Characteristics of the fourth order resonance in high intensity linear accelerators
- Institute for Basic Science, Daejeon (South Korea)
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
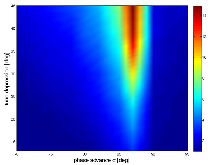
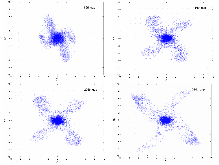
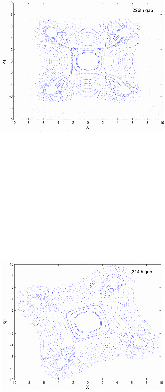
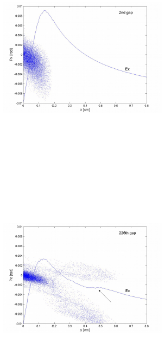
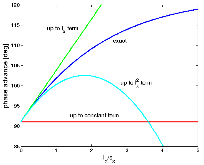
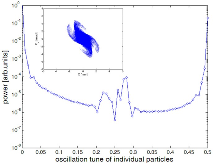
For the 4σ = 360° space-charge resonance in high intensity linear accelerators, the emittance growth is surveyed for input Gaussian beams, as a function of the depressed phase advance per cell σ and the initial tune depression (σo – σ). For each data point, the linac lattice is designed such that the fourth order resonance dominates over the envelope instability. Additionally, the data show that the maximum emittance growth takes place at σ ≈ 87° over a wide range of the tune depression (or beam current), which confirms that the relevant parameter for the emittance growth is σ and that for the bandwidth is σo – σ. An interesting four-fold phase space structure is observed that cannot be explained with the fourth order resonance terms alone. Analysis attributes this effect to a small negative sixth order detuning term as the beam is redistributed by the resonance. Analytical studies show that the tune increases monotonically for the Gaussian beam which prevents the resonance for σ > 90°. Lastly, frequency analysis indicates that the four-fold structure observed for input Kapchinskij-Vladmirskij beams when σ < 90°, is not the fourth order resonance but a fourth order envelope instability because the 1/4 = 90°/360° component is missing in the frequency spectrum.
- Research Organization:
- Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. (LBNL), Berkeley, CA (United States)
- Sponsoring Organization:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC)
- Grant/Contract Number:
- AC02-05CH11231
- OSTI ID:
- 1436155
- Alternate ID(s):
- OSTI ID: 1364184
- Journal Information:
- Physics of Plasmas, Vol. 24, Issue 6; ISSN 1070-664X
- Publisher:
- American Institute of Physics (AIP)Copyright Statement
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
Web of Science
Similar Records
Fourth order resonance of a high intensity linear accelerator*
Space charge induced beam instability in periodic focusing channel