A limited role for carbonic anhydrase in C4 photosynthesis as revealed by a ca1ca2 double mutant in maize.
Abstract
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) catalyzes the first biochemical step of the carbon concentrating mechanism of C4 plants, and in C4 monocots, it has been suggested that CA activity is near limiting for photosynthesis. Here, we test this hypothesis through the characterization of transposon induced mutant alleles of Ca1 and Ca2 in Zea mays. In addition, these two isoforms account for more than 85% of the CA transcript pool. A significant change in isotopic discrimination is observed in mutant plants, which have as little as 3% of wild-type CA activity, but surprisingly, photosynthesis is not reduced under current or elevated pCO2. However, growth and rates of photosynthesis under sub-ambient pCO2 are significantly impaired in the mutants. These findings suggest, that while CA is not limiting for C4 photosynthesis in Z. mays at current pCO2, it likely maintains high rates of photosynthesis when CO2 availability is reduced. Current atmospheric CO2 levels now exceed 400 ppm (~40.53 Pa) and contrast the low CO2 partial pressure (pCO2) conditions under which C4 plants expanded their range ~10 million years ago when the global atmospheric CO2 was below 300 ppm (~30.40 Pa). Thus, as CO2 levels continue to rise, selective pressures for high levels of CA maymore »
- Authors:
-
- Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, St. Louis, MO (United States)
- Washington State Univ., Pullman, WA (United States)
- Publication Date:
- Research Org.:
- Life Sciences Research Foundation, Baltimore, MD (United States)
- Sponsoring Org.:
- USDOE Office of Science (SC), Basic Energy Sciences (BES)
- Contributing Org.:
- Life Sciences Research Foundation
- OSTI Identifier:
- 1233449
- Grant/Contract Number:
- SC0008510
- Resource Type:
- Journal Article: Accepted Manuscript
- Journal Name:
- Plant Physiology (Bethesda)
- Additional Journal Information:
- Journal Volume: 165; Journal Issue: 2; Journal ID: ISSN 0032-0889
- Publisher:
- American Society of Plant Biologists
- Country of Publication:
- United States
- Language:
- English
- Subject:
- 59 BASIC BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Citation Formats
Studer, Anthony J., Gandin, Anthony, Kolbe, Allison R., Wang, Lin, Cousins, Asaph B., and Brutnell, Thomas P. A limited role for carbonic anhydrase in C4 photosynthesis as revealed by a ca1ca2 double mutant in maize.. United States: N. p., 2014.
Web. doi:10.1104/pp.114.237602.
Studer, Anthony J., Gandin, Anthony, Kolbe, Allison R., Wang, Lin, Cousins, Asaph B., & Brutnell, Thomas P. A limited role for carbonic anhydrase in C4 photosynthesis as revealed by a ca1ca2 double mutant in maize.. United States. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.237602
Studer, Anthony J., Gandin, Anthony, Kolbe, Allison R., Wang, Lin, Cousins, Asaph B., and Brutnell, Thomas P. 2014.
"A limited role for carbonic anhydrase in C4 photosynthesis as revealed by a ca1ca2 double mutant in maize.". United States. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.237602. https://www.osti.gov/servlets/purl/1233449.
@article{osti_1233449,
title = {A limited role for carbonic anhydrase in C4 photosynthesis as revealed by a ca1ca2 double mutant in maize.},
author = {Studer, Anthony J. and Gandin, Anthony and Kolbe, Allison R. and Wang, Lin and Cousins, Asaph B. and Brutnell, Thomas P.},
abstractNote = {Carbonic anhydrase (CA) catalyzes the first biochemical step of the carbon concentrating mechanism of C4 plants, and in C4 monocots, it has been suggested that CA activity is near limiting for photosynthesis. Here, we test this hypothesis through the characterization of transposon induced mutant alleles of Ca1 and Ca2 in Zea mays. In addition, these two isoforms account for more than 85% of the CA transcript pool. A significant change in isotopic discrimination is observed in mutant plants, which have as little as 3% of wild-type CA activity, but surprisingly, photosynthesis is not reduced under current or elevated pCO2. However, growth and rates of photosynthesis under sub-ambient pCO2 are significantly impaired in the mutants. These findings suggest, that while CA is not limiting for C4 photosynthesis in Z. mays at current pCO2, it likely maintains high rates of photosynthesis when CO2 availability is reduced. Current atmospheric CO2 levels now exceed 400 ppm (~40.53 Pa) and contrast the low CO2 partial pressure (pCO2) conditions under which C4 plants expanded their range ~10 million years ago when the global atmospheric CO2 was below 300 ppm (~30.40 Pa). Thus, as CO2 levels continue to rise, selective pressures for high levels of CA may be limited to arid climates where stomatal closure reduces CO2 availability to the leaf.},
doi = {10.1104/pp.114.237602},
url = {https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1233449},
journal = {Plant Physiology (Bethesda)},
issn = {0032-0889},
number = 2,
volume = 165,
place = {United States},
year = {Fri Apr 04 00:00:00 EDT 2014},
month = {Fri Apr 04 00:00:00 EDT 2014}
}
Web of Science
Figures / Tables:
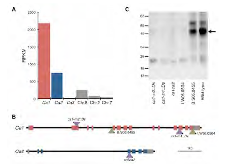 Figure 1: Ds insertional mutants disrupt the two most highly expressed CA genes. (a) Unique RNA-seq reads from the tip of the 3rd leaf of a maize seedling were mapped to the 3’ UTR of each carbonic anhydrase gene to quantify the expression of each member of the gene familymore »
Figure 1: Ds insertional mutants disrupt the two most highly expressed CA genes. (a) Unique RNA-seq reads from the tip of the 3rd leaf of a maize seedling were mapped to the 3’ UTR of each carbonic anhydrase gene to quantify the expression of each member of the gene familymore »
Works referenced in this record:
Regional mutagenesis using Dissociation in maize
journal, November 2009
- Ahern, K.
- Methods, Vol. 49, Issue 3
Somatic variegation and germinal mutability reflect the position of transposable element Dissociation within the maize R gene.
journal, September 1993
- Alleman, M.; Kermicle, J. L.
- Genetics, Vol. 135, Issue 1
Carbonic Anhydrase Activity Associated with the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC7942
journal, January 1989
- Badger, Murray R.; Price, G. Dean
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 89, Issue 1
The Role of Carbonic Anhydrase in Photosynthesis
journal, June 1994
- Badger, M. R.; Price, G. D.
- Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, Vol. 45, Issue 1
Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy for stable isotope studies of ecosystem–atmosphere CO2 exchange
journal, August 2003
- Bowling, David R.; Sargent, Steve D.; Tanner, Bert D.
- Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, Vol. 118, Issue 1-2
Ac-Immobilized , a Stable Source of Activator Transposase That Mediates Sporophytic and Gametophytic Excision of Dissociation Elements in Maize
journal, December 2005
- Conrad, Liza J.; Brutnell, Thomas P.
- Genetics, Vol. 171, Issue 4
Carbonic Anhydrase and Its Influence on Carbon Isotope Discrimination during C 4 Photosynthesis. Insights from Antisense RNA in Flaveria bidentis
journal, March 2006
- Cousins, Asaph B.; Badger, Murray R.; von Caemmerer, Susanne
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 141, Issue 1
A Transgenic Approach to Understanding the Influence of Carbonic Anhydrase on C 18 OO Discrimination during C 4 Photosynthesis
journal, August 2006
- Cousins, Asaph B.; Badger, Murray R.; von Caemmerer, Susanne
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 142, Issue 2
C4 photosynthetic isotope exchange in NAD-ME- and NADP-ME-type grasses
journal, March 2008
- Cousins, Asaph B.; Badger, Murray R.; von Caemmerer, Susanne
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 59, Issue 7
The Origins of C4 Grasslands: Integrating Evolutionary and Ecosystem Science
journal, April 2010
- Edwards, E. J.; Osborne, C. P.; Stromberg, C. A. E.
- Science, Vol. 328, Issue 5978
Carbon Isotope Discrimination measured Concurrently with Gas Exchange to Investigate CO2 Diffusion in Leaves of Higher Plants
journal, January 1986
- Evans, Jr; Sharkey, Td; Berry, Ja
- Functional Plant Biology, Vol. 13, Issue 2
Ternary effects on the gas exchange of isotopologues of carbon dioxide: Ternary effects on CO2 isotopologues
journal, February 2012
- Farquhar, Graham D.; Cernusak, Lucas A.
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 35, Issue 7
A gene homologous to chloroplast carbonic anhydrase (icfA) is essential to photosynthetic carbon dioxide fixation by Synechococcus PCC7942.
journal, May 1992
- Fukuzawa, H.; Suzuki, E.; Komukai, Y.
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Vol. 89, Issue 10
Intracellular Carbonic Anhydrase Is Essential to Photosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii at Atmospheric Levels of CO2 (Demonstration via Genomic Complementation of the High-CO2-Requiring Mutant ca-1)
journal, May 1997
- Funke, R. P.; Kovar, J. L.; Weeks, D. P.
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 114, Issue 1
Influence of Carbonic Anhydrase Activity in Terrestrial Vegetation on the 18O Content of Atmospheric CO2
journal, March 2001
- Gillon, J.
- Science, Vol. 291, Issue 5513
Carbonic Anhydrase Activity in Leaves and Its Role in the First Step of C 4 Photosynthesis
journal, June 1990
- Hatch, Marshall D.; Burnell, James N.
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 93, Issue 2
Functional Diversity, Conservation, and Convergence in the Evolution of the α-, β-, and γ-Carbonic Anhydrase Gene Families
journal, February 1996
- Hewett-Emmett, David; Tashian, Richard E.
- Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, Vol. 5, Issue 1
The Regulation of Gene Expression Required for C 4 Photosynthesis
journal, June 2010
- Hibberd, Julian M.; Covshoff, Sarah
- Annual Review of Plant Biology, Vol. 61, Issue 1
Carbonic anhydrases are upstream regulators of CO2-controlled stomatal movements in guard cells
journal, December 2009
- Hu, Honghong; Boisson-Dernier, Aurélien; Israelsson-Nordström, Maria
- Nature Cell Biology, Vol. 12, Issue 1
Inorganic Carbon Diffusion between C 4 Mesophyll and Bundle Sheath Cells : Direct Bundle Sheath CO
journal, December 1989
- Jenkins, Colin L. D.; Furbank, Robert T.; Hatch, Marshall D.
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 91, Issue 4
Photosynthesis, Productivity, and Yield of Maize Are Not Affected by Open-Air Elevation of CO 2 Concentration in the Absence of Drought
journal, January 2006
- Leakey, Andrew D. B.; Uribelarrea, Martin; Ainsworth, Elizabeth A.
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 140, Issue 2
Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform
journal, May 2009
- Li, H.; Durbin, R.
- Bioinformatics, Vol. 25, Issue 14
The developmental dynamics of the maize leaf transcriptome
journal, October 2010
- Li, Pinghua; Ponnala, Lalit; Gandotra, Neeru
- Nature Genetics, Vol. 42, Issue 12, p. 1060-1067
Extrinsic Photosystem II Carbonic Anhydrase in Maize Mesophyll Chloroplasts
journal, February 2002
- Lu, Yih-Kuang; Stemler, Alan J.
- Plant Physiology, Vol. 128, Issue 2
Carbonic anhydrase and the molecular evolution of C4 photosynthesis: Carbonic anhydrase and C4 photosynthesis
journal, July 2011
- Ludwig, Martha
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 35, Issue 1
Carbon kinetic isotope effects on the hydration of carbon dioxide and the dehydration of bicarbonate ion
journal, September 1984
- Marlier, John F.; O'Leary, Marion H.
- Journal of the American Chemical Society, Vol. 106, Issue 18
Carbon isotope fractionation between dissolved bicarbonate and gaseous carbon dioxide
journal, May 1974
- Mook, W. G.; Bommerson, J. C.; Staverman, W. H.
- Earth and Planetary Science Letters, Vol. 22, Issue 2, p. 169-176
Carbonic anhydrases in plants and algae: Carbonic anhydrases in plants and algae
journal, February 2001
- Moroney, J. V.; Bartlett, S. G.; Samuelsson, G.
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 24, Issue 2
The carbonic anhydrase isoforms of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: intracellular location, expression, and physiological roles
journal, March 2011
- Moroney, James V.; Ma, Yunbing; Frey, Wesley D.
- Photosynthesis Research, Vol. 109, Issue 1-3
Carbon isotope fractionation in plants
journal, January 1981
- O'Leary, Marion H.
- Phytochemistry, Vol. 20, Issue 4
Measurement of the isotope fractionation associated with diffusion of carbon dioxide in aqueous solution
journal, February 1984
- O'Leary, Marion H.
- The Journal of Physical Chemistry, Vol. 88, Issue 4
Carbon isotope effect on dehydration of bicarbonate ion catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase
journal, September 1985
- Paneth, Piotr; O'Leary, Marion H.
- Biochemistry, Vol. 24, Issue 19
The C4 plant lineages of planet Earth
journal, March 2011
- Sage, R. F.; Christin, P. -A.; Edwards, E. J.
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 62, Issue 9
Effects of low atmospheric CO2 on plants: more than a thing of the past
journal, January 2001
- Sage, Rowan F.; Coleman, John R.
- Trends in Plant Science, Vol. 6, Issue 1
Photorespiration and the Evolution of C 4 Photosynthesis
journal, June 2012
- Sage, Rowan F.; Sage, Tammy L.; Kocacinar, Ferit
- Annual Review of Plant Biology, Vol. 63, Issue 1
Carboxylating enzymes and carbonic anhydrase functions were suppressed by zinc deficiency in maize and chickpea plants
journal, October 2006
- Salama, Zeinab A.; El-Fouly, Mohamed M.; Lazova, Galia
- Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, Vol. 28, Issue 5
Genome-wide atlas of transcription during maize development
journal, March 2011
- Sekhon, Rajandeep S.; Lin, Haining; Childs, Kevin L.
- The Plant Journal, Vol. 66, Issue 4, p. 553-563
Characterization of a mutant lacking carboxysomal carbonic anhydrase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803
journal, September 2001
- So, Anthony K.; John-McKay, Meryl; Espie, George S.
- Planta, Vol. 214, Issue 3
The efficiency of C4 photosynthesis under low light conditions: assumptions and calculations with CO2 isotope discrimination
journal, April 2011
- Ubierna, Nerea; Sun, Wei; Cousins, Asaph B.
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 62, Issue 9
The efficiency of C 4 photosynthesis under low light conditions in Zea mays , Miscanthus x giganteus and Flaveria bidentis : Efficiency of light-limited C
journal, August 2012
- Ubierna, Nerea; Sun, Wei; Kramer, David M.
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 36, Issue 2
Genome-Wide Distribution of Transposed Dissociation Elements in Maize
journal, June 2010
- Vollbrecht, Erik; Duvick, Jon; Schares, Justin P.
- The Plant Cell, Vol. 22, Issue 6
Carbonic anhydrase and C4 photosynthesis: a transgenic analysis
journal, June 2004
- Von Caemmerer, S.; Quinn, V.; Hancock, N. C.
- Plant, Cell and Environment, Vol. 27, Issue 6
Temperature response of in vivo Rubisco kinetics and mesophyll conductance in Arabidopsis thaliana : comparisons to Nicotiana tabacum
journal, August 2013
- Walker, Berkley; Ariza, Loren S.; Kaines, Sarah
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 36, Issue 12
A Low-Cost Library Construction Protocol and Data Analysis Pipeline for Illumina-Based Strand-Specific Multiplex RNA-Seq
journal, October 2011
- Wang, Lin; Si, Yaqing; Dedow, Lauren K.
- PLoS ONE, Vol. 6, Issue 10
Comparative genomic analysis of C4 photosynthetic pathway evolution in grasses
journal, January 2009
- Wang, Xiyin; Gowik, Udo; Tang, Haibao
- Genome Biology, Vol. 10, Issue 6
Genome sequence of foxtail millet (Setaria italica) provides insights into grass evolution and biofuel potential
journal, May 2012
- Zhang, Gengyun; Liu, Xin; Quan, Zhiwu
- Nature Biotechnology, Vol. 30, Issue 6
Works referencing / citing this record:
The molecular evolution of C4 photosynthesis: opportunities for understanding and improving the world’s most productive plants
journal, November 2018
- Niklaus, Michael; Kelly, Steven
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 70, Issue 3
C 4 photosynthesis in C 3 rice: a theoretical analysis of biochemical and anatomical factors: C 4 photosynthesis in C 3 rice
journal, October 2016
- Wang, Shuyue; Tholen, Danny; Zhu, Xin-Guang
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 40, Issue 1
The draft genome of the C3 panicoid grass species Dichanthelium oligosanthes
journal, October 2016
- Studer, Anthony J.; Schnable, James C.; Weissmann, Sarit
- Genome Biology, Vol. 17, Issue 1
Cross species selection scans identify components of C 4 photosynthesis in the grasses
journal, July 2016
- Huang, Pu; Studer, Anthony J.; Schnable, James C.
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 68, Issue 2
Insights from transcriptome profiling on the non-photosynthetic and stomatal signaling response of maize carbonic anhydrase mutants to low CO2
journal, February 2019
- Kolbe, Allison R.; Studer, Anthony J.; Cornejo, Omar E.
- BMC Genomics, Vol. 20, Issue 1
Herbarium genomics retraces the origins of C 4 -specific carbonic anhydrase in Andropogoneae (Poaceae)
journal, March 2018
- Besnard, Guillaume; Bianconi, Matheus E.; Hackel, Jan
- Botany Letters, Vol. 165, Issue 3-4
Three-dimensional microscale modelling of CO 2 transport and light propagation in tomato leaves enlightens photosynthesis : 3-D modelling of photosynthesis in leaves
journal, July 2015
- Ho, Quang Tri; Berghuijs, Herman N. C.; Watté, Rodrigo
- Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 39, Issue 1
Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in osmotic and salt stress in Medicago truncatula using genome-wide high-throughput sequencing
journal, June 2015
- Wang, Tian-Zuo; Liu, Min; Zhao, Min-Gui
- BMC Plant Biology, Vol. 15, Issue 1
Translocation of Drought-Responsive Proteins from the Chloroplasts
journal, January 2020
- Li, Ping; Liu, Haoju; Yang, Hong
- Cells, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Online CO 2 and H 2 O oxygen isotope fractionation allows estimation of mesophyll conductance in C 4 plants, and reveals that mesophyll conductance decreases as leaves age in both C 4 and C 3 plants
journal, January 2016
- Barbour, Margaret M.; Evans, John R.; Simonin, Kevin A.
- New Phytologist, Vol. 210, Issue 3
Molecular diversity and selective sweeps in maize inbred lines adapted to African highlands
journal, September 2019
- Wegary, Dagne; Teklewold, Adefris; Prasanna, Boddupalli M.
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Emerging roles for carbonic anhydrase in mesophyll conductance and photosynthesis
journal, January 2020
- Momayyezi, Mina; McKown, Athena D.; Bell, Shannon C. S.
- The Plant Journal, Vol. 101, Issue 4
Molecular diversity and selective sweeps in maize inbred lines adapted to African highlands
journal, September 2019
- Wegary, Dagne; Teklewold, Adefris; Prasanna, Boddupalli M.
- Scientific Reports, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Cross species selection scans identify components of C 4 photosynthesis in the grasses
journal, July 2016
- Huang, Pu; Studer, Anthony J.; Schnable, James C.
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 68, Issue 2
Effects of reduced carbonic anhydrase activity on CO 2 assimilation rates in Setaria viridis : a transgenic analysis
journal, October 2016
- Osborn, Hannah L.; Alonso-Cantabrana, Hugo; Sharwood, Robert E.
- Journal of Experimental Botany, Vol. 68, Issue 2
Identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs involved in osmotic and salt stress in Medicago truncatula using genome-wide high-throughput sequencing
journal, June 2015
- Wang, Tian-Zuo; Liu, Min; Zhao, Min-Gui
- BMC Plant Biology, Vol. 15, Issue 1
Identification of Photosynthesis-Associated C4 Candidate Genes through Comparative Leaf Gradient Transcriptome in Multiple Lineages of C3 and C4 Species
journal, October 2015
- Ding, Zehong; Weissmann, Sarit; Wang, Minghui
- PLOS ONE, Vol. 10, Issue 10
Multiscale Metabolic Modeling of C4 Plants: Connecting Nonlinear Genome-Scale Models to Leaf-Scale Metabolism in Developing Maize Leaves
journal, March 2016
- Bogart, Eli; Myers, Christopher R.
- PLOS ONE, Vol. 11, Issue 3
Real-Time Determination of Photosynthesis, Transpiration, Water-Use Efficiency and Gene Expression of Two Sorghum bicolor (Moench) Genotypes Subjected to Dry-Down
journal, May 2017
- Fracasso, Alessandra; Magnanini, Eugenio; Marocco, Adriano
- Frontiers in Plant Science, Vol. 8
Translocation of Drought-Responsive Proteins from the Chloroplasts
journal, January 2020
- Li, Ping; Liu, Haoju; Yang, Hong
- Cells, Vol. 9, Issue 1
Figures / Tables found in this record: