Recycled Sm-Co bonded magnet filaments for 3D printing of magnets
- Ames Lab., Ames, IA (United States)
- Iowa State Univ., Ames, IA (United States). Dept. of Chemistry
- Ames Lab., Ames, IA (United States); Iowa State Univ., Ames, IA (United States). Dept. of Chemistry
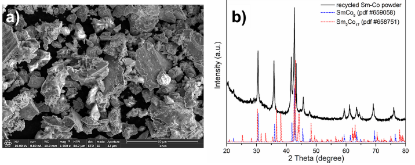
Recycling of rare earth elements, such as Sm and Nd, is one technique towards mitigating long-term supply and cost concerns for materials and devices that depend on these elements. In this work recycled Sm-Co powder recovered from industrial grinding swarfs, or waste material from magnet processing, was investigated for use in preparation of filament for 3D printing of bonded magnets. Recycled Sm-Co powder recovered from swarfs was blended into polylactic acid (PLA). Up to 20 vol.% of the recycled Sm-Co in PLA was extruded at 160°C to produce a filament. It was demonstrated that no degradation of magnetic properties occurred due to the preparation or extrusion of the bonded magnet material. Good uniformity of the magnetic properties is exhibited throughout the filament, with the material first extruded being the exception. The material does exhibit some magnetic anisotropy, allowing for the possibility of the development of anisotropic filaments. Finally, this work provides a path forward for producing recycled magnetic filament for 3D printing of permanent magnets.
- Research Organization:
- Ames Laboratory (AMES), Ames, IA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE), Energy Efficiency Office. Advanced Manufacturing Office; USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES). Chemical Sciences, Geosciences, and Biosciences Division
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-07CH11358
- OSTI ID:
- 1436430
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1416636
- Report Number(s):
- IS-J-9630; TRN: US1900182
- Journal Information:
- AIP Advances, Vol. 8, Issue 5; ISSN 2158-3226
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Production of complex shape magnets using additive manufacturing: A state-of-the-art analysis
|
journal | November 2019 |
Additive Manufacturing and Topology Optimization of Magnetic Materials for Electrical Machines—A Review
|
journal | January 2021 |
Similar Records
Tunable Porosity in Fused Filament 3D-Printed Blends of Intrinsically Porous Polymer and Thermoplastic Aliphatic Polyesters Polycaprolactone and Polylactic Acid
Tensile properties of 3D-printed wood-filled PLA materials using poplar trees