. 97, Issue 1; ISSN 2469-9985
- Publisher:
- American Physical Society (APS)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Cited by: 59 works
Citation information provided by
Web of Science
Web of Science
Mean-field description of heavy-ion scattering at low energies and fusion
|
journal | November 2018 |
An increase in the 12C + 12C fusion rate from resonances at astrophysical energies
|
journal | May 2018 |
Nuclear physics of the outer layers of accreting neutron stars
|
journal | July 2018 |
| Nuclear Physics of the Outer Layers of Accreting Neutron Stars | text | January 2018 |
Similar Records
Constraining the destruction rate of in stellar nucleosynthesis through the study of the reaction
Bayesian Estimation Of Thermonuclear Reaction Rates
Thermonuclear fusion rates for tritium + deuterium using Bayesian methods
Journal Article
·
Tue May 19 00:00:00 EDT 2020
· Physical Review C
·
OSTI ID:1425275
+13 more
Bayesian Estimation Of Thermonuclear Reaction Rates
Journal Article
·
Mon Oct 31 00:00:00 EDT 2016
· The Astrophysical Journal (Online)
·
OSTI ID:1425275
+2 more
Thermonuclear fusion rates for tritium + deuterium using Bayesian methods
Journal Article
·
Tue Jan 22 00:00:00 EST 2019
· Physical Review C
·
OSTI ID:1425275
+1 more